Difference Between X-Ray and CT-Scan
X-rays are one of the most used and readily available radiology investigations. It uses radiation in the form of X-rays to give a picture of a region of the human body. Hard calcified areas like bone appear white on X-rays while muscle and soft tissue appear black or gray.
A CT scan used X-rays to give a broad, sophisticated 3-dimensional view of a region of the human body. Sometimes a contrast dye is injected into one of the veins to give a better picture of the internal organs.
What is an X-ray?
Definition:
X-rays are one of the most used and readily available radiology investigations. It uses radiation in the form of X-rays to give a picture of a region of the human body. Hard calcified areas like bone appear white on X-rays while muscle and soft tissue appear black or gray.
Position:
Proper positioning is important to get an accurate X-ray picture. The patient is supposed to stand erect in between an x-ray machine and a photographic film. Usually, the positions are changed in between the process to get multiple views of the desired region such as lateral view or anteroposterior/posteroanterior views. If limb injury is involved, comparison pictures of the unaffected limb might as well be taken.
Types:
Two types of X-rays are soft X-rays and hard X-rays. Soft X-rays have a wavelength of 10 nanometers. Hard X-rays have a wavelength of 100 picometers and are found at a similar position of gamma rays at the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radiation:
X-rays use a single direct ray of radiation to produce a 2D image.
Pros:
X-rays are easily available and provide fast results unlike CT scans which need contrast and special measures prior to the process. X-rays also have nonmedical functions like its use in security check and quality control.
Cons:
Soft tissue injuries are not picked up on X-ray imaging. Also long-term exposure of X-rays is linked with malignancies such as leukemia or thyroid cancer.
What is a CT scan?
Definition:
A CT scan used X-rays to give a broad, sophisticated 3 dimensional view of a region of the human body. Sometimes a contrast dye is injected into one of the veins to highlight the diseased areas better on the CT scan films.
Position:
A CT scan machine is a hollow cylinder in which you are laid down and slid in and out. The machine has a rotatory movement and takes various cross sectional images of your body at various angles.
Types:
PET scan or positron emission tomography is a special type of CT scan in which a glucose containing radioactive tracer is injected into the veins prior to the test. The tracer is picked up on image in hyper functioning body regions. CT urography is a CT scan which focuses on the urogenital system.
Radiation:
In CT scan, numerous X-ray beams are thrown at different angles in order to generate a 3D image.
Pros:
CT scans are able to identify complex pathologies, tumors, inflammation and internal organ injuries.
Cons:
CT scan is a costly investigation. Some people are allergic to the CT contrast dye. Rarely can some people develop a life-threatening reaction to the contrast dye. Kidneys might be damaged by the contrast dye in a minority of people.
Difference Between X-Ray and CT-Scan
Definition:
X-rays are one of the most used and readily available radiology investigations. It uses radiation in the form of X-rays to give a picture of a region of the human body. Hard calcified areas like bone appear white on X-rays while muscle and soft tissue appear black or gray.
A CT scan used X-rays to give a broad, sophisticated 3-dimensional view of a region of the human body. Sometimes a contrast dye is injected into one of the veins to give a better picture of the internal organs.
Position:
Proper positioning is important to get an accurate X-ray picture. The patient is supposed to stand erect in between an x-ray machine and a photographic film. Usually, the positions are changed in between the process to get multiple views of the desired region such as lateral view or anteroposterior/posteroanterior views. If limb injury is involved, comparison pictures of the unaffected limb might as well be taken. A CT scan machine is a hollow cylinder in which you are laid down and slid in and out. The machine has a rotatory movement and takes various cross-sectional images of your body at various angles.
Types:
Two types of X-rays are soft X-rays and hard X-rays. Soft X-rays have a wavelength of 10 nanometers. Hard X-rays have a wavelength of 100 picometers and are found at a similar position to gamma rays on the electromagnetic spectrum.
PET scan or positron emission tomography is a special type of CT scan in which a glucose containing radioactive tracer is injected into the veins prior to the test. The tracer is picked up on images in hyper functioning body regions. CT urography is a CT scan which focuses on the urogenital system.
Radiation:
X-rays use a single direct ray of radiation to produce a 2D image. In CT scan, numerous X-ray beams are thrown at different angles in order to generate a 3D image.
Pros:
X-rays are easily available and provide fast results unlike CT scans which need contrast and special measures prior to the process. X-rays also have nonmedical functions like their use in security check and quality control.
CT scans are able to identify complex pathologies, tumors, inflammation and internal organ injuries.
Cons:
Soft tissue injuries are not picked up on X-ray imaging. Also, long-term exposure of X-rays is linked with malignancies such as leukemia or thyroid cancer.
CT scan is a costly investigation. Some people are allergic to the CT contrast dye. Rarely can some people develop a life-threatening reaction to the contrast dye. Kidneys might be damaged by the contrast dye in a minority of people.
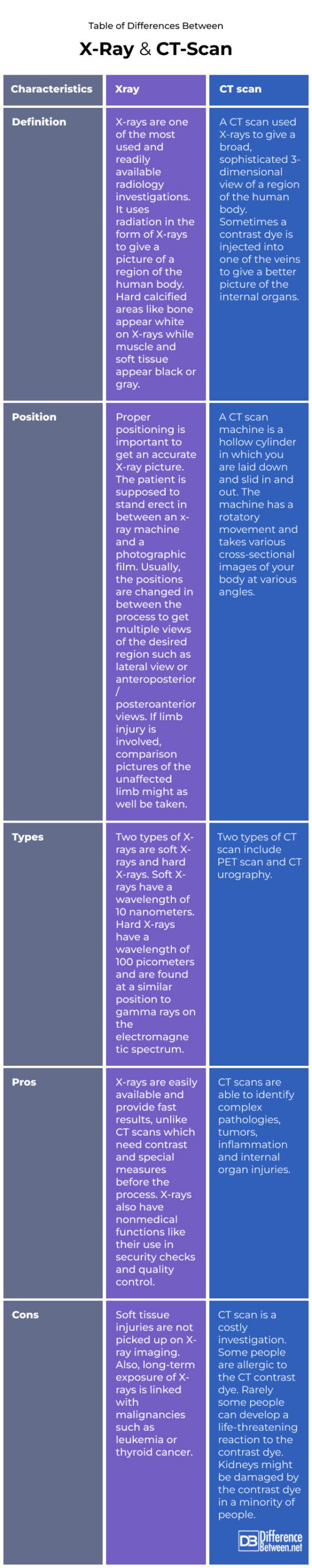
Table of differences Between X-Ray and CT-Scan
FAQs
What can a CT scan show that an X-ray Cannot?
CT scans can identify complex pathologies, tumors, inflammation, and internal organ injuries.
Which is better X-ray or CT scan?
A CT scan is better.
Why would an X-ray be ordered instead of a CT scan?
Fractures and bone injuries are better identified on X-rays.
What is the most common reason for a CT scan?
It is used in emergency conditions like head injuries.
Why would a doctor order a CT scan instead of an MRI?
It is used as an urgent investigation into head injuries and emergency conditions.
What can CT scans detect?
CT scans can identify complex pathologies, tumors, inflammation, and internal organ injuries.
What a CT scan Cannot detect?
Detailed soft tissue injuries, nerve ligaments and certain tumors might be missed on a CT scan.
Does a CT scan show all cancers?
Soft tissue carcinomas cannot be seen in a CT scan.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
4 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAC_-sJEqBI-x-ray/
[1]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAD-E33qL50-ct-scan-brain/
[2]Hashmi, Mohammad Farukh, et al. "Efficient pneumonia detection in chest xray images using deep transfer learning." Diagnostics 10.6 (2020): 417.
[3]Patel, Paula R., and Orlando De Jesus. "CT Scan." StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
[4]Kalender, Willi A. "X-ray computed tomography." Physics in Medicine & Biology 51.13 (2006): R29.

But x-ray doesn’t shown organs. It shows BONES!!!! Radiotransparent is what organs are.
.
That’s not true. X-rays can show soft tissues (organs) as well as hard tissues (bones). Different things have different radio-density. Only AIR is radio-transparent while dense bone is radio-opaque. Different tissues have different radio-densities depending on the density of cells and water/air that they contain. X-rays are used to diagnose problems like pleural effusion (water in the area around the lungs) tumours (dense masses in the stomach, lungs, etc.)
1 ct radiation are doing to 300 X tay
I have end stage COPD. My new pulmonologist has referred me for pulmonary therapy and the office says a lung xray done within the last year is required. I had my annual lung CT scan two months ago but they maintain I still need an xray. They couldn’t say why and I wonder if I really need the xray or if someone is interpreting Medicare coverage/rules too strictly?