Difference Between Ventilator and Respirator
Ventilators, which are often called respirators, are medical devices uses to artificially ventilate the lungs of patients who have trouble breathing or who are unable to breathe naturally. Early devices used bellows that were operated manually to inflate the lungs. Since the advent of respirators, medical professionals have devised various strategies to ventilate the lungs based on the condition of the patient. Today’s respirators employ an array of sophisticated components to ventilate the patients mechanically. However, ventilators and respirators are not the same thing.
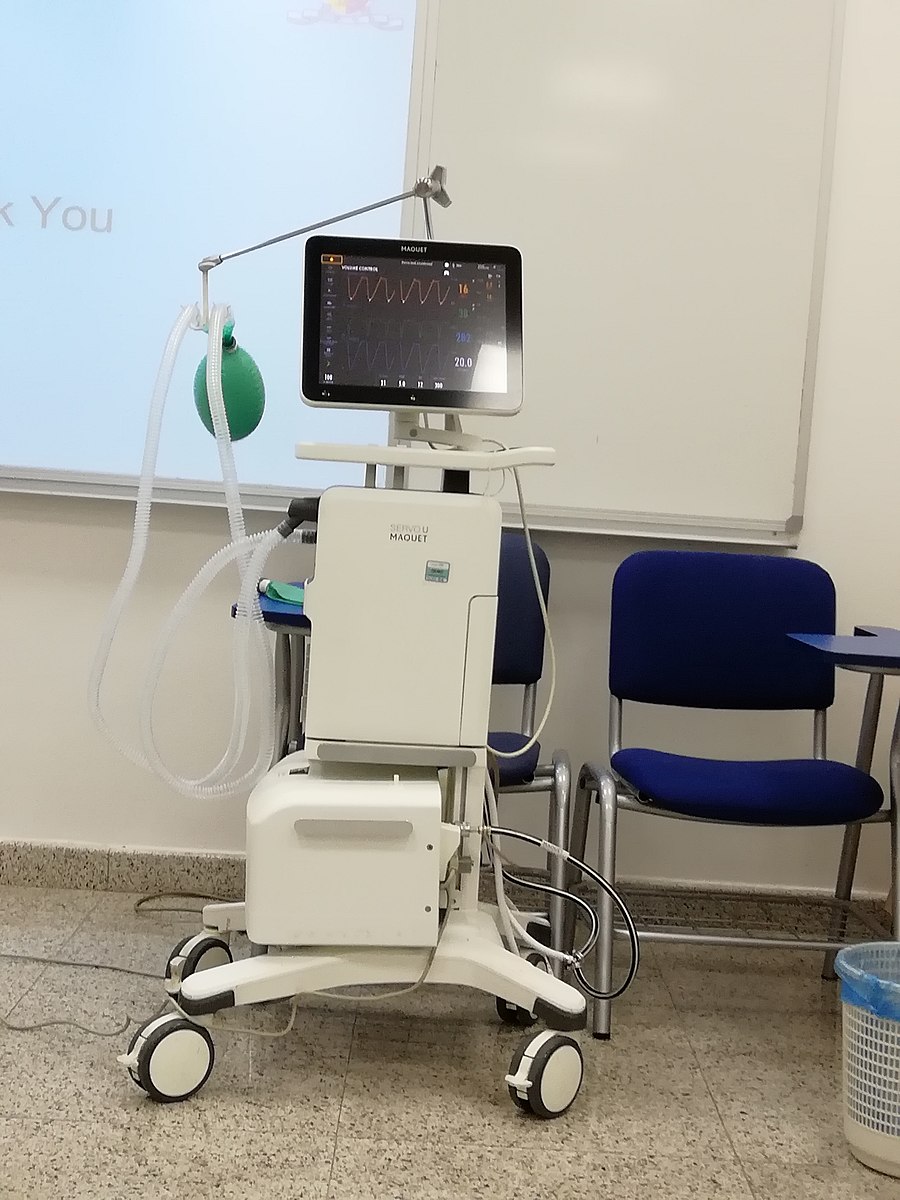
What is a Ventilator?
Ventilator is a medical device used in an intensive care setting to support mechanical ventilation. Ventilator is a type of breathing machine that helps provide oxygen to patients who are having trouble breathing or who are unable to breathe on their own. Ventilator support is necessary when spontaneous ventilation is inadequate for the sustenance of life meaning the patients are unable to sustain the level of ventilation required to maintain the gas exchange functions. Mechanical ventilation may be required in patients undergoing operating procedures or conditions due to physiological changes or other causes leading to oxygenation failure. It is a life-support machine that keeps the oxygen going to the brain, the heart and the kidneys. Ventilator is used to treat serious respiratory failure or respirator deficiency resulting from a variety of clinical causes. A ventilator is simply a device that supports mechanical ventilation.

What is a Respirator?
Inhalation is a major point of entry of toxic substances into the human body. A respirator is a mask-like device that protects the wearer from inhaling toxic substances including fumes, gases, vapors, and dust. It is worn over the mouth and nose to filter out airborne particles, chemicals or gases. Well, respirators are mainly categorized into two types: air-purifying respirator (APR), which provides breathable air by removing specific air contaminants, and the air-supplying respirator (ASR), which supplies an alternate breathable air from a source independent of the ambient atmosphere and includes self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) and supplied-air respirators (SARs). APRs range from disposable face masks, which are to be discarded after their recommended usage period to more sophisticated gas masks with replaceable cartridges. The ability of a respirator to do the job depends on the effectiveness of the respirator itself in a given environment and the type of respirator to be used.
Difference between Ventilator and Respirator
Device
– Both ventilators and respirators are two types of devices that facilitate breathing in different circumstances. However, a ventilator is a medical device that supports mechanical ventilation in an intensive care setting. It is a kind of life-support machine designed to move breathable air in and out of the lungs.
A respirator, on the other hand, is a mask-like device worn over the mouth and nose to filter out airborne particles, chemicals or gases. A respirator is mainly categorized into two types: air-purifying respirator (APR) and the air-supplying respirator (ASR).
Function
– Ventilator is a type of breathing machine that helps provide oxygen to patients who are having trouble breathing or who are unable to breathe on their own. It keeps the oxygen going to the brain, the heart and the kidneys. The primary function of a ventilator is to treat serious respiratory failure or respirator deficiency resulting from a variety of clinical causes.
On the other hand, APR provides breathable air by removing specific air contaminants and ASR supplies an alternate breathable air from a source independent of the ambient atmosphere.
Indications
– Indications for providing support for mechanical ventilation vary largely among patients. Common indications include conditions due to physiological changes, respiratory failure caused by some disease, medical or surgical procedures, or many other causes leading to oxygenation failure, such as head trauma, drug overdose, etc.
On the other hand, the clinical indications for respirator support include damage to respiratory system caused by exposure to harmful chemicals or gases, or aerosols and fine dust particles. Extremely low level of oxygen or high level of carbon dioxide is the main cause of respiratory failure.
Ventilator vs. Respirator: Comparison Chart

Summary of Ventilator and Respirator
Ventilators are sometimes called respirators because both the devices support artificial breathing, but they are not the same thing. Ventilators are medical devices that support mechanical ventilation and are required when the patient cannot maintain adequate ventilation because of serious respiratory failure or respirator deficiency resulting from a variety of clinical causes. Respirators, on the other hand, are mask-like devices worn over the mouth and nose to protect the respiratory tract by filtering out toxic substances including hazardous fumes, gases, vapors, and dust. They provide breathable air either by filtering specific air contaminants or supplying an alternate breathable air from an uncontaminated source.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Hasan, Ashfaq. Understanding Mechanical Ventilation: A Practical Handbook. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2010. Print
[1]Hasan, Ashfaq. Understanding Mechanical Ventilation: A Practical Handbook. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2010. Print
[2]Chang, David W. Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation. Boston, Massachusetts: Cengage, 2013. Print
[3]Slutsky, Arthur S. and Laurent Brochard. Mechanical Ventilation. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2006. Print
[4]Lei, Yuan. Medical Ventilator System Basics: A Clinical Guide. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 2017. Print
[5]Rajhans, Gyan and Bhawani Pathak. Practical Guide to Respirator Usage in Industry. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2002. Print
[6]Bronzino, Joseph D. and Donald R. Peterson. Medical Devices and Human Engineering. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2018. Print
[7]Image credit; https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mechanical_ventilator.jpg
[8]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:P100_ovm_respirator.jpg
