Difference Between Tokenization and Encryption
Tokenization as an effective obfuscation solution has become quite popular in recent times, especially with merchants. Tokenization is closely related to encryption and while one can draw parallels to encryption, it is quite different from encryption, in that tokenization uses tokens instead of keys to perform encryption. Let’s take a detailed look at how the two differ from each other.

What is Tokenization?
For some security reasons, sometimes it is necessary to obscure actual data and use a representation of that data instead. The term tokenization refers to a method to accomplish this. Tokenization is the practice of replacing any sensitive data, such as a social security number or credit card number, with a surrogate random value called a token. It is a system that separates words from the body of text and the token is a reference to the original data through a tokenization system. The system creates two distinct databases: one with the actual data and one with the tokens mapped to each piece of that data. In this method, the token server authenticates the user or the program calling the data, pulls the correct token from the token database, calls the actual data from the actual database, and then finally presents it to the user or program. Tokenization is often used for credit card processing for added security.
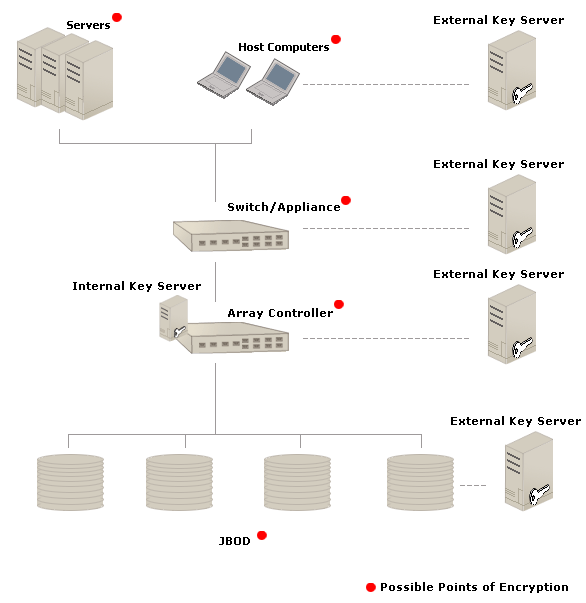
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the practice of encoding a message or information so that only authorized parties can access the data and those who are not authorized cannot access it. Encryption is a method of hiding a message. The science of encrypting and decrypting data is called cryptography. Encryption is one of the most effective ways to achieve data security; it translates data into a secret code, meaning it converts plaintext into ciphertext. Sensitive data or information is encrypted using an algorithm and a key. A key is a string of characters used within the encryption algorithm to conceal the data. Like a physical key, it is used to encrypt the data so that the recipient with the right key can decrypt it. The sender encrypts the plaintext into ciphertext, which is then transmitted to the intended party or the recipient, who then decrypts the ciphertext back into plaintext by decryption. A secret cipher key is required for decryption.
Difference between Tokenization and Encryption
Definition
– Both tokenization and encryption are methods used to secure sensitive information or data that is often transmitted over the Internet. While both are effective obfuscation solutions for data security, they are very different from each other. Tokenization is the method of replacing any sensitive data with a surrogate random value called a token, which is a reference to the original data through a tokenization system. Encryption, on the other hand, is the method of translating plaintext into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm and a key.
Method
– The tokenization system creates two distinct databases: one with the actual data and one with the tokens mapped to each piece of that data. It randomly generates a token value for plaintext and stores the mapping in a database. It is closely related to encryption except the process is irreversible with tokenization. Encryption, on the other hand, scrambles the data using a process that is reversible if you have the right key. The sender encrypts the plaintext into ciphertext, which is then transmitted to the recipient, who then decrypts the ciphertext back into plaintext by decryption.
Approach
– Tokenization system uses tokens to obscure sensitive data or information; it replaces the token value for the actual data in order to access the original data. The token server authenticates the user or the program calling the data, pulls the correct token from the token database, calls the actual data from the actual database, and then finally presents it to the user or program. On the other hand, there are two primary approaches to encryption in widespread use: symmetric and asymmetric encryption. In symmetric encryption, a single key is used for both encryption and decryption, whereas asymmetric encryption uses two keys: one key to encrypt the data and the other key to decrypt it.
Uses
– Tokenization method is often used for credit card processing for added security. The most common use for tokenization is to protect payment card data or bank account numbers, social security numbers, telephone numbers, email addresses and so on. Encryption, on the other hand, is used for both structured fields as well as unstructured fields. It is widely used to protect the communications of individuals and organizations from cybercriminals, and provide security of electronic transactions over the Internet, plus it also protects information stored on smartphones and other mobile devices.
Tokenization vs. Encryption: Comparison Chart

Summary of Tokenization vs. Encryption
In a nutshell, tokenization replaces any sensitive data, such as a social security number or credit card number, with a surrogate random value called a token in order to protect the data, whereas encryption is the method of translating plaintext into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm and a key. Tokenization randomly generates a token value for plaintext and stores the mapping in a database, whereas encryption scrambles the data so that only authorized parties can access the data and those who are not authorized cannot access it. While both are effective obfuscation solutions for data security, they have a distinct approach to cryptography.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Gnanasundaram, Somasundaram and Alok Shrivastava. Information Storage and Management (Second Edition). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. Print
[1]Kiayias, Aggelos. Financial Cryptography and Data Security: 21st International Conference, FC 2017, Sliema, Malta, April 3-7, 2017, Revised Selected Papers. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2017. Print
[2]Malisow, Ben. Certified Cloud Security Professional: Official Study Guide (Second Edition). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2019. Print
[3]Stspleton, Jeff. Security without Obscurity: A Guide to Cryptographic Architectures. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2018. Print
[4]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Piont-of-encryption.gif
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:How_mobile_payment_tokenization_works.png
