Difference Between Private and Public Cloud
Cloud computing is the next big thing after the proliferation of the Internet and it has changed the way we work. It is a service model that delivers on-demand computing resources over the Internet – from computing power to computing infrastructure, applications, business processes and personal collaboration. Today, virtually all businesses are using cloud services and may not even aware of it. There are countless benefits derived from cloud infrastructure addressing business needs and delivering simplicity, and driving business growth and innovation. Cloud computing is offered in three different forms: Private Cloud, Public Cloud and Hybrid Cloud. We take a look at Private and Public Cloud deployment models and identify the key differences between the two.
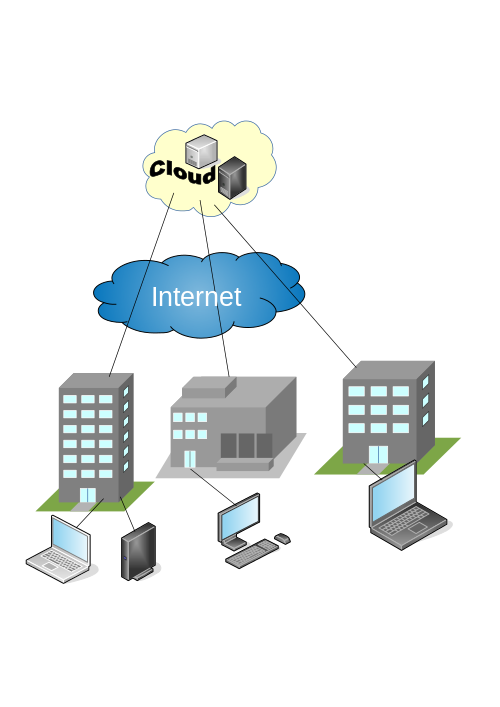
What is Public Cloud?
Public cloud is a cloud deployment model in which a third-party cloud provider owns and provides the resources and other supporting infrastructure to multiple users. It is a cloud infrastructure wherein the computing resources are shared among multiple users. It is like a multi-tenant environment, where a cloud service provider makes computing resources, such as storage and applications, available to multiple users. Public clouds are the most common cloud deployment model. The services offered in the public cloud are usually free or based on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you pay only for the services you use. The public cloud provider owns, manages, and operates all computing resources on-premise and resources available to users are shared across all customers. Cloud service providers in the public cloud domain are AWS, Google, SalesForce, and so on. A public cloud is typically accessible by anyone who wants to opt for the services but because of its one-size-fits-all approach, it is not the most secure model.
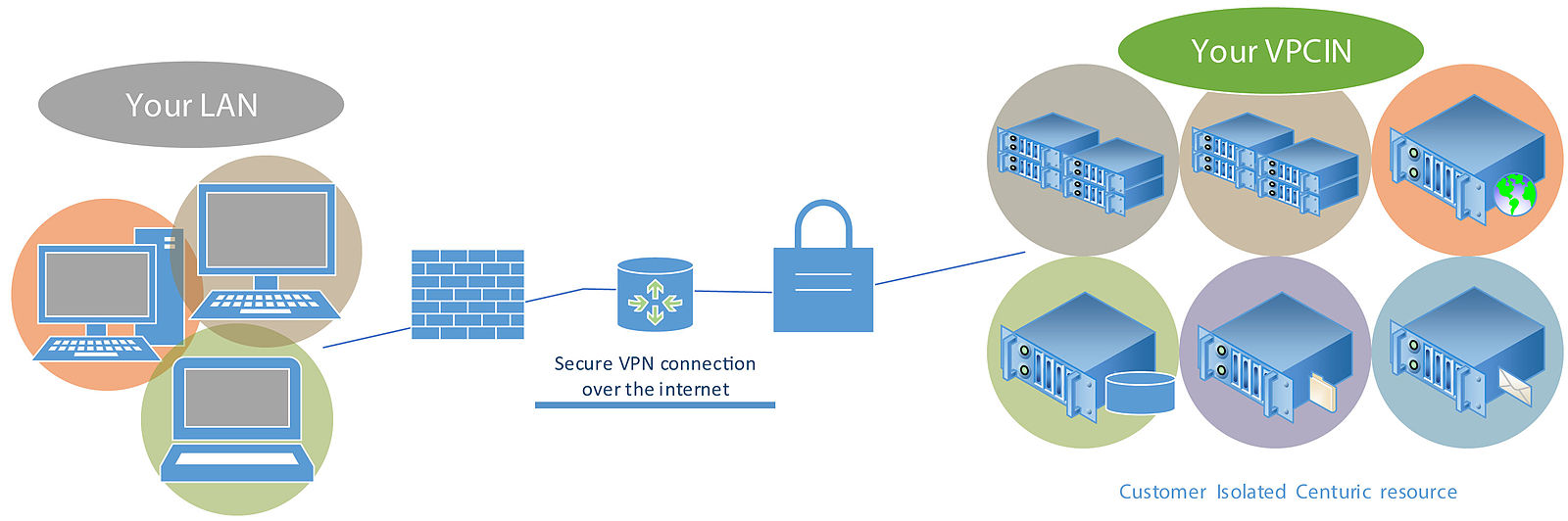
What is Private Cloud?
Private cloud is a dedicated cloud infrastructure reserved and operated for a single entity or organization. A private cloud, as the name suggests, refers to the on-demand cloud computing services offered over the internet within a public cloud environment. A private cloud means a highly virtualized cloud data center on-premise or it can be private space dedicated for a single organization within a third-party cloud vendor data center designed for handling company’s workloads. When an organization requires a secure environment due to regulatory governance, they tend to go for private cloud infrastructure because they provide a well-managed environment and address security concerns by accessing VPNs. A private cloud is basically a lot like a public cloud because they share a lot of common characteristics such as elasticity, scalability and self-service provisioning.
Difference between Private and Public Cloud
Model
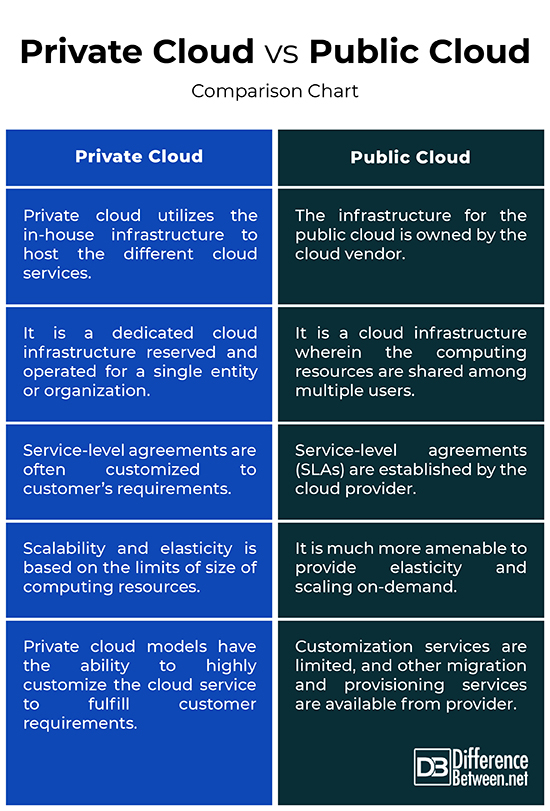
– Public cloud is a cloud deployment model based on a cloud provider typically offering pre-configured and published offerings. It is a cloud infrastructure wherein the computing resources are shared among multiple users. Private cloud is basically a lot like a public cloud, but the major difference is the control over the environment. Private cloud is a dedicated cloud infrastructure reserved and operated for a single entity or organization. In a private cloud infrastructure, you or a trusted partner control the service management.
Cost
– The services offered in the public cloud are usually free or based on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you pay only for the services you use. With public clouds, users can save a lot of money as they do not have to pay for the data center costs like the hardware cost, infrastructure cost, and IT staff. Plus, by dividing computing resources among multiple users, the cloud providers are able to maximize their profits. Private clouds, on the other hand, are cost-effective for medium to large workloads.
Scalability
– The public cloud is much more amenable to provide elasticity and scaling on-demand since the computing resources are shared among multiple users. Scalability is one of the hallmarks of the public cloud model; efficient infrastructure scaling is achieved by performing both vertical and horizontal scaling. Servers can be deployed in minutes or hours to meet the increasing needs of users. However, larger organizations and government entities desire the flexibility and scalability of public cloud offerings.
Customization
– Any over-provisioned resources in the public cloud are well utilized as they can be shared among multiple users and the data centers are geographically dispersed, so even if a data center suffers an outage, the cloud service of a user remains unaffected. However, some unique requirements of larger organizations such as customizations in the procurement, security, and governance processes, are difficult to accomplish using public cloud. Private cloud models have the ability to highly customize the cloud service to fulfill customer requirements.
Private Cloud vs. Public Cloud: Comparison Chart
Summary
In a nutshell, larger organizations and government entities prefer the flexibility and scalability of public cloud offerings, but some unique requirements always force them to consider private cloud services at the end of the day. Only private clouds have the ability to highly customize the cloud service to meet customers’ requirements. On the positive side, a public cloud model is much more amenable to provide elasticity and on-demand scaling since the resources are shared among multiple users. Besides, the aim of a private cloud is to provide users with a flexible and agile private infrastructure rather than selling cloud services to the public.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Qiu, Meikang and Keke Gai. Mobile Cloud Computing: Models, Implementation, and Security. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2017. Print
[1]Hurwitz, Judith S. et al. Cloud Computing For Dummies. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. Print
[2]Vacca, John R. Security in the Private Cloud. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 2017. Print
[3]Bond, James. The Enterprise Cloud: Best Practices for Transforming Legacy IT. California, United States: O'Reilly Media, Inc., 2015. Print
[4]Sitaram, Dinkar and Geetha Manjunath. Moving To The Cloud: Developing Apps in the New World of Cloud Computing. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2011. Print
[5]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b9/Public_Cloud.svg/500px-Public_Cloud.svg.png
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Virtual_Private_Cloud_Isolated_Network.jpg
