Difference Between Phishing and Spoofing
With improved technology and worldwide internet access, cyber intrusions have become a widely used medium for committing white collar crimes including identity theft, data breach, and credit card fraud, among others. Spoofed emails and phishing are the most common ways in which cyber criminals or fraudsters can harm, manipulate or destroy a computer system or network and cause financial harm. Phishing and spoofing are somewhat synonymous in that they refer to forged or fake electronic documents. Phishing typically uses spoofing techniques, but spoofing is not necessarily considered to be phishing.
Spoofing is type of a scam in which a malicious party posing as a legitimate user or business party attempt to steal information from the other party or to trick them to do something worse. Phishing, often utilized in conjunction with a spoofed email, is an act of obtaining personal, sensitive information such as passwords, bank account details, and credit card numbers directly from the end user through the internet. Spoofed emails are typically designed to cause damage to a computer system or network, whereas phishing emails are designed to obtain personal information for financial gain. Both are technique used by cybercriminals to mislead email recipients. However, they have their fair share of differences.

What is Phishing?
Phishing is a variation on the word “fishing”, which means potential spammers will throw bait hoping someone will “bite”. Phishing is a kind of spam attack often utilized in conjunction with a spoofed email made to look as if it comes from a legitimate source. It is an act of sending an unsolicited email falsely claiming to be coming from a legitimate source or a verified sender in an attempt to dupe the recipient into divulging personal, sensitive information such as credit card numbers, bank details, and passwords. Scammers would make the recipient believe that the email has come from a trusted source or website like a bank, for example. The email directs the user to a website which looks legitimate where they are asked to update personal information. However, the website is not genuine and was set up only as an attempt to obtain user’s information.
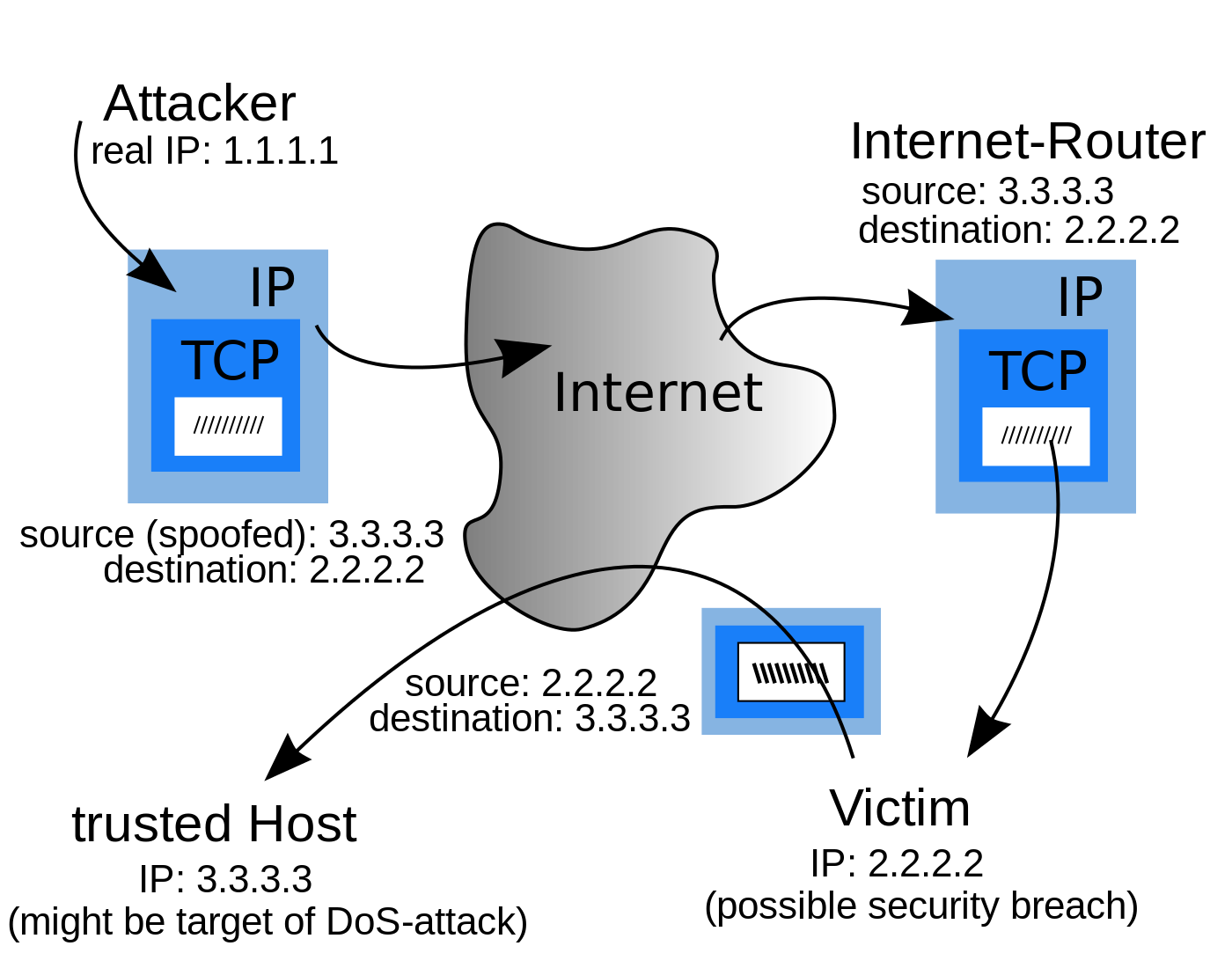
What is Spoofing?
Unlike phishing, spoofing is a way to dupe individuals of their personal and financial information to cause a multitude of security or other problems. Spoofing is basically a cybercriminal activity that involves impersonating a user making him believe that the email came from a trusted source and duping them to gain unauthorized access to their systems in an attempt to steal sensitive information or plant a virus or malware to cause them unrest. Some people call phishing spoofing. In simple terms, spoofing is pretending to be something you are not, whether by looking like that something or by pretending to have come from a verified source although that something was sent by someone other than the actual source. Spoofing can also be performed on data being transmitted across a network, enabling the culprit to get access to data stored on computing systems.
Difference between Phishing and Spoofing
Meaning Phishing and Spoofing
Phishing and spoofing are often confused with each other. In fact, phishing typically uses spoofing techniques, but spoofing is not necessarily considered to be phishing. Many kinds of internet related forgery may refer to spoofing but it is somewhat different from phishing.
Spoofing is a way to dupe individuals of their personal and financial information to cause a multitude of security or other problems. Phishing, on the other hand, is a kind of spam attack often utilized in conjunction with a spoofed email made to look as if it comes from a legitimate source.
Purpose
The main purpose of phishing is to divulge the victims into obtaining personal, sensitive information such as credit card number, bank details, social security number and other sensitive information to compromise the victims’ online security.
Spoofing is when a perpetrator impersonates another user duping him to gain unauthorized access to his system or network in an attempt to steal sensitive information or plant a virus or malware into his system to cause him some damage. Spoofing is mostly used in denial-of-service attacks with the sole intention of flooding the target with overwhelming volume of traffic.
Techniques
Phishing attacks are carefully planned and executed as a set of intricately planned activities. A phishing scam may involve several different email campaigns and web servers. Phishing attacks can be initiated via emails or instant messages. The email directs user to a visit a website which appeared to be legitimate where they are asked to update personal details such as passwords, social security number, credit card number, and bank account information. The website is however, bogus and set up only to steal user’s information.
On the other hand, spoofing attacks are generally categorized into email spoofing, website spoofing, and IP spoofing.
Phishing vs. Spoofing: Comparison Chart

Summary of Phishing vs. Spoofing
In a nutshell, phishing is yet another variation of spoofing, which occurs when an attacker attempts to obtain personal or financial information from the victim using fraudulent means, most often by impersonating as another user or organization, in order to steal their personal, sensitive data such as account numbers and passwords. Spoofing attack is generally planned as a way to divulge individuals into obtaining personal or financial information which the attacker will use to steal their identity and use their details for their interest. Spoofing is the creation of TCP/IP packets using somebody else’s IP address.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Whitman, Michael E. and Herbert J. Mattord. Principles of Information Security. Boston, Massachusetts: Cengage, 2009. Print
[1]Lininger, Rachael and Russell Dean Vines. Phishing: Cutting the Identity Theft Line. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2005. Print
[2]Gordon, Adam and Steven Hernandez. The Official (ISC) 2 Guide to the SSCP CBK. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2016. Print
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:IP_spoofing_en.svg
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/de/illustrations/betrug-phishing-e-mail-angriff-3933004/
