Difference Between Phishing and Spam
Cyber threat is the biggest threat these days with companies and organizations constantly struggling to keep their information safe. The global IT industry spends billions of dollars on security alone in one year – that is more than the GDP of the two-thirds of the nations in the world. And the high-tier organizations are still not safe from prying eyes and potential hackers. Every week, if not day, there’s some news regarding some sort of data breach where thousands of email accounts were compromised or credit card numbers were stolen or something more dangerous. We get security updates for our home computers as soon as some new virus or malware takes over the internet. Every day there’s a new threat roaming the web compromising our security.
These so-called cyber threats are not new – in fact, these threats have been threatening the information security on the internet since ages and they are not stopping. The most prevalent threats associated with internet security and the most common are phishing and spam, each of which presents distinct problems to the integrity of IT operations one way or another. Phishing is an evolution of the word fishing, commonly used by hackers who replaced the letter “f” with “ph” in a hacker dialect. In phishing, the email represents the lure part and the victims are the prey who took the bait. Phishing and spam are the darker side of all the technological advances we enjoy these days. The question is – is phishing same as a spam? Let’s take a look.

What is Phishing?
Phishing is a relatively new technique for age-old con schemes with the purpose of luring the victims into disclosing some valuable or personal information such as social security numbers, credit card numbers, and other personal information which might compromise their online security. It is the most common form of cyber attack which involves emails which is the attacker’s weapon of choice. A phishing attack begins with a lure, such as a formal request to update account information or verify account numbers, from a verified source, mostly financial institutions which seem legitimate at the moment. Attackers often use HTML and scripts from legitimate sites to make their versions appear legitimate. Most of the victims take the bait and click on the bogus links only to get robbed off or worse.
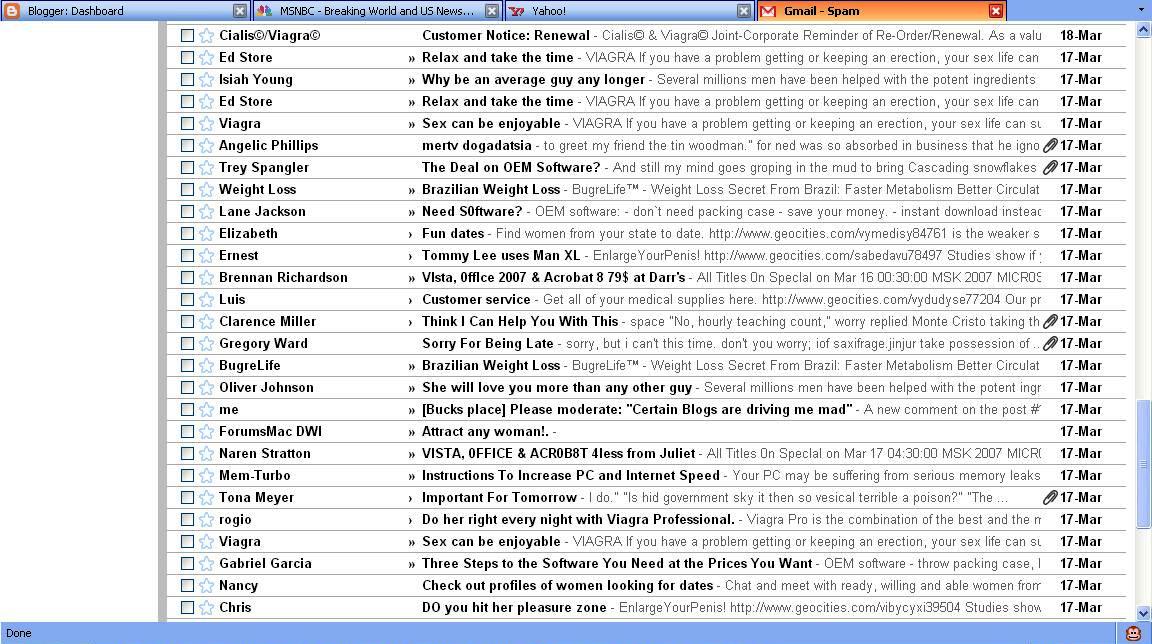
What is Spam?
Spam is yet another form of email attack which may refer to many varieties of exploitation and bad behavior that comes in the category of malware. Spam is unsolicited, unwanted emails flooding your inboxes which is annoying. Those commercial unsolicited emails, often from non-trusted sources or from online sellers trying to sell something are commonly referred to as spam. Spam are emails sent in mass quantities by hackers or cyber criminals to create problems for individuals or network administrators. This result in cluttered inboxes, phishing scams, taxed bandwidth, unwanted storage space, etc. The problem with unsolicited emails in your inbox is you’re most likely to miss some important emails in between.
Difference between Phishing and Spam
-
Definition of Phishing and Spam
– Phishing is the most common form of cyber attack in which the victims are lured by emails, text messages, or calls by the attacker who appear to be a legitimate source or organization into revealing their personal information, such as social security numbers, bank accounts, credit card numbers, account passwords, and more.
– Spam is an electronic equivalent of unsolicited emails, typically sent in masses to a large group of people in order to spread malware, carries out phishing attack, or for advertising. Spam is mostly junk newsgroup postings representing email advertising for some sort of product or service.
-
Objective of Phishing Vs. Spam
– Spam is a form of commercial advertising in the form of emails because emails are still one of the most cost-effective means of advertising. The purpose of spamming is to send commercial emails with commercial content to as many recipients as possible in bulk with the purpose of making some money from recipients who actually respond to the emails.
-Unlike spam, phishing is not limited to just emails. Phishing is quite popular with cybercriminals looking to trick the people into clicking on malicious links with the purpose of obtaining sensitive information or take control of their system.
-
Techniques in Phishing Vs. Spam
– Phishing attacks are intricately planned and executed in an organized manner. They are carefully designed to lure the victims into sharing or revealing their personal information such as login and password so that the attacker can gain control of the victim’s online world such as social networking sites, bank accounts, emails, and more.
– Spamming is hiding the true content of the emails to make the victims spend their valuable money on products that don’t actually exist or counterfeit goods, mostly advertising products such as pharmaceutical stuff or sometimes, security software.
Phishing vs. Spam: Comparison Chart

Summary of Phishing Vs. Spam
Phishing and spam are the darker side of all the technological advances we enjoy these days and are the common threats to information security on the internet. Today, every business is a cyber business and the cyberspace has given the world unprecedented power as well as unprecedented dependence. As a consequence, cybersecurity is an absolute prerequisite. Today, phishing and spamming are the most prevalent threats associated with internet security, each of which possesses a threat to the integrity of cyber world. Phishing is luring users into disclosing valuable information such as credit card details, account passwords, and social security numbers, while spam is a form of commercial advertising in the form of unsolicited emails.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Sullivan, Dan. The Definitive Guide to Controlling Malware, Spyware, Phishing, and Spam. San Francisco, California: Realtime Publishers, 2005. Print
[1]James, Lance. Phishing Exposed. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2005. Print
[2]Kostopoulos, George. Cyberspace and Cybersecurity. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2017. Print
[3]Image credit: http://thewhizzer.blogspot.com/2007/03/e-mail-spam-and-general-whinge.html
[4]Image credit: https://media.defense.gov/2010/Mar/30/2000380364/780/780/0/100330-F-0000M-001.JPG
