Difference Between Internet of Things and Blockchain
The Internet of Things (IoT) is probably the next paradigm shift in the IT world since the cloud and the biggest technological innovation since the advent of the internet. The IoT promises to make things, including consumer electronics part of the Internet environment. This opens vast opportunities for new innovations that will further build novel types of interactions between things and humans. We now live in a world where almost every electronic device is connected to the internet or will be in the near future. The way things are going, the IoT will bring about the next industrial revolution and will dramatically transform the way we interact with technology. Blockchain is a manifestation of the Internet of Things that makes machine-to-machine transactions possible.
What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the next paradigm shift in the IT world that supports integration, exchange and analytics of data generated by smart devices. The IoT is a global network of uniquely identifiable “things” that are connected to the internet. These things have the ability to sense, communicate, and program. It is a system of internet-connected things that are able to send and receive data over a wireless network with or without human intervention. The IoT devices leverage machine learning techniques to use the data collected by the sensors. There’s a huge list of devices, including lights, thermostats, cars, refrigerators, fitness trackers, and so on, that can be connected to the IoT. So, IoT refers to the billions of smart devices that are connected to the internet, and are capable of sending, receiving and sharing data. The IoT is as disruptive as the internet itself, particularly when combined with big data and predictive analytics. The idea is to connect everything to the internet in real time.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a disruptive technology that underpins digital currency. It is a global, distributed, highly-secure database that differs from the typical database in the way it stores information; it stores things of monetary value but without any governing body. Blockchain is a new digital medium for value that ensures the safety and security of your exchanges online. It is like a ledger of transactions that is distributed across the entire business network. Using cryptography, blockchain provides an open decentralized database to record every transaction that has monetary value, such as property, car, land, patents, stocks, bonds, copyrights, just anything of value. Blockchain, like the name suggests, is a chain of records called blocks that contain all the records of every transaction ever made across a peer-to-peer network. And only the network members who have access can view the transactional records.
Difference between Internet of Things and Blockchain
Technology
– The IoT is a global network of physical objects, called things that are connected to the Internet, and have the ability to sense, communicate, and program. It’s a disruptive technology that supports integration, exchange and analytics of data generated by smart devices. The thing in the Internet of Things can be anything, from an implant to a biochip transponder, a smart light, a car with built-in sensors, or anything with the ability to send or receive data over a network.
Blockchain, on the other hand, is an open decentralized database that keeps record of every transaction involving monetary value, such as property, car, land, patents, stocks, bonds, copyrights, just anything of value.
Concept
– The concept of IoT is to connect everything to the internet in real time, from tiny sensors capable of sensing to much powerful backup servers used for data analysis and information extraction. The goal is to create a world of interconnected things which are capable of sensing and communicating among themselves with or without human intervention. Blockchain is essentially a digital ledger that records transactions across a peer-to-peer network as blocks, while keeping them secure by encrypting and authenticating the transactions.
Applications
– Many industries have already adopted IoT to simplify and automate many different processes. Some real life applications of IoT are smart wearables like fitness trackers, traffic and weather monitoring, fleet management, smart agriculture, smart home appliances, smart security systems, and so on.
The infamous digital currency “Bitcoin” was the first application of blockchain technology. Blockchain is used in a wide range of use cases, such as payment processing, supply chains monitoring, loyalty rewards program, data sharing, copyright protection, digital voting, medical recordkeeping, weapons tracking, and much more.
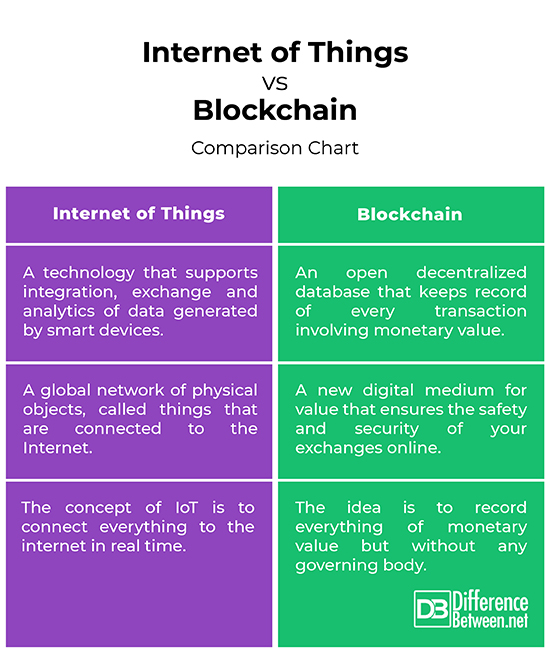
Internet of Things vs. Blockchain: Comparison Chart
Summary
In a nutshell, IoT is a network of interconnected things which are capable of sensing, actuating and communicating with each other and with the environment, with or without human intervention. The idea is to make everyday objects and the everyday environment make smart, so that they’d be able to process and provide information in real time. In principle, every object can be turned into a smart object if manipulated. Blockchain leverages IoT solutions to make machine-to-machine transactions possible, keeping records of every transaction ever made across a peer-to-peer network. Together, they offer many potential benefits and allow smart devices to function autonomously without the need for any central authority. They are not contradictory technologies; in fact, they complement each other.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Lacity, Mary C. Blockchain Foundations: For the Internet of Value. Arkansas, United States: University of Arkansas Press, 2020. Print
[1]Hassan, Qusay F. Internet of Things A to Z: Technologies and Applications. New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons, 2018. Print
[2]Buyya, Rajkumar and Amir Vahid Dastjerdi. Internet of Things: Principles and Paradigms. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2016. Print
[3]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/es/vectors/blockchain-criptomoneda-red-virtual-3277336/
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4355/36802620122_fe3ca90fca_c.jpg
