Difference Between Fog Computing and Edge Computing
Internet of Things (IoT) has been poised as the next big evolution after the Internet promising to change our lives by connecting the physical entities to the Internet in a ubiquitous way leading to a smart world. The IoT devices are all around us connecting wearable devices, smart cars and smart home systems. In fact, studies suggest that the rate at which these devices are integrating themselves into our lives, it is expected that more than 50 billion devices will be connected to the Internet by 2020. Till now, the basic use of Internet is to connect computational machines to machines while communicating in the form of web pages. But IoT goes one step further.
However, to accommodate such massive number of connected devices and to efficiently manage the massive influx of data being collected from each device requires a scalable architecture. In addition, the majority of the devices that make up the Internet of Things are resource constrained; resources such as bandwidth and storage, and computing power are scarce. Such challenges can be mitigated by extending the functions of cloud computing closer to the IoT devices. Fog Computing, also known as Edge Computing is a potential solution that extends the Cloud layer to be closer to the things that produce and consume data. But what are these two technologies and how they differ from each other?
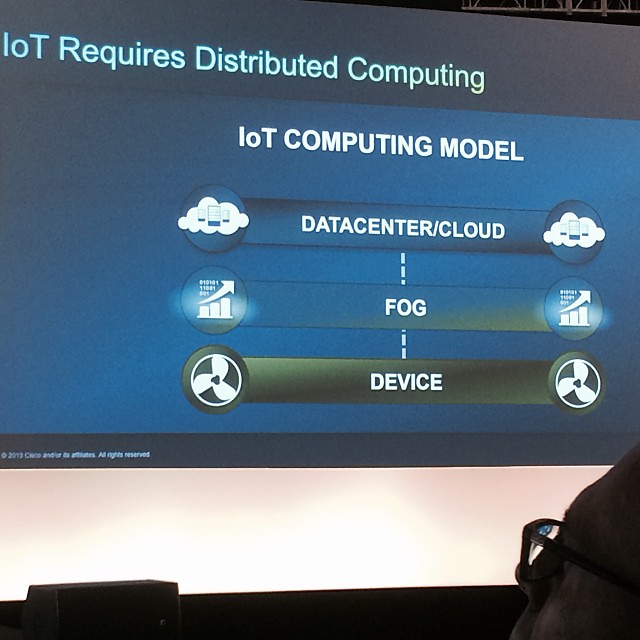
What is Fog Computing?
The term Fog Computing was coined by Cisco and defined as an extension of cloud computing paradigm from the core of network to the edge of network. Fog computing is an intermediate layer that extends the Cloud layer to bring computing, network and storage devices closer to the end-nodes in IoT. The devices at the edge are called fog nodes and can be deployed anywhere with network connectivity, alongside the railway track, traffic controllers, parking meters, or anywhere else. It is an extension of cloud computing not its replacement. It reduces the latency and overcomes the security issues in sending data to the cloud. Due to the close integration with the end devices, it enhances the overall system efficiency, thereby improving the performance of critical cyber-physical systems.
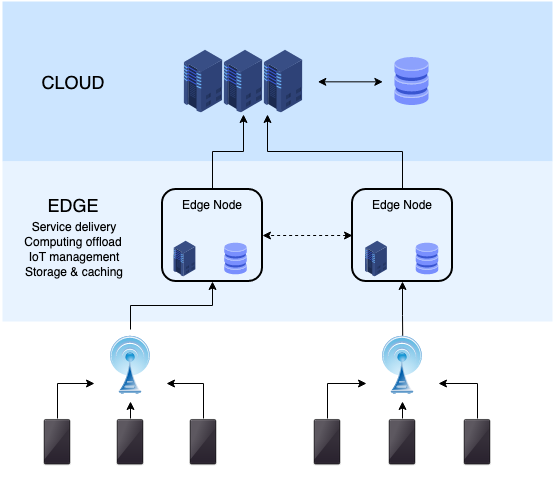
What is Edge Computing?
Although, the main objectives of edge computing and fog computing are same – that is to lower network congestion and reduce end-to-end delay – however, they differ in how they process and handle the data and where the intelligence and computing power are placed. Edge computing is an architecture that uses end-user clients and one or more near-user edge devices collaboratively to push computational facility towards data sources, e.g, sensors, actuators and mobile devices. It pushes the computational infrastructure to the proximity of the data source and the computing complexity will also increase correspondingly. In such architecture, any device with compute, storage and networking capabilities can serve as a near-user edge device. Typically, edge resources are configured in an ad hoc manner to improve the overall system performance.
Difference between Fog Computing and Edge Computing
Concept
– Although, the main objectives of edge computing and fog computing are same – that is to lower network congestion and reduce end-to-end delay – however, they differ in how they process and handle the data and where the intelligence and computing power are placed. Both the terms are often used interchangeably, as both involve bringing intelligence and processing power to the where the data is created. Fog computing pushes intelligence down to the local area network level of the network architecture, while processing data in a fog node or the IoT gateway. Edge computing places the intelligence and power of the edge gateway into the devices such as programmable automation controllers.
Data Communication
– In Fog Computing, the data communication between the data generating devices and the Cloud environment requires a number of steps; communication is first directed to the i/o points of a PAC after which it is sent to a protocol gateway that converts data to an understandable format. Data is then transmitted to a Fog node of local network after which the data is directed to the Cloud for storage. In Edge Computing, on the other hand, the communication is much simpler and there are potentially less points of failure.
Architecture
– Fog computing is a decentralized computing infrastructure that extends cloud computing and services to the edge of the network in order to bring computing, network and storage devices closer to the end-nodes in IoT. The goal is to improve efficiency and reduce the amount of data transported to the cloud for processing, analysis and storage. Edge computing, on the other hand, is an older expression predating the Fog computing term. It is an architecture that uses end-user clients and one or more near-user edge devices collaboratively to push computational facility towards data sources, e.g, sensors, actuators and mobile devices.
Fog Computing vs. Edge Computing: Comparison Chart

Summary
In a nutshell, Fog Computing and Edge Computing are often used to mean the same architecture, and therefore, the terms are regarded as interchangeable; however, a subtle distinction can be made. Although, both offer a potential solution that extends the Cloud layer to be closer to the things that produce and consume data, the main difference is to do with how they handle the data and where the intelligence and computing power are placed. In Fog computing, intelligence is at the local area network, where as in Edge computing, intelligence and power of the edge gateway are in smart devices such as programmable automation controllers.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Edge_computing_infrastructure.png
[1]Image credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/wjarrettc/10555582084
[2]Pethuru, Raj and Anupama Raman. Handbook of Research on Cloud and Fog Computing Infrastructures for Data Science. Pennsylvania, USA: IGI Global, 2018. Print
[3]Mahmood, Zaigham. Fog Computing: Concepts, Frameworks and Technologies. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2018. Print
[4]Cao, Jie, et al. Edge Computing: A Primer. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2018. Print
[5]Munir, Kashif. Advancing Consumer-Centric Fog Computing Architectures. Pennsylvania, USA: IGI Global, 2018. Print
[6]Rahmani, Amir M., et al. Fog Computing in the Internet of Things: Intelligence at the Edge. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2017. Print
