Difference Between Big Data and Data Science
Data was no longer regarded as static or stale, whose usefulness or worthiness was finished once the purpose for which it was collected is served. Rather, data became a raw material of business, a vital element, used to create a new form of economic value. In fact, data is a treasure trove of innovation and services in today’s digital world, ready to prove its worth with the right tools. Technological advances and the proliferation of Internet gave rise to a whole new universe of new content, new data, and new information sources all around us. The sciences like astronomy and genomics coined the term “Big Data”. The concept is now migrating to all functional areas of human endeavor. Regardless of how one defines it, the phenomenon of Big Data is ever more present and ever more important. Big Data has enormous value potential in it and countless opportunities to shape the future. Data Science is the principal means to discover and tap that potential.
What is Big Data?
There is no specific definition of Big Data, regardless; the phenomenon of Big Data is omnipresent. Big Data is an all-inclusive term that refers to the volume of information so large, so vast and so complex that cannot be managed with conventional data processing tools. The quantity of information no longer fit into the memory that computers use for processing, so engineering started working on new tools that could analyze it all. This gives rise to new processing technologies such as Google’s MapReduce and Hadoop, which came out of Yahoo. The basic idea behind Big Data is that everything we do leaves a digital trace, or data, which can be analyzed to obtain actionable insights. Big Data is characterized by four V’s – volume, variety, velocity, and veracity. At the most basic level, Big Data is a collection of data that can be analyzed for business purposes.

What is Data Science?
Big Data has enormous value potential in it and Data Science is the principal means to discover and tap that potential. Data Science is an interdisciplinary field which deals with all things data, providing ways to benefit from Big Data. The ability to gather data electronically prompted the emergence of the exciting new field of Data Science – to bring together the disciplines of computer science and statistics to analyze the insanely huge volumes of data leading to knowledge discovery. The idea behind Data Science is to identify patterns, discover relationships, and to make sense of the raw data. It is a field that deals with the complex world of data while using a blend of tools and algorithms to extract useful information from the data.
Difference between Big Data and Data Science
Definition
– Big Data refers to the large volumes of data that are too vast and complex to be stored and processed with traditional data processing applications. Big Data includes all kinds of data, which help deliver the right information, to the right person, in the right quantity, in order to help make informed decisions. Data Science is a field which comprises of everything related to data including the ways to benefit from Big Data. Data Science is the principal means to discover and tap the potential of Big Data.
Concept
– Big Data is characterized by four V’s – volume, variety, velocity, and veracity. It reflects everything from volumes of data to the complexity of data types and structures to the speed of new data creation. Big Data is data or information that can be used to analyze insights which results in informed decisions and strategic business moves. The ability to gather data electronically resulted in the emergence of the field of Data Science, which brings together the disciplines of computer science and statistics in order to analyze the insanely huge volumes of data that might lead to knowledge discovery.
Purpose
– The real value of Big Data is not in the large volumes of data but what we can do with it. It’s not the amount of data that makes a difference but the ability of analysts to analyze the vast and complex data sets which could not be done before. The purpose is to help businesses create new growth opportunities or to achieve a significant advantage over traditional business practices. The purpose of Data Science is to exploit the opportunities that Big Data presents using new data architectures, principles, tools, and algorithms.
Big Data vs. Data Science: Comparison Chart
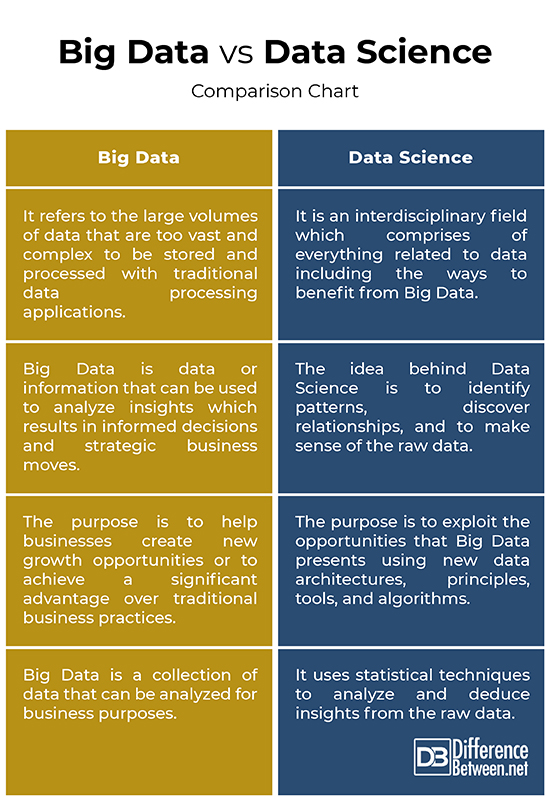
Summary of Big Data vs. Data Science
Big Data has enormous value potential in it and Data Science is the principal means to discover and tap that potential. Big Data is data or information that can be used to analyze insights. The ultimate aim of working with Big Data is to extract useful information. Data Science exploits the opportunities Big Data presents using new methods derived from statistics, computer science and artificial intelligence. While applying the practices of Data Science to Big Data is a valuable differential strategy, it’s likely to be a standard core competency in the not so distant future.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Data Science and Big Data Analytics: Discovering, Analyzing, Visualizing and Presenting Data. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. Print
[1]Data Science and Big Data Analytics: Discovering, Analyzing, Visualizing and Presenting Data. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. Print
[2]Mayer-Schönberger, Viktor and Kenneth Cukier. Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform How We Live, Work, and Think. Boston, Massachusetts: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2013. Print
[3]Maheshwari, Anil. Big Data. Chennai, India: McGraw Hill Education India, 2017. Print
[4]Holmes, Dawan E.. Big Data: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press, 2017. Print
[5]O’Neil, Cathy and Rachel Schutt. Doing Data Science: Straight Talk from the Frontline. Sebastopol, California: O’Reilly Media, 2013. Print
[6]Image credit: https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2020/04/18/08/14/data-5058177_960_720.jpg
[7]Image credit; https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:BigData_2267x1146_trasparent.png
