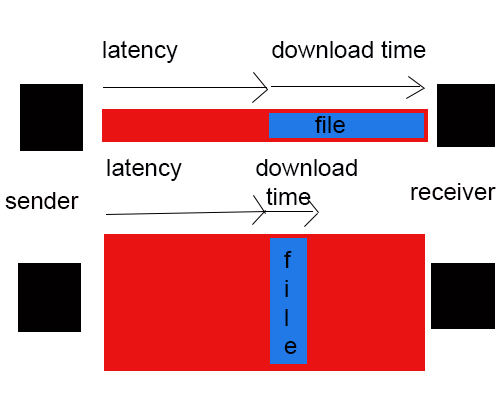
Bandwidth and latency are the primary performance network metrics important to high speed networking. The two may sound surprisingly similar, so to better understand the two, take an example of a train that takes four hours to travel from Edinburgh to Birmingham. So here, the ‘latency’ of the train journey is four hours. And the train carries 400 people, so the bandwidth would be 400 people in four hours, or 100 people an hour. Let’s say if the train could go twice as fast, it would take only two hours to complete the journey and so, the latency would be halved but the train would still carry 400 people. Now, the bandwidth is doubled to 200 people per hour. Bandwidth actually refers to the maximum data transfer rate of a network while latency is the delay that occurs over a network while communicating.

What is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth is the amount of data transferred over a defined period of time. Bandwidth is the single most important factor in the performance of your website. When web hosts talk about bandwidth, they mean specifically how many bytes of data are transmitted per month. It’s more like the free minutes on your cell phone package and if you exhaust your bandwidth allowance, you’ll be charged extra for every extra megabyte of data transferred. Bandwidth of the Internet connection determines the amount of information that can be transmitted in a given unit of time. In the recent years, the term bandwidth has been popularly used to refer to the capacity of a digital communications line, typically measured in some number of bits per second. Bandwidth may be characterized as network bandwidth, digital bandwidth or data bandwidth. For example, a gigabit Ethernet connection delivers a bandwidth of 1,000 Mbps.
What is Latency?
Latency refers to the amount of time it takes for a packet to travel from one point on a network to another. Latency is a way to measure speed, the time delay it takes to send information from one point to another. It is measured as some amount of time, usually in milliseconds. If your web server is accessed over the Internet, then much of your latency is mostly due to the store-and-forward nature of routers. The router must accept an incoming packet into a buffer, look at the header information, and then decide where to send the packet. However, the router has to look for an open slot before it sends the packet. The latency of the packets therefore depends strongly on the number of router hops between the web server and the user. On cable Internet connections, typically latencies can be 100 ms and with satellite internet connections, it can be 500 ms or higher.
Difference between Bandwidth and Latency
Definition
– Bandwidth and latency both play critical roles in determining network system performance. Bandwidth is a measure of frequency ranges, typically used for digital networking communications. In terms of computing, bandwidth is the maximum rate of transfer of data over a defined period of time across a given path. Latency, on the other hand, is a way to measure speed, the time delay it takes to send information from one point to another. Latency refers to the amount of time it takes for a packet to travel from one point on a network to another.
Measure
– The term bandwidth has been commonly used to refer to the capacity of a digital communications line, typically measured in some number of bits per second. Bandwidth may be characterized as network bandwidth, digital bandwidth or data bandwidth. It was originally measured in bits per second, or bps. However, with today’s networks, bandwidth is typically higher and expressed as megabits per second (Mbps), gigabits per second (Gbps), or terabits per second (Tbps). Latency refers to any kind of delay in data communications over a network and it is measured as some amount of time, usually in milliseconds (ms).
Bandwidth vs. Latency: Comparison Chart

Summary of Bandwidth vs. Latency
In a nutshell, both bandwidth and latency are crucial for a great web browsing experience, but the distinction can be pretty confusing. Both are the primary performance network metrics important to high speed networking, but they are the equally misunderstood aspect of data networks when it comes to optimizing bandwidth speeds. Bandwidth is better described as the maximum data transfer rate of a network, but it is not to be confused with a measure of internet speed. Bandwidth actually measures the amount of data that can be transferred over a network for a definite period of time. Latency, on the other hand, is the delay that occurs over a network while communicating. Latency is the amount of time it takes for a packet to travel from one point on a network to another.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024

