Difference Between ADF and JSF
Most of today’s big enterprise applications run on the Java EE (Enterprise Edition) platform which comprises of a set of APIs and the application servers which implement these APIs. The Java EE platform is built on top of the Java SE (Standard Edition) platform and has been improved considerably over the last couple of years. The Enterprise Java application development has become much easier with annotations, dependency injection, EJB 3.0, and JPA. However, the technology is not perfect; it has certain gaps in it. First it lacks tooling support for a visual development experience, plus the Java EE specification fails to cover all the generic needs. The best way to deal with these gaps in the technology is to use a framework that abstracts the complexity of the platform.
The Oracle ADF framework is the most popular application framework that builds on Java EE standards to simplify and accelerate next generation enterprise application development. It provides a Java framework for building enterprise applications by providing out-of-the-box infrastructure services and a declarative development experience. Java JSF, short for JavaServer Faces, is a new emerging technology used for developing web applications based on Java technologies. Building user interfaces is one of the tedious parts of web application development and JSF simplifies the development integration of web-based user interfaces. Technology moves very fast so does business applications and their role in the growing customer base.
What is Oracle ADF?
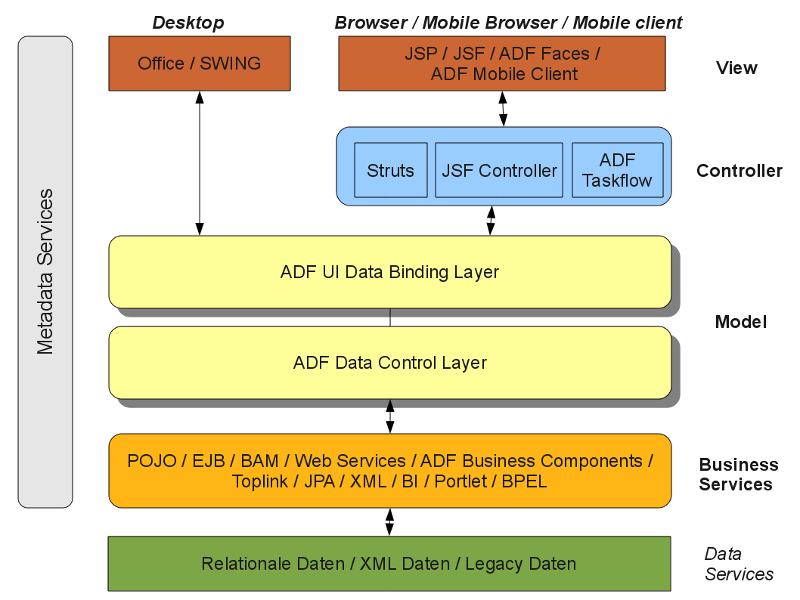
Oracle Application Development Framework, or simply referred to as Oracle ADF, is an end-to-end application development framework built on Java EE standards and open-source technologies for the sole purpose of simplifying development of next generation enterprise applications. The right choice of the tool of development is crucial for success of any business application. Oracle ADF is the popular choice among developers when it comes to enterprise application development because of the flexibility it provides to meet the requirements of different phases of an application lifecycle. The idea is to fill in the gaps in the core Java EE technology to simplify enterprise application development.
What is Java JSF?
JavaServer Faces, or JSF, is a standard Java framework for building component-based user interfaces for web applications. It’s a standardized display technology which was formalized in a specification through the Java Community Press. It’s a web application used to simplify and accelerate development integration of web-based user interfaces. It’s based on Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture which uses XML – view templates or Facelet views. It contains multiple core features including XML-based tag libraries, Managed Beans, and a template based component system.
Difference between ADF and JSF
-
Basic of ADF and JSF
Oracle Application Development Framework, simply called Oracle ADF, is an end-to-end Java EE framework that builds on Java EE standards and open source technologies to simplify building enterprise applications. It’s one of the few best frameworks used to build rich enterprise applications and capable of meeting today’s challenges. JavaServer Faces, or JSF, on the other hand, is one of the best tools used to develop web applications based on Java technologies. It is a standard Java framework used for building component-based user interfaces for Web applications. It was developed by Java Community Press (JCP).
-
Architecture
Oracle ADF is based on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture in which multiple modules can be bundled together to build a complete composite ADF application. The MVC design splits an application into three layers: model layer, view layer, and the controller. The Oracle ADF is based on four layers: Business Service Layer, Model Layer, View Layer, and the Controller Layer. Java JSF application is similar to any other web application based on Java technology and contains JavaBeans, a custom tag library to represent event handlers and to render UI components, server-side helper classes, validators, and navigation handlers.
-
Components
Oracle ADF is actually four parts which provide ready-to-use data control implementations for common business service technologies: ADF Business Components, ADF Controller, ADF Model, and ADF Faces. ADF Model is the central part of the ADF which allows you to create ADF applications based on different types of business services. The main components that make JSF are UI Components, Renderer, Backing beans, Validator, Converter, Event Handlers, and Navigation handlers. Applications that contain any ADF technologies are generally referred to as ADF applications and web applications that incorporate ADF technologies are called Fusion web applications.
-
Significance
The Oracle ADF provides complete solution for building enterprise applications right from implementation to the post-production phase and the declarative nature of ADF improves developer’s productivity. It is ideal for those who want to create applications that can search, create, modify, display, and validate data using web, mobile and desktop interfaces. JSF, on the other hand, is a popular choice among web developers because of the flexibility it provides. It simplifies web application development by providing a component-centric approach to develop web user interfaces. It uses the page controller pattern, thus aids in page rich applications.
ADF vs. JSF: Comparison Chart

Summary of ADF Vs. JSF
Oracle ADF is a popular out-of-the-box Java EE framework integrated through the ADF model layer. The term ADF has become a synonym for declarative Java and Java EE development in Oracle JDeveloper. It is a complete Java EE framework that simplifies and accelerates next generation enterprise applications so that they should be smart enough to adapt with the modern-day changes in the business ecosystem. JavaServer Faces (JSF) is a new standard Java framework for building component-based user interfaces for web applications. It simplifies web application development by following a component-centric approach for developing Java web user interfaces.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Purushothaman, Jobinesh. Oracle ADF Real World Developer's Guide. Birmingham: Packt Publishing, 2012. Print
[1]Harwani, B.M. Java Server Faces: A Practical Approach For Beginners. New Delhi: PHI Learning, 2009. Print
[2]Nimphius. Oracle Fusion Developer Guide. NYC: Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2010. Print
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d9/ADF11g_architecture.png
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/JavaServerFacesSimplifiedLifecycle.svg/500px-JavaServerFacesSimplifiedLifecycle.svg.png
