Difference between Ego and Attitude
What is Ego?
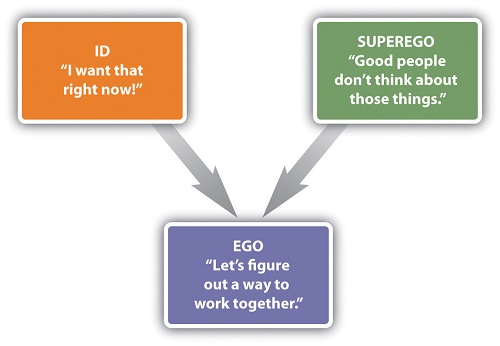
Ego is a person’s sense of self-esteem, self-importance, self-respect, self-image or self-confidence. It’s the part of mind that usually mediates between the conscious and the unconscious and is responsible for reality testing and sense of personal identity.
It’s the identity of our own construction and an identity that is false, our own personality, talents and abilities. But at the end, the mental construct of our self is artificial.
Each person has a different ego. This ego is unique and hard to be seen. It hides behind opinions that appear true which are attachments to description of our identity.
The easy way on how to spot ego is by the trail of emotional reactions it leaves behind. The most deceptive aspects of the ego are that it generates powerful emotional reactions. It then blames us for how it made us feel. Perhaps there is also a victim interpretation of betrayal or injustice underneath.
Characteristics of the Ego
- It gives continuity and consistency to behaviour by providing a personal point of reference. This relates to the events of the past that are retained in memory. Usually actions of the present and of the future are represented in anticipation and imagination.
- The ego maintains the world as an illusion- the ego doesn’t allow you to see the world in awe and wonderment. It keeps us isolated and separated, biased and judgemental, for that reason the ego is said to be an illusion.
- The ego has never been satisfied- when the ego gets what it thinks, it wants more. Such as a person can have big house, expensive vehicles, fine clothes, money and can never be satisfied.
- The ego is also elusive- this when you think, you have gotten rid of the ego, it will reappear as something else, another thought, another concept, or another bias. The ego will do everything in its power to remain alive and well.
What is Attitude?
Attitudes are formed from observing our own behaviours. We form attitudes not due to exposure or associative learning, but from observations of our own behaviour. An attitude usually involves three things such as an attitude object, a set of beliefs that either the object is good or bad and a tendency to behave toward the object to keep or get rid of it.
One of the key dimensions of attitude is strength or resistance to change and how much information does the attitude holder have to back up and interpret his beliefs.
They measure how he or she can view an object from several points of view. Theoretical and research considerations suggest that, if attitude intensity is high, strength is also apt to be high.
Characteristics of attitude
- The attitude object- attitudes usually vary in relative to requirements they tend to serve. Attitudes of an individual towards the pictures serve only entertainment needs but to an employee it serves strong needs for achievement and recognition.
- Attitudes have consistency- attitudes are relatively consistent with the behaviour they reflect, however, attitudes are not necessarily permanent. Attitudes do change.
- Strength- attitudes that are based on direct experience with the object may be held with greater certainty, hence attitudes that are formed based on affect are more certain than attitudes based on cognition.
- It characterizes valence. Valence is the degree or grade of likeness or unlikeness toward the entity. If a person is fairly unconcerned toward an object then his attitude has low valence.
Difference between ego and attitudes
- Attitude has no mirror image. Ego is mirror image of what’s inside and hence leads human perception in a world of duality.
- Attitude makes you totally different from others whereas ego makes you alone from others.
- Ego is how you feel about yourself while attitude is how you physically manifest these thoughts and feelings.
- The attitude does not necessarily create an identity as it is generalized, whereas ego essentially creates identity.
Difference between ego and attitude
ATTITUDE |
EGO |
| 1.Attitude makes one to feel that she/he is totally different from others. | The ego makes one to feel that he or she is alone from the others. |
| 2. Attitude is the settled way of thinking or feeling about something or someone. | Ego is a person’s sense of self-esteem or self-importance. |
| 3. Attitude is its following that is reflected in behaviour of an individual. | Ego in one way can be considered as the investigative authority. |
| 4. Attitude deludes the self in other departments needed to keep body and mind healthy. | When the ego is attaches in excess its reflected in our behaviour. |
| 5. Attitude makes nature in self which create negative energy and attracts people with the same charge, hence can lead to ignorance. | With the ego its responsible to handle such feelings hence one is position of making better decision. |
| 6. Attitudes have no mirror image. | Ego is mirror image of soul and hence leads human perception in a world of duality. |
| 7. Attitude mostly affects the thinking and has no sense of drama hence cannot play the role of up and down of mankind. | Ego is also necessary for the drama of all kind and has a great role to play in all the ups and down of mankind. |
Summary of ego and attitude
- Social scientists often focus on attitude by looking simply at how good or bad the people feel.
- Attitude has different dimensions such as how much information does the attitude holder have to backup and interpret his ideas, how change resistant is the attitude and how intense the attitude holder feel about the object.
- Ego means the extent to which one thinks highly of one’s self.
- Difference between Ego and Attitude - February 19, 2018
- Difference Between Cavalier King Charles Spaniel and King Charles Spaniel - April 10, 2011
- Difference Between Eastern Religions and Western Religions - April 10, 2011
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]A.H and Chaiken, S. The Psychology of attitudes. Fort Worth Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich.
[1]Sigmund Freud. The Ego and the id.1923 print.
[2]Carolyn sheriff, Muzafer Sherif and Robert Nebergall, Attitude and Attitude Change. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders co., 1965 print.
[3]"Image Credit: http://open.lib.umn.edu/intropsyc/chapter/11-2-the-origins-of-personality/"
[4]"Image Credit: http://www.indizoom.com/2012/11/quotes-by-henry-ford.html"


I read this article because I am working on myself and trying to change the negative character traits I possess and am unhappy with. Times my ego has created situations I wasn’t proud of, and wished I was more humble. Thanks for your insight and explanation of two big ones I will work on