The differences between Lice and Crabs
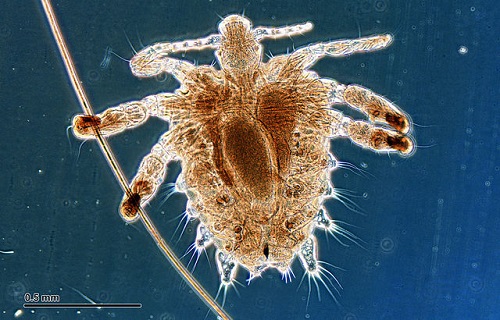
Introduction
Lice is the common name for the Phthiraptera species, which consists of 5000 insects. These are parasites which live on warm blooded hosts, while serving as carriers for diseases such as typhus. Humans host three species of lice namely;
- Head louse: as the name says, these lice are found mainly in hair, at the nape of the neck, and posterior to the ears
- Body louse: colonize in clothing seams, move to the body only when feeding
- Pubic louse[i]: commonly known as crabs, colonize in areas of thick hair growth especially in pubic area, as well as facial hair, armpits, and chest hair. They are least likely to be found on the scalp area.
Lice infestation on the human host is known as pediculosis. All lice on the human body survive by feeding on human blood. They are unable to fly or jump, or walk well on flat surfaces. Thus, are spread by close contact amongst individuals. Luckily the head louse and pubic louse are not vectors for human diseases / pathogens, like the body louse. Which, transmits Epidemic Typhus, Relapsing fever, and Trench fever. The diseases caused by lice remain a major public health concern, in poverty stricken populations where hygiene is poor, resulting in a favourable environment for the prevalence of lice.
History
Lice have plagued humanity throughout history and were most present / widely distributed in the middle ages. Soldiers fighting in the First World War suffered immensely due to lice and the diseases they carried, as did German soldiers in the Second World War.
Physical attributes
Adult head lice are light grey in colour, dorso-ventrally flattened, with a length of 2.1 mm to 3.3 mm. They have 6 legs and attach their eggs to the base of the hair shaft.
Body lice are between 2.3 mm to 3.6 mm in length, and appear as yellow to white in colour. They also have 6 legs like that of head lice. However, body lice bear two antenna from the head. In contrast to head lice, live and lay eggs on items of clothing, linen, towels etc.
Pubic lice are light brown and much smaller in comparison, with a length of 1.1 mm to 1.8 mm. Adult pubic lice are crab like in appearance, hence the common name “crabs”. Similar to head and body lice, the pubic lice have 6 legs, with a round body. Where the two front legs are larger than the latter 4. Adults lay eggs on the hair shaft, close to the skin[ii].
Life cycle
The female louse lays approximately 300 eggs / nits in her lifetime, on hair follicles, clothing seams, and base of pubic hair shaft. Eggs hatch into nymphs after 6 to 10 days. Nymphs mature into adults after 10 days, and live up to 30 days. These lice feed on blood up to 5 times per day. Adult head lice die in less than 24 hours of separation from host, while adult body lice can survive between 3 to 5 days after host separation. While pubic lice survive between 24 to 48 hours after separated from host[iii].
Causes of infestations
Infestation of head lice occurs through close bodily contact, and brushes. Interestingly, the most common lice infestation is that of the head louse, amongst children between the ages of 3 to 11 years. Additionally it is seen more commonly in populations of low socio-economic status, where there are 4 or more children per family, as well as clustering of students in school contexts. With an infestation rate of 37%[iv].
On the other hand, body lice is transmitted through contact with clothing and linen (i.e. clothes are inefficiently washed, cleaned, and changed, or lack thereof). Such conditions are prevalent in crowded and unhygienic environments like homeless shelters, orphanages, refugee camps, etc. Body lice are a major public health concern, due to the carrier diseases mentioned before. With a developed countries infestation rate being 11% to 22% under normal conditions. While, infestation rates escalate to 80% in poverty stricken and unhygienic conditions.
Pubic lice infestation is also transmitted through close body to body contact i.e. sexual contact and are more commonly found in adults. These lice are not vectors for disease. However, secondary infection can transpire due to excoriated skin from scratching. Studies are insufficient regarding infestation rates of pubic lice, with an average rate of 2%.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestation includes pruritus (intense itching) and a rash. Head lice also cause a tickling sensation, irritability, and sleeplessness. Repeated body lice infestation can cause thickened skin over abdomen due to excessive scratching causing a darker, thicker band of skin known as “vagabond’s disease”. Pubic lice also causes pruritus, irritability, fatigue, and mild fever in patients. Infected individuals should additionally be evaluated for sexually transmitted diseases.
Diagnosis
However diagnosis is comparable across all three human host parasites. That is diagnosis is confirmed by identifying live nymph or adult louse.
Treatment
Head lice are treated using pediculicides (kill lice) and ovicides (kill eggs) combined with routine retreatments. Pediculicides are also used to treat body lice. However, improving personal hygiene will treat body lice. Such as regular change of clean the clothes, bedding, and towels used by infected person. These items should be washed in hot water and tumble dried using the hot cycle.
Pubic lice are treated using over the counter drugstore ointments containing permethrin, or pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide. Lindane shampoo and malathion lotion are prescription medications also used to treat pubic lice.
Prevention and Control
Head lice
- Avoid head to head contact
- Do not share clothing, towels, brushes, etc.
- Avoid lying on beds, couches, chairs etc., that the infected individual has used
- Machine wash and dry fabric items in hot water (130° F)
Body lice
- Regular bathing, regular change of clothing
- Regular cleaning and washing of clothing, linen, towels, etc.
- Do not share clothing items with infected persons, nor linen, towels, etc.
- Fumigate if necessary
Pubic lice
- Sexual partners or contacts of infected individual need to be assessed for lice and treated accordingly
- Sexual contact should be avoided until persistent reinfection is ruled out
- Do not use clothing, linen, towels etc. of infected individual
- Machine wash fabric items with hot water (130° F)[v]
Comparison of lice and crabs
| Head Louse | Body Louse | Pubic Louse (Crab louse) |
| Found mainly in hair, at the nape of the neck, and posterior to the ears | Colonize in clothing seams, move to the body only when feeding | Colonize in areas of thick hair growth especially in pubic area, as well as facial hair, armpits, and chest hair |
| Secondary infections due to excoriated skin from scratching | Acts as a carrier for other diseases such as Epidemic Typhus, Relapsing fever, and Trench fever | Secondary infections due to excoriated skin from scratching. |
| Adult head lice die in less than 24 hours of separation from host | Adult body lice can survive between 3 to 5 days after die after host separation. | Adult pubic lice survive between 24 to 48 hours after separated from host[vi] |
| Infestation of head lice occurs through close bodily contact, and brushes | Transmitted through contact with clothing and linen | Transmitted through close body to body contact i.e. sexual contact |
| Infestation rate of 37% | Infestation rate between 11% to 22% under normal conditions and escalation to 80% in poverty stricken and unhygienic conditions | Average infestation rate of 2% |
| Clinical manifestation includes pruritus (intense itching) and a rash. Head lice also cause a tickling sensation, irritability, and sleeplessness. | Clinical manifestation includes pruritus (intense itching), rash, vagabonds disease | Clinical manifestations include pruritus, irritability, fatigue, and mild fever |
| Appear to be flattened and longer. Similar in appearance to a flea. Light grey in colour. | Appear to be flattened and longer. Yellow to white in colour. | Appear to be short and crab like. Light brown in colour. |
| Treated using pediculicides (kill lice) and ovicides (kill eggs) combined with routine retreatments. | Improved personal hygiene Such as regular change of clean the clothes, bedding, and towels used by infected person. Pediculicides can also be used to treat body lice | Treated using over the counter drugstore ointments containing permethrin, or pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide. Oher prescription medications such as Lindane shampoo and malathion lotion are used to treat pubic lice as well. |
| Length of 2.1 mm to 3.3 mm | 2.3 mm to 3.6 mm in length | Length of 1.1 mm to 1.8 mm |
| Lay eggs on hair shaft base | Lay eggs on clothing seams and fibres | Lay eggs on hair shaft |
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0][i] Louse. (2017, April 20). Retrieved April 21, 2017, from https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Louse
[1][ii] Last updated on March 26th, 2017 by Samuel Peterson. (n.d.). Crabs STD (Pubic lice) detailed Pictures & Images. Retrieved April 21, 2017, from https://www.std-gov.org/std_picture/crabs_std_pubic_lice_pictures.htm
[2][iii] Badiaga, S., & Brouqui, P. (2012). Human louse‐transmitted infectious diseases. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 18(4), 332-337.
[3][iv] Head lice infestations: A clinical update. (2004). Paediatrics & Child Health, 9(9), 647–651.
[4][v] Parasites - Lice. (2013, September 24). Retrieved April 21, 2017, from https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/lice/
[5][vi] Badiaga, S., & Brouqui, P. (2012). Human louse‐transmitted infectious diseases. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 18(4), 332-337.
[6]https://hi.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E0%A4%9A%E0%A4%BF%E0%A4%A4%E0%A5%8D%E0%A4%B0:Crab_louse_(251_23)_Female,_from_a_human_host.jpg
