Difference Between Somatic Delusions and Hypochondriasis
People with hypochondria can consider the possibility that the feared illness is not actually present. People with somatic-type delusional condition, on the other hand, are utterly convinced that the cause of their ailments is physical. Thus, the degree of delusion separates delusional disease from hypochondria.

Somatic delusions
Somatic delusions can be incredibly stressful, uncomfortable, and terrifying. They frustrate loved ones as well, who find it difficult to convince them again and time again. Somatic delusions (highly stressful), in which the patient thinks there is a physical problem (issues related to physical health) with some or all of their body, can be present in a wide range of mental illnesses, including mood disorders like severe depression and bipolar disorder as well as psychotic disorders like schizophrenia

Hypochondriasis
One sort of anxiety problem is hypochondria. It is sometimes referred to as hypochondriasis, disease anxiety condition, or health anxiety. It’s common for folks to occasionally worry and be concerned about their health. However, those who have hypochondria are extremely concerned that they are, or will soon be, terribly ill.
Difference between Somatic delusions and Hypochondriasis
Definition
Somatic delusions
An incorrect perception that a person’s internal or exterior body functions are abnormal is known as a somatic delusion. This idea may also include the notion that one’s physical appearance is extremely atypical.
It is also referred to as monosymptomatic hypochondriacal psychosis, and it is a relatively uncommon type of delusion. People with somatic delusions find it challenging to be persuaded that their symptoms or beliefs are incorrect. The most frequent type of somatic illusion seen in people is parasitic infestations.
Hypochondriasis
A person with hypochondriasis or hypochondria is someone who worries excessively and unnecessarily about having a serious illness. The definition of hypochondria has evolved over time, and the term is not new. Despite the lack of a formal medical diagnosis, it has been asserted that this incapacitating disease is the result of an incorrect assessment of the state of the body or mind. A hypochondriac is a person who suffers from hypochondriasis. Regardless of how small the symptom may be, hypochondriacs overreact to any physical or psychological symptom and believe they either have or are soon to be diagnosed with a dangerous illness.
Causes
Somatic delusions
A variety of environmental, genetic, neurological, biochemical, and psychological factors can contribute to somatic illusion. For instance, abnormally high amounts of the neurotransmitter dopamine coupled with reduced cerebral blood flow may lead to the emergence of these delusions. Other mental or neurological conditions can also cause this kind of illusion. Below is a list of somatic delusion’s contributing factors:
- Delusions are a primary sign of schizophrenia.
- Psychopathic disorder
- schizophrenia-like condition
- collective psychotic disorder
- for a brief period of time
- addiction-related psychotic disorder
- (Typically seen during manic phases) bipolar disorder
- major depressive disorder with psychotic symptoms
- Dementia
Hypochondriasis
The causes include:
Family/Genetic influences
Disorder of cognition or perception
Faulty thoughts/interpretation of physical signs.
Treatment
Somatic delusions
Medication
- Antidepressants
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Serotonin and norepinephrine inhibitors (SNRIs)
Cognitive behavioral therapy – helps individuals with somatic delusions recognize and stop getting negative thoughts
Family therapy
Hypochondriasis
- Drug treatment
- Stress management
- Exposure Therapy
- Psychotherapy
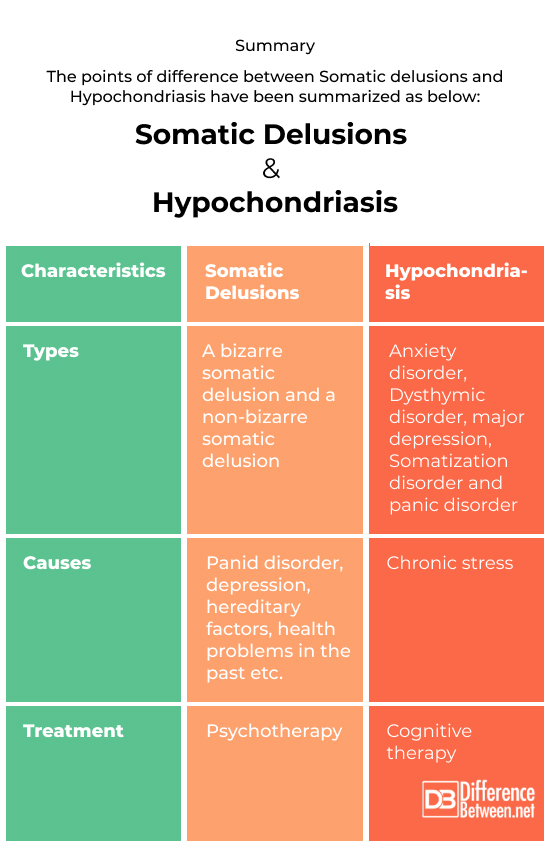
Summary
The points of difference between Somatic delusions and Hypochondriasis have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
What is the difference between hypochondriac and somatic?
Somatization disorder (characterized by an extreme focus on physical symptoms — such as pain or fatigue) is a dramatic, externalizing disorder, whereas hypochondriasis (health anxiety) is described as an apprehensive, internalising disturbance.
What is the difference between somatization and somatic delusions?
The presentation of psychological or emotional elements as physical (somatic) symptoms is termed as somatization.
Somatic delusions (frightening, unpleasant, and highly stressful), in which the patient thinks there is a physical problem (issues related to physical health) with some or all of their body, can be present in a wide range of mental illnesses, including mood disorders like severe depression and bipolar disorder as well as psychotic disorders like schizophrenia (a mental health condition where people experience psychosis – hallucinations) and schizophreniform disorder (a psychotic disorder that affects how you act, think, relate to others, express emotions and perceive reality).
What is the difference between somatic delusions and illness anxiety disorder?
The patient’s focus on symptoms rather than a preoccupation with sickness (worrying excessively that you are or may become seriously ill) and the related worry distinguishes somatic symptom disorder (when a person has a significant focus on physical symptoms, such as pain, weakness) from illness anxiety disorder. The disorder of somatic symptoms and a medical condition may coexist.
What is a hypochondriacal delusion?
These are common in adults. It features of schizophrenia (condition where people experience psychosis – hallucinations (seeing, hearing, feeling, tasting or smelling things) and depressive disorder (a mood disorder that results in a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest and can interfere with your daily chores).
What is an example of a somatic delusion?
The most common example is fatigue and weakness, a person infested by insects and parasites.
What is an example of a hypochondriacal delusion?
Example of a hypochondriacal delusion is a person suffering from slight cough may think that they are having tuberculosis.
What are hypochondriac examples?
- Getting lot of medical tests done
- Problems in sleeping
- Always thinking that they suffer from serious health conditions
- Spend hours browsing internet and reading about signs and symptoms of their illness that does not exist
What is an example of hypochondriasis defence mechanism?
Focusing intently on bodily signs and how they might present themselves could provide alleviation from life-satisfaction feelings.
What is hypochondriacal disorder also known as?
It is also known as hypochondriasis, health anxiety, and illness anxiety disorder
What causes hypochondriacal delusions?
People with hypochondria (anxiety disorder) can consider the possibility that the feared illness does not actually exist. People with somatic-type delusional condition (a delusion that something is wrong with his or her body), on the other hand, are utterly convinced that the cause of their ailments is physical.
Can anxiety cause somatic delusions?
Patients with anxiety and depression frequently have somatic signs and symptoms such abdominal/stomach discomfort, tiredness or fatigue, and chest pain. Thirty percent of people who are depressed or anxious also have concurrent somatic symptoms.
Do people with hypochondriasis pretend to be sick?
Hypochondriacs don’t falsify test findings; instead, they really believe they are ill. Malingerers are those who make up an illness in order to receive money or avoid serving in the military.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Creed, F., & Barsky, A. (2004). A systematic review of the epidemiology of somatisation disorder and hypochondriasis. Journal of psychosomatic research, 56(4), 391-408.
[1]Paolini, E., Moretti, P., & Compton, M. T. (2016). Delusions in first-episode psychosis: Principal component analysis of twelve types of delusions and demographic and clinical correlates of resulting domains. Psychiatry research, 243, 5-13.
[2]Rosenfeld, D. (1984). Hypochondrias, somatic delusion and body scheme in psycho-analytic practice. The International Journal of Psycho-Analysis, 65, 377.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEVocXohi8-woman-in-beige-top-staring/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADSKzIItNs-hypochondriasis-confirm-grunge-concept/
