Difference Between Positive TB Skin Test and Negative TB Skin Test
A positive TB skin test is when the result indicates that bacteria that cause tuberculosis are present. A negative TB skin test is when the result indicates that bacteria that cause tuberculosis are absent.
What is Positive TB skin test?
Definition:
A positive TB skin test is when the Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST) indicates that a person has the tuberculosis bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis in their body based on the appearance of the skin prick test after 48 to 72 hours.
Method:
A special syringe is used to inject 0.1 ml of tuberculin into the skin. This is actually a protein that has been extracted from the bacterium and carefully modified and purified. The idea is that if you have been exposed to a TB infection that your immune system will quickly rush to the site of the injection. Here the white blood cells, the T cells, will arrive and release chemicals called lymphokines that attract more immune system cells and cause swelling of the area. After 48 to 72 hours the patient needs to return to have the raised area that occurs measured. The measurement needs to be taken across the arm at right angles to the long axis of the arm, and the measurement is done in millimeters. It is the raised part that is measured, not the extent of the redness that is present.
Appearance:
A positive result from the test is a hardened swollen raised area on the skin of a certain size depending on the history of the person being tested. Patients who have a suppressed immune system or who have been in contact with a person who is ill with TB can show a swelling of more than 5 mm in diameter. Individuals recently arrived from a country where the disease is very prevalent or people working with the bacterium in the lab may show a raised area of more than 10 mm in diameter. A positive result for a person who does not have any risk factors is a swelling of 15 mm in diameter.
Limitations:
A positive test cannot be used to determine if a person has an active infection or a dormant infection. Further testing such as chest X-rays or sputum analysis needs to be done to determine this. A further limitation is that occasionally there are false positive test results due to a person having been exposed to a different type of bacteria that is closely related to M. tuberculosis. In addition, a person who has recently had the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine may also show a positive result on this test.
Recommended action:
If the diagnosis of TB is confirmed, then the person needs to receive treatment as soon as possible. The condition is contagious especially in a person who is actively coughing. Patients need to avoid contact with others and may need to be isolated. They are also given a course of antibiotics to take which needs to be completed.
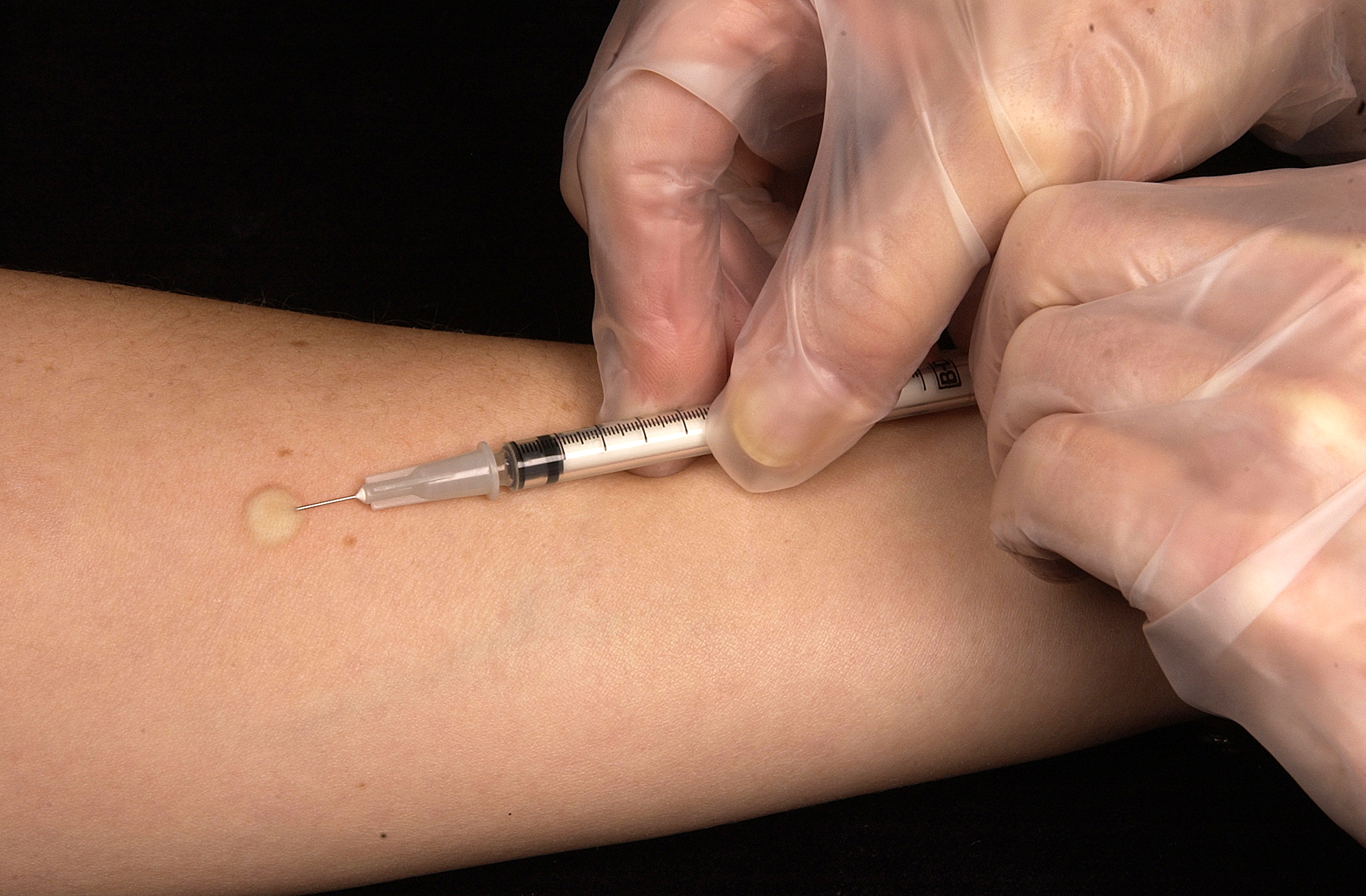
What is Negative TB skin test?
Definition:
A negative TB skin test is when the Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST) indicates that a person does not have the tuberculosis bacterium in their body based on the appearance of the skin prick test after 48 to 72 hours.
Method:
The same method of testing is done in which a small amount of tuberculin protein is injected into the skin and then the raised area measured after a 48 to 72 hour time period. In a negative test the lymphocytes will not move to the injection site as quickly and so the raised area will not be very big, or diagnostically very big.
Appearance:
In the case of a negative TB skin test there will not be a red raised area or bump present, or if there is any indication of such an area it will be less than 5 mm in diameter when measured.
Limitations:
Unfortunately, there are some limitations to this test in certain situations. For instance, individuals who have HIV or are very ill may not react to the skin test in the way that is expected. This means that it is possible to have false negative test results in these situations.
Recommended action:
If tuberculosis is still suspected based on symptoms then either the TB skin test can be repeated or further diagnostic testing can be done. Blood can be tested, sputum can be analyzed and chest X-rays can be done to further test if TB is present. If TB is not suspected due to the person being in a low-risk category and having no symptoms, then nothing further needs to be done. If symptoms do appear later a person can always be retested for TB at a later date.
Difference between Positive vs. Negative TB skin test?
-
Definition
A positive TB skin test is when the Mantoux tuberculin skin test indicates that a person has the bacteria or has been exposed to M. tuberculosis. A negative TB skin test indicates that a person has not been exposed to M. tuberculosis.
-
Raised area
A raised area is always present in a positive skin test. This is not always the case with a negative skin test.
-
Diameter of the raised area
In a positive test, the raised area will be more than 5 or 10 mm in diameter in high-risk people, or more than 15 mm in low-risk people. In a negative test any raised area will be less than 5 mm in diameter.
-
Limitations
In a positive skin test, false positives can occur if one has had the BCG vaccine recently, and a test cannot indicate if an infection is active or dormant. In a negative skin test, false negatives can occur in people with HIV or who are very ill.
-
Recommended action
If a person has a positive TB skin test then once the diagnosis is confirmed treatment with antibiotics should begin. If a person has a negative TB skin test but has symptoms, then further testing should be done.
Table comparing Positive vs. Negative TB skin test

Summary of Positive vs. Negative TB skin test
- A positive TB skin test can indicate that a person has a dormant or active TB infection.
- A negative TB skin test can show that a person does not have any type of TB infection.
- There are both false positive and false positive TB skin tests that physicians need to be aware of.
- If a person does have TB then antibiotics need to be started as soon as possible.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk%3AMantoux_test#/media/File:Mantoux_tuberculin_skin_test.jpg
[1]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Negative_Mantoux_Test.jpg
[2]Nayak, Surajit, and Basanti Acharjya. "Mantoux test and its interpretation." Indian dermatology online journal 3.1 (2012): 2.
[3]Tierney, Dylan and Edward A. Nardell. “Tuberculosis (TB)”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/mycobacteria/tuberculosis-tb#v1010798
[4]Yang, Hongliang, Nicole A. Kruh-Garcia, and Karen M. Dobos. "Purified protein derivatives of tuberculin—past, present, and future." FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology 66.3 (2012): 273-280.

It’s going to be end of mine day, however before finish I am reading this enormous paragraph to improve my know-how.