Difference Between Pneumonia and Lung Infection
Lung infection is a condition characterized by the penetration, multiplication, and excretion of toxins from various microorganisms in the lungs. As a result of this pathological process, the lung tissue responds with an inflammatory response. Pneumonia is one of the most common lung infections.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs, affecting separately or simultaneously the alveoli and the tissue that surrounds them. The infection causes an inflammatory response in which the alveoli fill with fluid (exudate or transudate). This leads to some of the typical symptoms of pneumonia such as cough, fever, difficulty breathing, etc.
Usually, pneumonia is a complication of upper respiratory tract infections, with the inflammatory process gradually descending to the bronchial mucosa, overtaking the smallest branches of the bronchi and the lung itself.
Pneumonia can be caused by:
- Infectious agents – bacteria (aerobic and anaerobic), viruses (coronaviruses, adenoviruses, rhinoviruses), fungi and molds (Candida, Actinomyces, Aspergillus);
- Chemical factors – irritant gases, aspiration of gastric juice;
- Physical factors – radiation, trauma, foreign body in the bronchi;
Pneumonia can be:
- Depending on the etiology – infectious and non-infectious pneumonia;
- Depending on the presence of prior diseases – primary and secondary pneumonia;
- Depending on the localization of the inflammatory process – alveolar and interstitial pneumonia;
- Depending on the spread of the inflammatory process – lobar, lobular, segmental, unilateral, and bilateral pneumonia.
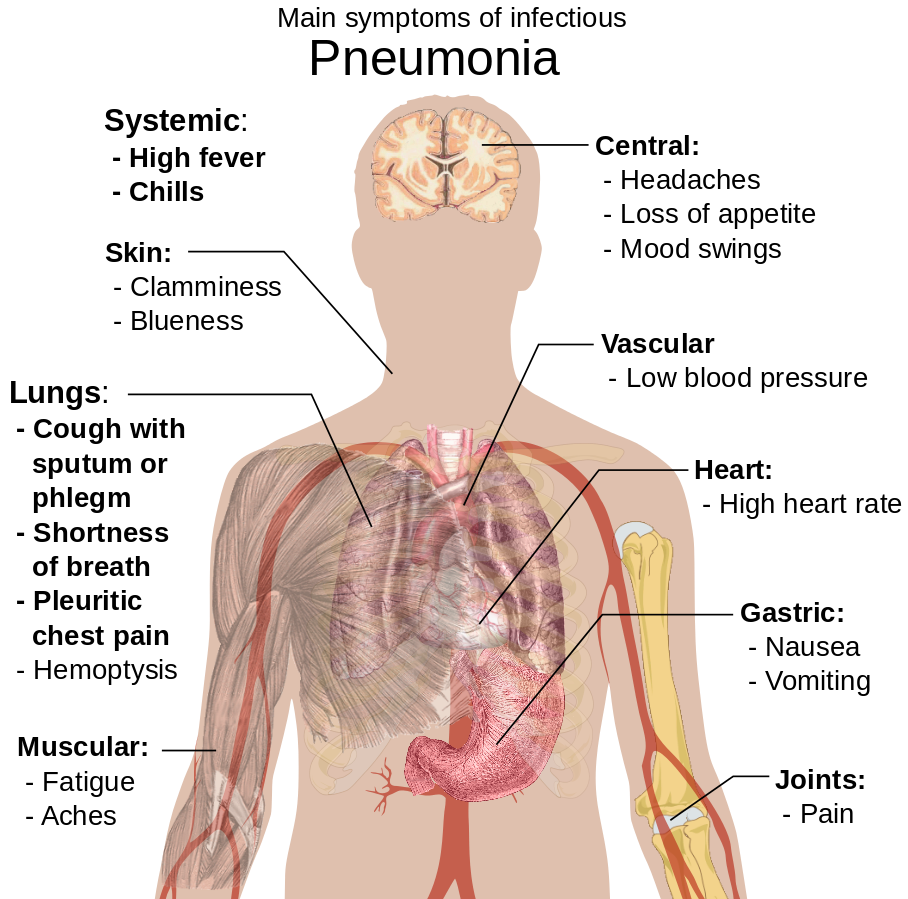
The symptoms of pneumonia include fever, wet cough, excessive expectoration, usually after coughing, chills, chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, cyanosis, lack of appetite and thirst, vomiting. Pneumonia does not always occur with all the listed symptoms. Some bacteria cause asymptomatic pneumonia, manifested only with a general malaise. This can make it difficult to diagnose the condition.
The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s medical history and examination. If pneumonia is suspected, an X-ray test is made. Bacterial, histological or radiometric examination may be performed.
The treatment depends mainly on the cause of the disease. It may include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, fever-reducing medications, pain killers, expectorants. Aspiration pneumonia is treated by removing the foreign object.
What is Lung Infection?
Lung infection can affect the lungs in the alveoli and/or the surrounding tissue (pneumonia), larger airways (bronchitis), or lead to the destruction of the lung tissue (tuberculosis).
Lung infections can be caused by a variety of factors, including infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi), chemical (irritant gases, aspiration of gastric juice) and physical (radiation, trauma, foreign body in the bronchi) factors.
Lung infections include:
- Pneumonia – an inflammatory lung disease caused by streptococci, other bacteria, viruses, or rarely by other factors, affecting individually or simultaneously the pulmonary alveoli and the tissue that surrounds them.
- Bronchitis – an acute or chronic inflammatory lung disease affecting the lungs and bronchi.
- Tuberculosis – a specific chronic inflammatory disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which mainly affects the lungs, but can also affect the central nervous system, lymphatic vessels, digestive system, bones, joints, and even the skin. Most often it affects the upper lung.
Lung infections occur with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the type and cause of the infection. In general, the patient feels pain and tension in the chest, fever (between 38-40 degrees), chills, dry or wet cough, nasal secretion, presence of phlegm, sometimes mixed with blood, sneezing, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, wheezing, respiratory distress, loss of appetite, weight loss, chills, night sweats, gastrointestinal disorders, bluish skin color, etc.
The diagnosis of lung infection is made based on the patient’s medical history and examination. If a lung infection is suspected, an X-ray test is prescribed. Bacterial, histological or radiometric examination may be performed. Tuberculosis is diagnosed via a PPD tuberculin skin test.
The treatment of lung infections depends mainly on the cause of the disease. In case of a bacterial infection is prescribed antibiotic treatment, in case of viral infection – antiviral drugs, in case of fungal infection – antifungals, in case of tuberculosis – tuberculistatic drugs. Some medications can be prescribed to treat the symptoms and to stimulate the immune system.
Difference Between Pneumonia and Lung Infection
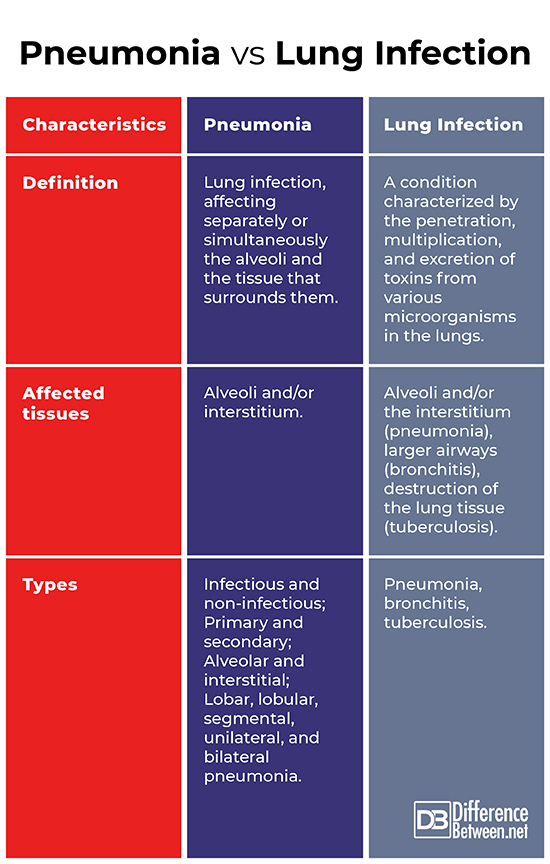
Definition
Pneumonia: Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs, affecting separately or simultaneously the alveoli and the tissue that surrounds them.
Lung Infection: Lung infection is a condition characterized by the penetration, multiplication, and excretion of toxins from various microorganisms in the lungs.
Affected tissues
Pneumonia: Pneumonia affects alveoli and/or interstitium.
Lung Infection: Lung infection can affect the lungs in the alveoli and/or the surrounding tissue (pneumonia), larger airways (bronchitis), or lead to the destruction of the lung tissue (tuberculosis).
Types
Pneumonia: Pneumoniacanbeinfectious and non-infectious; primary and secondary; alveolar and interstitial; lobar, lobular, segmental, unilateral, and bilateral pneumonia.
Lung Infection: Lunginfectionsincludepneumonia, bronchitis, and tuberculosis.
Pneumonia Vs. Lung Infection
Summary:
- Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs, affecting separately or simultaneously the alveoli and the tissue that surrounds them. It is one of the most common lung infections.
- Lung infection is a condition characterized by the penetration, multiplication, and excretion of toxins from various microorganisms in the lungs.
- Pneumonia affects alveoli and/or interstitium. Lung infection can affect the lungs in the alveoli and/or the surrounding tissue (pneumonia), larger airways (bronchitis), or lead to the destruction of the lung tissue (tuberculosis).
- Lung infections, including pneumonia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi), chemical (irritant gases, aspiration of gastric juice) and physical (radiation, trauma, foreign body in the bronchi) factors.
- The treatment of lung infections and pneumonia depends on the causative agent and may include antibiotics, antiviral preparations, antifungals, symptomatic and immunostimulatory treatment.
- Pneumonia can be infectious and non-infectious; primary and secondary; alveolar and interstitial; lobar, lobular, segmental, unilateral, and bilateral pneumonia. Lung infections include pneumonia, bronchitis, and tuberculosis.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Kon, K., M. Rai. The Microbiology of Respiratory System Infections. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc. 2016. Print.
[1]Kon, K., M. Rai. The Microbiology of Respiratory System Infections. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc. 2016. Print.
[2]Warrell, D., T. Cox, J. Firth. Oxford Textbook of Medicine, Vol. 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2010. Print.
[3]Yankova, Z. New Guide to Pulmonary Diseases and Tuberculosis. Sofia: Medical University Press. 2012. Print.
[4]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/de/vectors/lunge-menschliche-diagramm-atemwege-39981/
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Symptoms_of_pneumonia.svg
