Difference Between Paresthesia and Paralysis
Paresthesia is an uncomfortable feeling of burning, itching, tingling or pins and needles sensation in any of the limbs due to nerve compression. Paralysis is the loss of function of the nerves either partially or completely, affecting both sensory and motor nerves of the affected area.

What is paresthesia?
An uncomfortable feeling of burning, itching or tingling on the skin due to no apparent reason is known as paresthesia. Everyone has experienced paresthesia at some point in their life.
Symptoms
Symptoms of paresthesia are:
- Numbness in limbs
- Pins and needles like sensation, often referred to as “arm or leg has fallen asleep”.
- Sensation of tingling in the affected part
- Itching that doesn’t have any apparent reason and doesn’t resolve easily.
- Chronic pain if paresthesia is due to nerve compression
- Hot or cold sensation
Causes
Causes of paresthesia are usually simple like prolonged pressure on the nerve of the affected limb. Sitting too long in the same position can cause paresthesia of lower limbs. While sleeping for hours on one arm can result in paresthesia of the said arm. This type of paresthesia is usually harmless and is due to poor circulation. It doesn’t require treatment.
However, when paresthesia is caused by nerve damage, it can be chronic and requires treatment. It can be of two types:
- Radiculopathy
- Neuropathy
Radiculopathy is when the root nerves are compressed due to any anatomical or physical pathology. For example herniated disc, anatomical narrowing of nerve canal, a mass or lesion pressing on the nerves, etc. It can present as cervical radiculopathy (neck pain, paresthesia of upper limbs,weakness of affected side of hand and arm)
Neuropathy is when nerves are compressed due to pathological conditions like diabetes, autoimmune diseases, multiple sclerosis, kidney diseases, thyroid diseases, etc. Neuropathy is chronic and requires management of the underlying condition.
This type of neuropathy can become permanent paralysis if left untreated.
Risk factors
Risk factors for paresthesia are:
People with chronic diseases like Diabetes, MS, rheumatoid arthritis, kidney disease etc.
People with professional hazard causing the repetitive movement of affected limb
People with compromised immunity or poor posture
Treatment
Treatment depends upon the underlying cause. If numbness is caused due to hyperglycemia, consider treating the high blood sugar to relieve the symptoms.
If it is due to poor posture or herniated disk, physiotherapy combined with medication and surgery can help.
Take a break if professional hazard is the cause of persistent Paresthesia.
Treating the underlying cause can cure the symptoms most of the times.

What is Paralysis?
Paralysis is defined as complete or partial loss of the function and sensation of a specific area of the body, usually due to nerve damage.
Paralysis can be temporary or permanent. Permanent paralysis is usually irreversible and can cause disability.
Paralysis usually begins with pins and needles sensation in the body, leading to complete loss of sensation.
Types of paralysis
Different types of paralysis according to the location of paralysis are:
- Monoplegia (one arm or one leg affected)
- Hemiplegia (arm or leg of the same side)
- Paraplegia (both legs are affected)
- Quadriplegia (both arms and both legs)
Paralysis can be flaccid which causes flabby muscles that appear shrunken, or it can be spastic which causes spasms or twitching in the affected muscles.
It can also be irreversible or temporary.
Causes
Causes of paralysis are
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Injury to the spinal cord
- Post polio virus
- Guillain Barre syndrome
- Congenital anomalies
- Cerebral palsy
Symptoms
Symptoms are quite simple and easy to identify. It can cause loss in the sensation of the affected body part, alongwith loss in movement and coordination. There is no pain in paralysis due to loss of nerve sensations.
Treatment
Treatment of paralysis depends upon the cause. It can be treated by
- Physiotherapy
- Exercises
- Surgery or even amputation in worst case scenario
- Occupational therapy
- Botox and other medicines for spastic paralysis
- Aids for mobility
Difference between Paresthesia and Paralysis
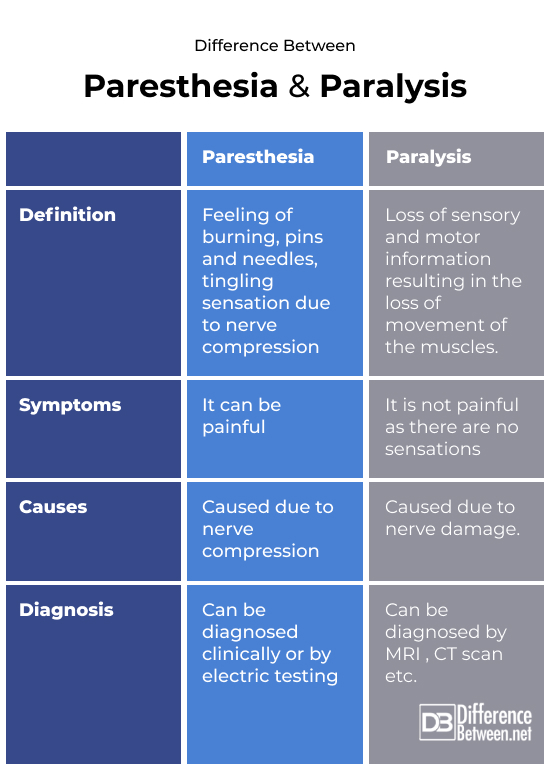
Summary of Difference between Paresthesia and Paralysis
- Paresthesia is the burning and tingling sensation due to nerve compression while paralysis is the loss of sensory and motor information resulting in the loss of movement in the muscle.
- Paresthesia doesn’t involve loss of movement or motor response. Paralysis results in loss of movement and coordination.
- Paresthesia can be caused by pressure on nerves, radiculopathy or poor circulation of blood while paralysis can be caused by stroke, trauma or damage to the nerve by injury.
- Paresthesia is diagnosed by history and medical examination, neurological examination while paralysis is diagnosed by CT scan, MRI and x-rays.
- Treatment of paresthesia is physiotherapy and exercise while paralysis might need surgery, medication, physiotherapy and occupational therapy to regain strength and movement in the muscles.
FAQs
What is the difference between paralysis and paresthesia?
Paralysis is the loss of movement and sensation due to nerve damage while paresthesia is the feeling of burning, pinching or tingling in the affected arm or leg due to nerve compression.
Is paraesthesia paralyzed?
Paresthesia is burning, tingling and crawling of skin type sensation in the affected part, it is not paralysis.
What are examples of paresthesia?
Examples of paresthesia are pins and needles sensations, numbness or tingling pain.
What is the difference between paraesthesia and numbness?
Paresthesia is the sensation of pins and needles, burning or tingling while numbness means not feeling any sensations, and feeling no pain or sensation.
Can you walk with paresthesia?
Yes it is possible to walk around with paresthesia as it doesn’t affect the motor part of muscles.
When is paresthesia permanent?
Paresthesia is permanent when the compressed nerve is left untreated for a long period of time and nerve damage is extensive.
What is the common name for paresthesia?
Common name of paresthesia is “pins and needles” sensations.
What is another name for paresthesia?
Another name for paresthesia is “pins and needles” sensation.
What neurological causes paresthesia?
Multiple sclerosis is the most common neurological cause of paresthesia.
- Difference Between Cystocele and Rectocele - September 8, 2023
- Comparison Between DHEA and DHEA Sulfate - September 1, 2023
- Difference Between Osteoporosis and Osteopenia - June 14, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Paresthesia. Paresthesia - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics. (n.d.). Retrieved March 9, 2023, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/paresthesia#:~:text=Paresthesias%20are%20common%20and%20follow,the%20fourth%20and%20fifth%20fingers
[1]R;, K. J. J. R. K. L. O. R. P. (n.d.). Load carriage-related paresthesias: Part 1: Rucksack Palsy and Digitalgia Paresthetica. Journal of special operations medicine : a peer reviewed journal for SOF medical professionals. Retrieved March 9, 2023, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28088822/
[2]SpinalCord.com. (n.d.). Types of paralysis: Monoplegia, hemiplegia, paraplegia, and Quadriplegia. Types of Paralysis: Monoplegia, Hemiplegia, Paraplegia, and Quadriplegia. Retrieved March 9, 2023, from https://www.spinalcord.com/types-of-paralysis
