Difference Between Parasomnia and Dyssomnia

What is parasomnia?
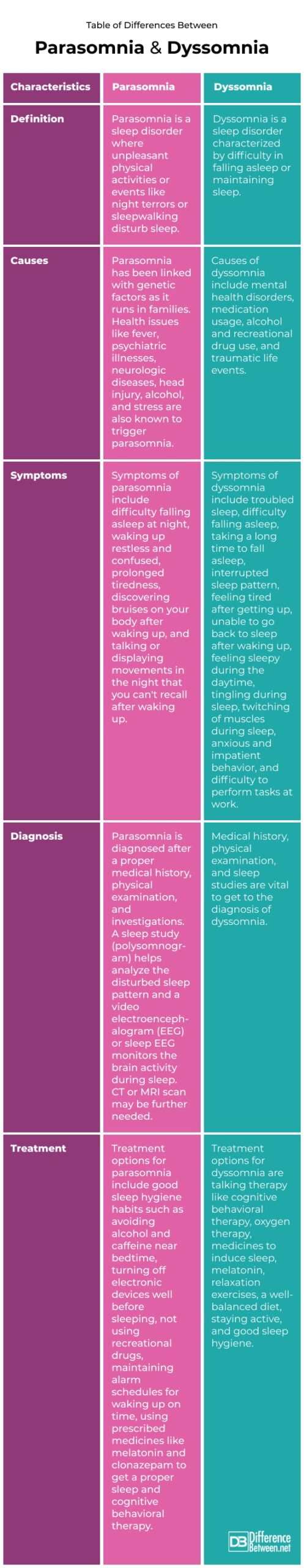
Definition:
Parasomnia is a sleep disorder where unpleasant physical activities or events like night terrors or sleepwalking disturb sleep.
Causes:
Parasomnia has been linked with genetic factors as it runs in families. Health issues like fever, psychiatric illnesses, neurologic diseases, head injury, alcohol, and stress are also known to trigger parasomnia.
Types:
Parasomnia is divided into non-rapid eye movement sleep (non-REM) and rapid eye movement sleep (REM). Sleep terrors, sleepwalking, and confusional arousals are parasomnia seen in non-REM sleep whereas nightmare disorder and recurrent sleep paralysis are seen in REM sleep.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of parasomnia include difficulty falling asleep at night, waking up restless and confused, prolonged tiredness, discovering bruises on your body after waking up, and talking or displaying movements in the night that you can’t recall after waking up.
Diagnosis:
Parasomnia is diagnosed after a proper medical history, physical examination, and investigations. A sleep study (polysomnogram) helps analyze the disturbed sleep pattern and a video electroencephalogram (EEG) or sleep EEG monitors the brain activity during sleep. CT or MRI scan may be further needed.
Treatment:
Treatment options for parasomnia include good sleep hygiene habits such as avoiding alcohol and caffeine near bedtime, turning off electronic devices well before sleeping, not using recreational drugs, maintaining alarm schedules for waking up on time, using prescribed medicines like melatonin and clonazepam to get a proper sleep and cognitive behavioral therapy.

What is dyssomnia?
Definition:
Dyssomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep or maintaining sleep.
Causes:
Causes of dyssomnia include mental health disorders, medication usage, alcohol and recreational drug use, and traumatic life events.
Types:
Types of dyssomnia are intrinsic sleep disorders, extrinsic sleep disorders, and circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of dyssomnia include troubled sleep, difficulty falling asleep, taking a long time to fall asleep, interrupted sleep pattern, feeling tired after getting up, unable to go back to sleep after waking up, feeling sleepy during the daytime, tingling during sleep, twitching of muscles during sleep, anxious and impatient behavior, and difficulty to perform tasks at work.
Diagnosis:
Medical history, physical examination, and sleep studies are vital to get to the diagnosis of dyssomnia.
Treatment:
Treatment options for dyssomnia are talking therapy like cognitive behavioral therapy, oxygen therapy, medicines to induce sleep, melatonin, relaxation exercises, a well-balanced diet, staying active, and good sleep hygiene.
Difference between parasomnia and dyssomnia
Definition:
Parasomnia is a sleep disorder where unpleasant physical activities or events like night terrors or sleepwalking disturb sleep. Dyssomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep or maintaining sleep.
Causes:
Parasomnia has been linked with genetic factors as it runs in families. Health issues like fever, psychiatric illnesses, neurologic diseases, head injury, alcohol, and stress are also known to trigger parasomnia. Causes of dyssomnia include mental health disorders, medication usage, alcohol and recreational drug use, and traumatic life events.
Types:
Parasomnia is divided into non-rapid eye movement sleep (non-REM) and rapid eye movement sleep (REM). Sleep terrors, sleepwalking, and confusional arousals are parasomnia seen in non-REM sleep whereas nightmare disorder and recurrent sleep paralysis are seen in REM sleep. Types of dyssomnia are intrinsic sleep disorders, extrinsic sleep disorders, and circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of parasomnia include difficulty falling asleep at night, waking up restless and confused, prolonged tiredness, discovering bruises on your body after waking up, and talking or displaying movements in the night that you can’t recall after waking up. Symptoms of dyssomnia include troubled sleep, difficulty falling asleep, taking a long time to fall asleep, interrupted sleep pattern, feeling tired after getting up, unable to go back to sleep after waking up, feeling sleepy during the daytime, tingling during sleep, twitching of muscles during sleep, anxious and impatient behavior, and difficulty to perform tasks at work.
Diagnosis:
Parasomnia is diagnosed after a proper medical history, physical examination, and investigations. A sleep study (polysomnogram) helps analyze the disturbed sleep pattern and a video electroencephalogram (EEG) or sleep EEG monitors the brain activity during sleep. CT or MRI scan may be further needed.
Medical history, physical examination, and sleep studies are vital to get to the diagnosis of dyssomnia.
Treatment:
Treatment options for parasomnia include good sleep hygiene habits such as avoiding alcohol and caffeine near bedtime, turning off electronic devices well before sleeping, not using recreational drugs, maintaining alarm schedules for waking up on time, using prescribed medicines like melatonin and clonazepam to get a proper sleep and cognitive behavioral therapy. Treatment options for dyssomnia are talking therapy like cognitive behavioral therapy, oxygen therapy, medicines to induce sleep, melatonin, relaxation exercises, a well-balanced diet, staying active, and good sleep hygiene.
Table of differences between parasomnia and dyssomnia
FAQs
What is the difference between dyssomnia and insomnia?
Dyssomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep or maintaining sleep.
Insomnia is the inability to fall asleep.
What are the 4 types of parasomnias?
Nightmares, night terrors, bed wetting, and sleepwalking.
What is the difference between sleep disorders and parasomnias?
Sleep disorders are the disorders involving quality and quantity of sleep. Parasomnia is a sleep disorder where unpleasant physical activities or events like night terrors or sleepwalking disturb sleep.
What are the three dyssomnias of sleep?
Types of dyssomnia are intrinsic sleep disorders, extrinsic sleep disorders, and circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
What is an example of parasomnia?
Sleepwalking is an example of parasomnia.
Which sleep disorders are examples of dyssomnias?
Sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, periodic limb movement disorder, and hypersomnia are examples of dyssomnias.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
References :
[0]Kotagal, Suresh. "Treatment of dyssomnias and parasomnias in childhood." Current treatment options in neurology 14 (2012): 630-649.
[1]Kotagal, Suresh. "Treatment of dyssomnias and parasomnias in childhood." Current treatment options in neurology 14 (2012): 630-649.
[2]Millichap, J. Gordon. "Dyssomnias and Parasomnias." Pediatric Neurology Briefs (2007): 44-45.
[3]Barthlen, Gabriele M., and Charles Stacy. "Dyssomnias, parasomnias, and sleep disorders associated with medical and psychiatric diseases." The Difference between parasomnia and dyssomnia
[4]Parasomnia is a sleep disorder where unpleasant physical activities or events like night terrors or sleepwalking disturb sleep. Dyssomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty in falling asleep or maintaining sleep.
[5]Mount Sinai journal of medicine, New York 61.2 (1994): 139-159.
