Difference Between Migraine and Cluster Headache
A migraine is a type of neurological problem where there is one-sided head pain, nausea and sensitivity to light. A cluster headache is a type of head pain which always occurs in cycles and is located behind or around an eye.
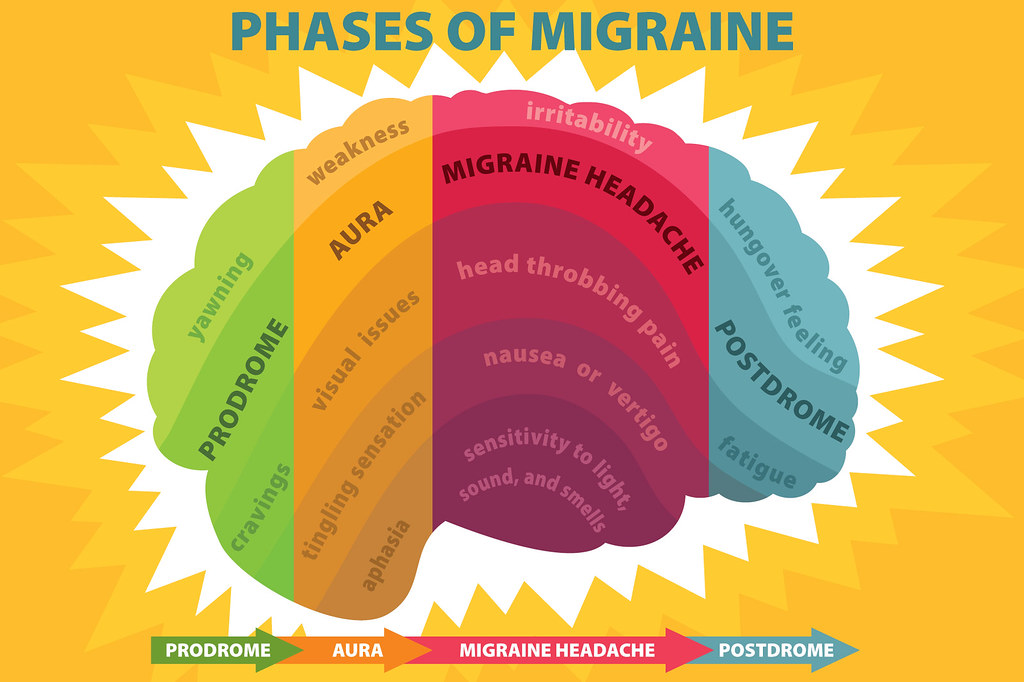
What is Migraine?
Definition:
A migraine is a neurological problem that causes debilitating pain in the head and several other disabling symptoms such as sensitivity to light, nausea, and dizziness.
Symptoms:
Symptoms include severe pain in the head, located on only one side of the head. The pain is a throbbing sensation and can last for several hours to a few days. The person may feel nauseated, be very sensitive to light and sound, and may also feel dizzy and weak. Some people get an aura of flashing lights immediately preceding the headache. The symptoms can last anywhere from between about 4 hours up to as long as about 3 days. Patients prefer to lie still in a darkened room when having an attack.
Diagnosis:
Physical symptoms and signs including when the headaches first started, and it starts usually at an age younger than 50 years, as well as the associated light sensitivity and throbbing nature of the headache. Imaging such as X-rays or MRI scans can rule out other causes for the head pain.
Causes:
The exact cause of a migraine is not known in most cases, but several factors seem to trigger an attack. This includes hormonal changes, certain chemicals such as MSG in foods, certain foods such as cheese or ice-cream, changes in the weather, and fatigue. Studies have also shown that some types of migraines, such as familial hemiplegic migraine, appear to be caused by inherited genetic mutations.
Treatment:
Analgesic medications and anti-nausea medications can help with symptoms. The use of dihydroergatimine and triptans works for some people while other types of medications including beta-blockers or anti-convulsants such as topirimate, work for others.

What is Cluster headache?
Definition:
A cluster headache is when severe pain occurs in the head, specifically around one or both eyes, and it occurs in clusters or cycles that vary from weeks to even months.
Symptoms:
The most notable symptom is extreme pain focused around or behind one of your eyes. You may notice that your eye is red and watering, and your eye may also swell, and you may have nasal congestion and a runny nose. The face may flush and the eyelid on the affected side of the head may also droop. The pain often happens at the same time each day or night and the person can become very restless. The condition often occurs at cyclical times and is hence called a cluster headache.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is made based on the symptoms, particularly the cyclical way that the painful headaches occur, and the location of the pain. Cluster headaches are more common in men than women.
Causes:
There do not appear to be triggers in the case of cluster headaches, unlike with migraines. The exact cause of cluster headaches is not known but scientists think it may be linked to some issue with the hypothalamus. For some reason, cluster headaches are more common in people between 20 and 50 years of age, and more typically they occur in men.
Treatment:
A cluster headache cannot be cured but can be treated with various painkillers such as triptans and injectable dihydroergotamine. Sometimes oxygen therapy can also help to alleviate the symptoms of an attack. Prednisone and verapamil can also help prevent attacks.
Difference between Migraine and Cluster headache?
Definition
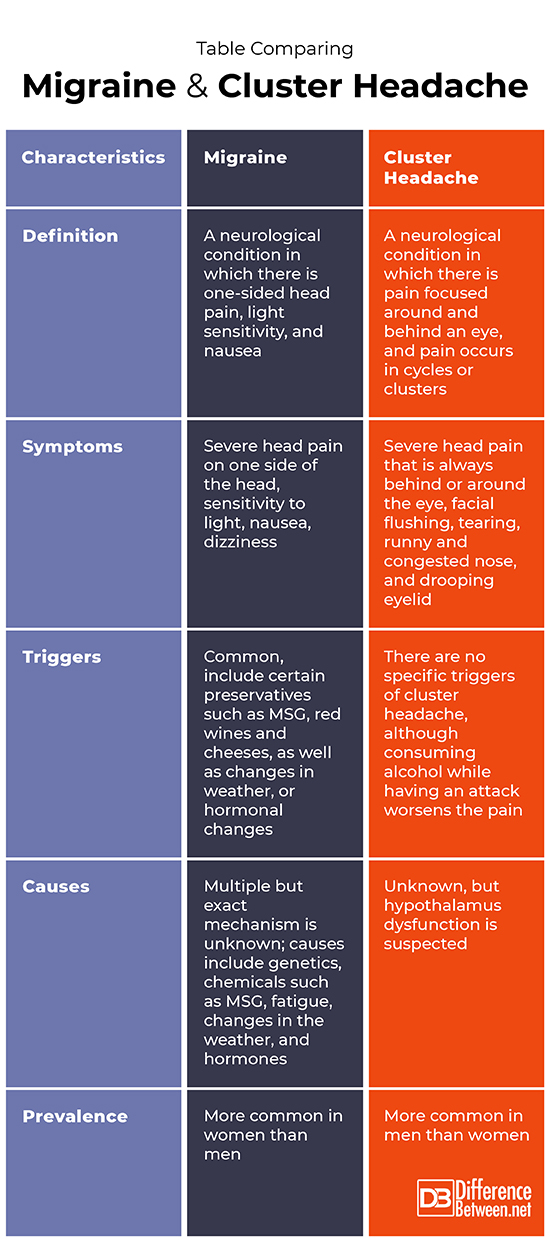
A migraine is a neurological condition in which there is one-sided head pain, light sensitivity, and nausea. A cluster headache is head pain that is focused behind or around an eye and that occurs in cycles.
Symptoms
Severe head pain on one side of the head, sensitivity to light, dizziness, and nausea are symptoms of a migraine. Severe head pain that is always behind or around the eye, facial flushing, tearing, runny or congested nose, and a drooping eyelid are all symptoms of a cluster headache.
Triggers
A migraine often has specific triggers such as preservatives like MSG, certain foods and drinks, hormonal changes, or weather changes. A cluster headache has no specific trigger but can be made worse by drinking alcohol during an attack.
Causes
Migraines appear to havemultiple causes, but the exact mechanism is unknown; causes include genetics, chemicals such as MSG, fatigue, changes in the weather, and hormones. The cause of cluster headaches is not known but hypothalamus dysfunction is suspected as a possible causative factor.
Prevalence
Migraines are more common in women than men, while cluster headaches are more common in men than in women.
Table comparing Migraine and Cluster headache
Summary of Migraine Vs. Cluster headache
- Migraine and cluster headache are both neurological conditions that cause head pain.
- Migraine and cluster headache can often be treated with similar medications such as dihydroergotamine and triptans.
- Migraines affect more women than men and have various triggers.
- Cluster headaches affect more men than women and typically are not triggered by specific factors.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Silberstein, Stephen D. “Cluster Headache”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders/headache/cluster-headache
[1]Silberstein, Stephen D. “Cluster Headache”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders/headache/cluster-headache
[2]Silberstein, Stephen D. “Migraine”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders/headache/migraine
[3]Spadaro, Maria, et al. "A G301R Na+/K+-ATPase mutation causes familial hemiplegic migraine type 2 with cerebellar signs." Neurogenetics 5.3 (2004): 177-185.
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4676/39384099324_92140f7876_b.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2019/07/27/15/41/headache-4367062_960_720.jpg
