Difference Between Hangnail and Ingrown Nail
What are hangnail and ingrown nail?
Hangnail is the jagged skin along the sides of the nail. Hangnail appears on fingers (rare conditions it can be around a toenail). Ingrown nail is a medical condition in which the edges of a toenail curves or grows into the soft flesh. Ingrown nail appears on the toes.
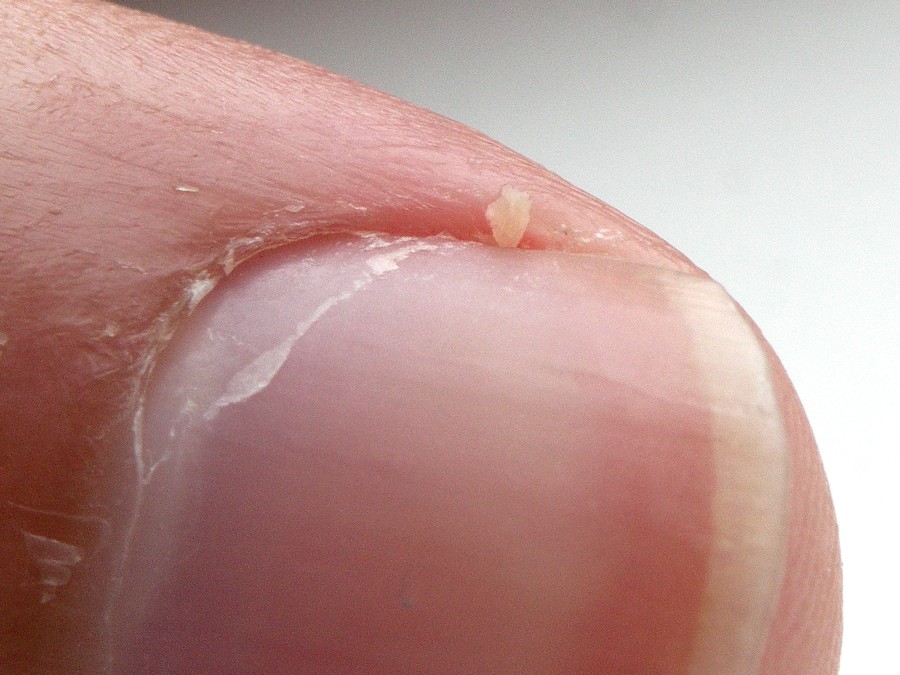
Hangnail
Hangnails are those irritating, snaggy chunks of skin that rigidly stick out from the corners or sides of your fingernails. Hangnails do not occur on toes unlike ingrown nails. The hangnails are tiny, but the discomfort, pain, swelling and soreness, hangnails cause is not.
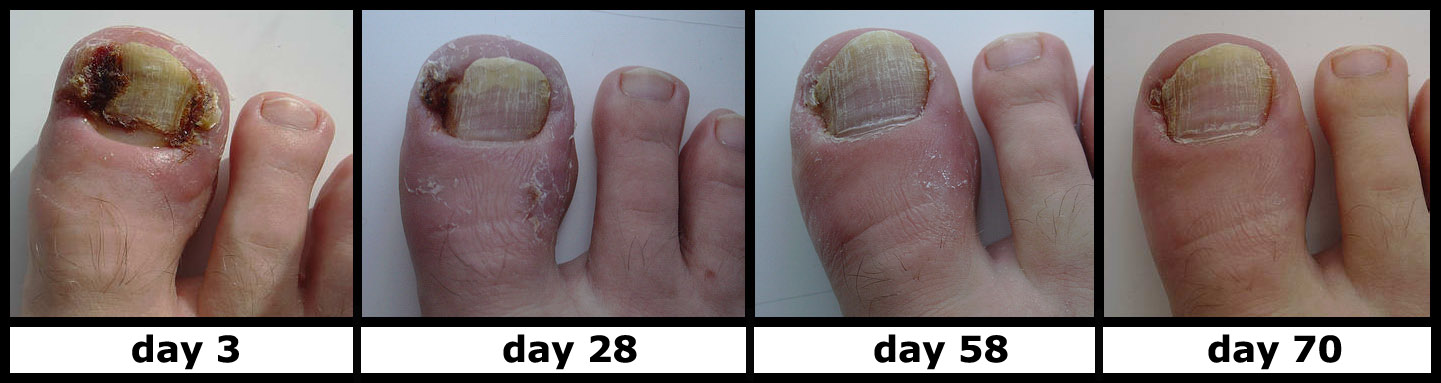
Ingrown nail
Ingrown toenails occur when the edges or corners of your nails grow into the skin adjacent to the nail. The big toe very often gets an ingrown toenail. In most of the cases, ingrown toenails can be treated at home. However, in case the infection grows and there are some more complications, then medical treatment is needed. One has to be even more careful of complications if one is suffering from diabetic conditions as that can result in poor circulation.
Difference between hangnail and ingrown nail
Description
Hangnail
It is basically referred to the irritating and torn chunk of skin along the sides of the nail.
Ingrown nail
It usually impacts the big toe. It is a painful medical condition in which the corners of the toe nail grow or curve into an extra soft flesh.
Symptoms
Hangnail
Early signs include
- Change in colour of the nail
- Inflammation
- Irritation
- Nail becomes weak
- Infection travels from the finger nail to the nail bed
- Blisters
- Skin feels hot to touch
- High temperature and chills
- Soreness and throbbing pain in the finger
- Pus in hangnail area
- Puffy skin around the hangnail
Ingrown nail
Early signs include:
- Fluid that later becomes pus builds up near the infected area
- Skin around the ingrown nail becomes hard to touch, swollen or tender
- Pain when toe experiences any pressure
If the ingrown nail in the toe becomes infected, then signs include:
- pus oozing out of the infected area
- the area becomes sore and painful
- blood oozing out of the infected area
- overgrowth of skin around the toe
Causes
Hangnail
- Crazy dry hands and nails
- Hangnails are also caused because of excessive finger picking (trauma). Its more common in people who have the uncontrollable urge of picking their nails and the surrounding regions
- Some people, because of their nature of work and occupations, are more likely to get hangnails. These people include;
- Medical doctors
- People working in food industry
- Nurses
- Builders (construction industry)
- Carpenters
Ingrown nail
According to NHS – National Health Services (NHS), ingrown toenails happen in both males and females. In teens and young people, ingrown toenails happen because they usually have moisture laden and sweaty feet. There are many causes of ingrown toenails. These include;
- Trimming and cutting toenails in a wrong and incorrect manner. Toes nails should be trimmed straight across. Angling the corners of the toe nails make the nail to grow inwards into the skin.
- Another cause is curved and irregular nails
- Shoes that put tremendous pressure on the toes and toenails for example footwear that is too tight or flat for your feet.
- Toenail injury due to accident, something very heavy dropping on your feet with pressure or kicking something like a ball repeatedly
- Genetic susceptibility or predisposition
- Poor and wrong posture
- Unhygienic condition of your feet like feet being dirty and sweaty Another cause is feet being aggressively in action during athletic activities putting pressure on the toe nails for longer duration of time
When feet are under tremendous pressure for a longer duration of time, toenails also experience pressure and that can damage and increase the occurrence if ingrown toenails. These activities include:
- Kickboxing
- Soccer
- Ballet
- Football
Diagnosis
Hangnail
Physical examination for signs of infection. In case there is pus, then to analyze the level of infection, the doctor could send the pus sample to laboratory.
Ingrown nail
Your general practitioner can conduct a physical examination and if it is identified that there is a possibility of any infection, then he would recommend an X-ray. X-ray helps to see the depth of the ingrown nail into the skin. An X-ray will also help to determine the cause of your ingrown nail; whether it was caused due to injury or by wrong method of trimming the toe nails.
Prevention
Hangnail
- Proper skin care
- Ensure to protect your hands with gloves during winters (colder months)
- Cover your hands with work gloves while gardening, dishwashing, washing clothes or any other activity that could put pressure on the skin around the nails.
Ingrown nail
- Preventing ingrown toenails requires certain lifestyle changes that include;
- Toenails should not be cut too short
- Ensure to wear proper sandals or chappals, moisture free socks
- Ensure that the toe nails are regularly trimmed and the edges are not allowed to curve in
- In case you are working in hazardous work stations, steel-toe-boots should be worn
Treatment
Hangnail
- Soak the nail in warm water for fifteen minutes to four times per day. As a result, blood circulation will increase and heal and clean the area
- Trimming the edges of the hangnail after it becomes soft from warm water soak minimizes further infection.
- Ensure that the affected region of the nail does not become dry. Keep it moisturized
- Application of anti-fungal creams and anti-biotic creams can also expedite recovery. Topical steroids are also beneficial.
- In case the hangnail develops pus (abscess), the pus needs to be drained to prevent further infection and pain. It is important to immediately consult a doctor for this medical procedure. The doctor will give local anesthesia and using surgical incision, rain out the pus. He will then clean the area and place a medicated gauze strip on the wound for a couple of days until the area heals and becomes dry
- RICE technique is also recommended to reduce swelling and pain
R – Rest
I – Ice
C – Compression
E – Elevation
- OTC – Over the counter pain killers and anti-inflammatories are also helpful
Ingrown nail
- Soak in warm, soapy water. Add Epsom salt for additional relief
- Pack the area with dental floss or cotton
- Pain relievers (Advil, Motrin IB)
- Apply antibiotic ointment
- Matricectomy – Technique to eliminate all or some of the cells at the bed of the nail to stop the nail from growing.
- Nail avulsion – Removal of the nail or part of the nail
- Wear open-toed shoes or sandals
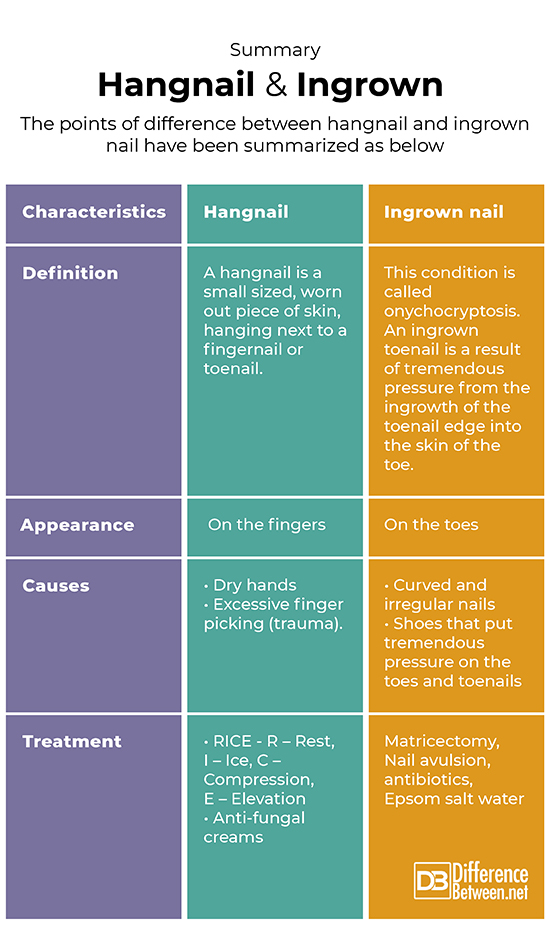
Summary
The points of difference between hangnail and ingrown nail have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bryant, A., & Knox, A. (2015). Ingrown toenails: the role of the GP. Australian family physician, 44(3), 102.
[1]Jangra, R. S., Gupta, S., Singal, A., & Kaushik, A. (2019). Hangnail: A simple solution to a common problem. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 81(5), e123-e125.
[2]Mayeaux Jr, E. J., Carter, C., & Murphy, T. E. (2019). Ingrown toenail management. American family physician, 100(3), 158-164.
[3]Singal, A., & Arora, R. (2015). Nail as a window of systemic diseases. Indian dermatology online journal, 6(2), 67.
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Daumennagel_mit_Nagelhaut_und_Niednagel.jpg
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ingrown.nail_therapy.by.stick_EN.jpg
