Difference Between Giardiasis and Amebiasis
Giardiasis is an illness caused by Giardia while amebiasis is an infection caused by Entamoeba.

What is Giardiasis?
Definition:
Giardiasis is a gastrointestinal illness in which the small intestine is affected by infection with a unicellular flagellated organism.
Causative organism and transmission:
The cause of giardiasis is the protist organism Giardia. This parasite is transmitted to a person when they swallow contaminated water. Certain forms of sexual behavior can also cause person-to-person transmission of Giardia.
Symptoms:
Diarrhea is the main symptom. The watery stool also smells bad and the person will experience abdominal distension and painful muscle spasms in the gut. Nausea and fatigue are also common signs of infection.
Complications:
Malabsorption of nutrients and chronic bowel problems can occur if a person has giardiasis.
Diagnosis:
Nuclear amplification tests can detect the genome of the parasite from a stool sample of an infected person.
Treatment:
Treatment includes medications such as metronidazole.

What is Amebiasis?
Definition:
Amebiasis is a condition that happens when the large intestine is infected with a type of pathogenic amoeba.
Causative organism and transmission:
Entamoeba histolytica is the amoeba that can infect the large intestine and causes the illness known as amebiasis. This parasite can be caught when drinking or eating infected liquids and food. There is also feces to oral transmission and the amoeba can be transmitted during some types of sexual activity.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of amebiasis include pain in the abdomen, flatulence, and diarrhea alternating with constipation.
Complications:
Amebiasis can spread to the liver causing an abscess and it can also spread to other organs including the brain.
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis of amebiasis can be done by molecular tests where the genetic material of the parasite is searched for in a stool sample. Enzyme immunoassay can also be done using the stool. Microscopic examination of the parasite in stool can be attempted but may not always be possible.
Treatment:
Amoebiasis can be treated using medication such as metronidazole and diloxanide furoate. The latter medication is specifically to rid the intestinal tissues of the cyst stage of the Entamoeba parasite.
Difference between Giardiasis and Amebiasis?
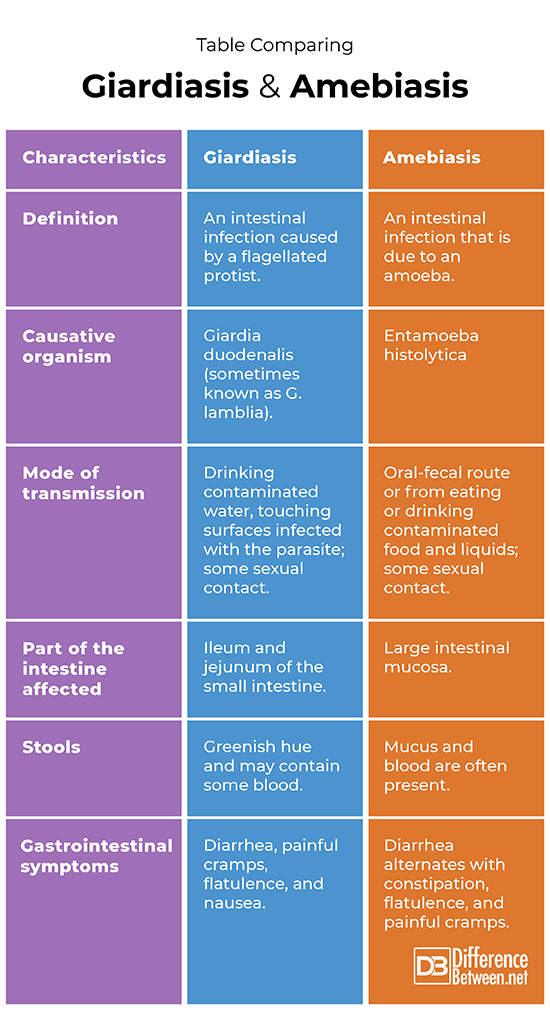
Definition
Giardiasis is an infection of the intestines which is caused by a flagellated protist. Amebiasis is an intestinal infection due to a pathogenic amoeba.
Causative organism
The organism that causes giardiasis is Giardia duodenalis (G. lamblia is the alternative name). The organism that is responsible for amebiasis is Entamoeba histolytica.
Mode of transmission
People get infected by Giardia when they drink contaminated water, touch surfaces infected with the parasite, or by some types of sexual contact. People get amebiasis through the oral-fecal route, from eating or drinking contaminated food and liquids, or from some kind of sexual contact.
Part of the intestine affected
In giardiasis, it is the ileum and jejunum of the small intestine that is affected. In amebiasis, it is the mucosa of the large intestine that is affected.
Stools
In the case of giardiasis, stools are watery, have a greenish hue and may have blood present. In the case of amebiasis, stools have blood and mucus in them.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
The gastrointestinal symptoms of giardiasis include diarrhea, painful cramps, flatulence, and nausea. The gastrointestinal symptoms of amebiasis include diarrhea alternating with bouts of constipation, painful cramps, and flatulence.
Table comparing Giardiasis and Amebiasis
Summary of Giardiasis Vs. Amebiasis
- Giardiasis and amebiasis are both caused by parasites that infect the gastrointestinal tract.
- Giardiasis is due to Giardia and it affects the small intestine.
- Amebiasis is caused by Entamoeba, which affects the large intestine.
FAQ
What is the difference between amebiasis and amoebiasis?
There is no difference between amebiasis and amoebiasis; both terms refer to the same condition, which is infection with Entamoeba histolytica.
Is Giardia a type of amoeba?
Giardia is not a type of amoeba because it has flagella. Instead, it is a type of flagellated protist.
What are 3 symptoms of amebiasis?
Amebiasis causes diarrhea and constipation, belly cramps, and flatulence.
How do you confirm amoebiasis?
Confirmatory diagnosis is made by immunoassay or molecular tests on the stool looking for evidence of the Entamoeba parasite that causes amebiasis.
How is amebiasis treated?
The infection is often treated with antiparasitic medicine like metronidazole and medicine to kill the cysts such as diloxanide furoate.
How is amoebic dysentery caused?
Amoebic dysentery is a diarrheal illness caused by Entamoeba histolytica. The parasite damages the lining of the large intestine causing diarrhea and other symptoms.
What are signs of Giardia in humans?
Giardia affects the small intestine and, as a result, causes watery diarrhea, malabsorption of nutrients, painful bowel spasms, and nausea.
How long does Giardia last in humans without treatment?
Giardia can last for 6 weeks and may be very difficult to recover from without proper treatment.
What is the most common cause of Giardia?
The most common way people get infected with the parasite is by swallowing water in which Giardia is found. This can happen when swimming or simply drinking from rivers and streams where the parasite is found.
What happens if Giardia goes untreated?
The person can end up with chronic diarrhea, malnutrition, dehydration, and even irritable bowel syndrome if Giardia is not treated.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Escobedo, Angel A., et al. "Sexual transmission of giardiasis: a neglected route of spread?" Acta Tropica 132 (2014): 106-111.
[1]Marie Chelsea, and Petri Jr. William A. “Amebiasis (Entamebiasis)”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2022, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/intestinal-protozoa-and-microsporidia/amebiasis
[2]Wright, Stephen. "Amoebiasis and giardiasis." Medicine 33.8 (2005): 47-50.
