Difference Between Erectile Dysfunction and Premature Ejaculation

What is Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation
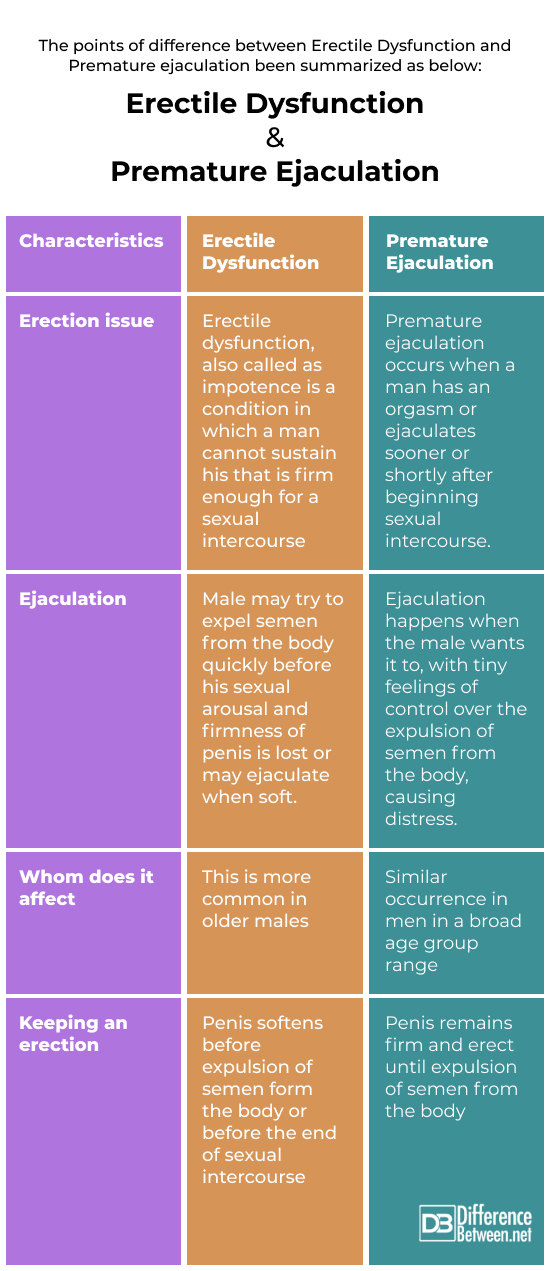
The primary sexual issue that men report to their doctor is Erectile Dysfunction (ED), which affects up to 30 million men. ED is characterized as difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection that is sufficiently firm for sexual intercourse. While occasional problems with erections are common, if ED is progressive or occurs regularly during sexual activity, it is not normal and requires treatment. On the other hand, when a person reaches orgasm earlier than desired by either themselves or their partner, it is called premature ejaculation. This can occur either prior to or immediately after penetration.

Similarity
The occurrence of premature ejaculation can be a consequence of erectile dysfunction. It is possible for both erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation to happen concurrently, and they may have an impact on each other. It is crucial to acknowledge that these conditions can coexist and affect individuals in various ways.
Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction refers to the incapability of achieving or maintaining an erection that is adequate for sexual activity. The majority of cases of erectile dysfunction are linked to vascular, neurologic, psychologic, and hormonal conditions, and the use of drugs can also be a contributing factor. The assessment process usually involves examining for underlying disorders and testing testosterone levels.
Premature ejaculation
When male reaches orgasm earlier than desired by either himself or his partner, it is called premature ejaculation
Difference between Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation
Definition
Erectile dysfunction
If a man is unable to achieve or maintain an erection that is firm enough for sexual activity, it could indicate a physical or psychological problem. This condition, known as erectile dysfunction, can lead to stress, strain on relationships, and low self-esteem. It is important for individuals with this condition to undergo an assessment for both physical and psychological issues.
Premature ejaculation
The act of ejaculating involves the release of semen from the body. Premature ejaculation (PE) refers to instances where ejaculation occurs earlier than desired by the man or his partner during sexual activity. Rapid ejaculation, premature climax, and early ejaculation are other terms used to describe PE. Although PE may not necessarily be a cause for concern, it can negatively affect sexual pleasure and relationships.
Symptoms
Erectile dysfunction
- Difficulties in obtaining an erection
- Sustaining an erection
- Decreased sexual desire
Premature ejaculation
Premature ejaculation is primarily characterized by the inability to hold back ejaculation for over three minutes following penetration, and it may also manifest during any type of sexual activity including self-stimulation.
Causes
Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can be caused by physical conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, and obesity. Besides, mental health problems such as relationship difficulties, anxieties, depression, stress, and other psychological issues can also affect sexual desire. It is crucial to address both physical and mental health issues to prevent and treat erectile dysfunction.
Premature ejaculation
Serotonin, a natural substance produced by nerves in the body, may be a contributing factor to premature ejaculation (PE). Increased levels of serotonin in the brain can lead to a longer time before ejaculation, while lower levels can result in a shorter time to ejaculation and PE. Additionally, psychological issues such as depression, stress, and unrealistic expectations about sexual performance can also be involved in PE. Age-related changes in erections and ejaculation can also cause PE in older men, as they may experience weaker, shorter-lasting erections and a reduced warning period before ejaculation occurs.
Treatment
Erectile dysfunction
Various methods for treating erectile dysfunction are available, including medications known as oral phosphodiesterase inhibitors, prostaglandins that can be administered through the urethra or directly into the penis, devices that create a vacuum to promote blood flow, and surgical implants.
Premature ejaculation
Premature ejaculation can be treated through a variety of methods, including behavioral strategies, medication, and counseling. It may require some experimentation to determine the most effective treatment or combination of treatments. Combining behavioral treatment with drug therapy may offer the best results.
Summary
The points of difference between Erectile Dysfunction and Premature ejaculation been summarized as below:
FAQ
Can you have both erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation?
ED and PE often go hand in hand and can have a reciprocal relationship. A significant portion of individuals who experience ED also suffer from PE, with rates ranging from 30-60%. Moreover, those with ED may develop PE as they hurry to ejaculate due to their inability to maintain an erection, leading to a habitual pattern of premature ejaculation. It is crucial to understand the interplay between these conditions to provide effective treatment.
How do you know if he has premature ejaculation?
According to a research study that included 500 couples, the typical duration for ejaculation after initiating sexual activity was approximately 5.5 minutes. However, this duration may be more extended for men who engage in sexual intercourse with other men. As per international standards, premature ejaculation is described as frequently ejaculating within one minute of commencing sexual intercourse with one’s partner.
What are the two types of premature ejaculation?
- primary premature ejaculation
- secondary premature ejaculation
What is the difference between ejaculation and erectile?
The term “erection” describes the state of sexual arousal that enables a male to engage in sexual intercourse, and if a male is unable to achieve or sustain an erection, it is known as erectile dysfunction. “Ejaculation” refers to the process of expelling semen from the male reproductive organ.
How long should a man last before ejaculating?
The time taken for a man to reach orgasm and ejaculate can vary due to multiple factors and is not fixed. On average, it takes around five to seven minutes for a man to complete the process when timed with a stopwatch. However, the time range can vary extensively, ranging from less than a minute to more than thirty minutes.
How long can the average man stay erect?
Typically, a man’s erection can persist for a period ranging from a few minutes up to approximately thirty minutes. During sleep, men experience an average of five erections per night, each having a duration of roughly twenty-five to thirty-five minutes.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Jannini, E. A., & Lenzi, A. (2005). Epidemiology of premature ejaculation. Current opinion in urology, 15(6), 399-403.
[1]Shamloul, R., & Ghanem, H. (2013). Erectile dysfunction. The Lancet, 381(9861), 153-165.
[2]Yafi, F. A., Jenkins, L., Albersen, M., Corona, G., Isidori, A. M., Goldfarb, S., ... & Hellstrom, W. J. (2016). Erectile dysfunction. Nature reviews Disease primers, 2(1), 1-20.
