Difference Between Diarrhea and Loose Stool
What is Diarrhea?
Diarrhea is a condition of abnormally frequent intestinal evacuations with loose, fluid stools.
It is one of the most common health complaints. It can range from a temporary, mild condition, to a potentially life-threatening one.
Diarrhea is defined based on the frequency of bowel movements and the consistency of the stools. In general, more than three loose stools per day are considered diarrhea.
The symptoms of diarrhea are:
- Loose stools;
- Watery stools;
- Bloating in the belly;
- Abdominal pain;
- Cramps;
- An urgent feeling to have a bowel movement;
In some cases, as a result of diarrhea, more serious symptoms may also occur:
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Fever;
- Weight loss;
- Dark urine;
- Blood or mucus in the stool;
- Severe pain in the rectum or abdomen;
- Decrease in the amounts of urine;
- Dry skin;
- Rapid heart rate;
- Irritability;
- Headache;
- Confusion, etc.
Diarrhea can be acute or chronic. Acute diarrhea lasts a few days, while chronic diarrhea usually lasts more than three weeks.
Diarrhea is a result of reduced absorption of fluids from the intestine, increased secretion of fluids into the intestine, or rapid passage of stool through the intestine.
The acute diarrhea is most often caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic infection. It can be caused also by food allergy, food poisoning, or starting a new medication.
The chronic diarrhea is most often caused by:
- Inflammatory bowel disease;
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- Bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine;
- Infectious diseases;
- Fat malabsorption;
- Carbohydrate malabsorption;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Allergies to certain foods;
- Colon cancer, etc.
The treatment of diarrhea may include different home remedies, medications, oral rehydration solutions, and in some cases – antibiotics. Drinking plenty of fluids is very important to avoid dehydration. In mild cases of acute diarrhea, treatment may not be necessary. In chronic or persistent diarrhea any underlying causes have to be treated in addition to the symptoms of diarrhea.

What is Loose Stool?
Stools that are more watery and loose than normal are called loose stools. Usually, they are not associated with significant health risks.
The symptoms of loose stool are:
- Loose stools;
- Watery stools;
- Bloating in the belly;
- Abdominal pain;
- Cramps;
- An urgent feeling to have a bowel movement;
In some cases, more serious symptoms may also occur:
- Blood or mucus in the stool;
- Duration longer than 2 days.
The causes of loose stool are:
- Certain foods, drinks, supplements, medications;
- Infections;
- Food poisoning;
- Food allergies;
- Upset stomach;
- Indigestion, etc.
Drinking plenty of fluids is very important to avoid dehydration. In most cases of loose stool special treatment is not necessary. In some cases, dietary changes are necessary in order to avoid the consumption of foods triggering loose stools. If required, treatment may include different home remedies, medications, oral rehydration solutions, and in some cases – antibiotics.
Difference Between Diarrhea and Loose Stool
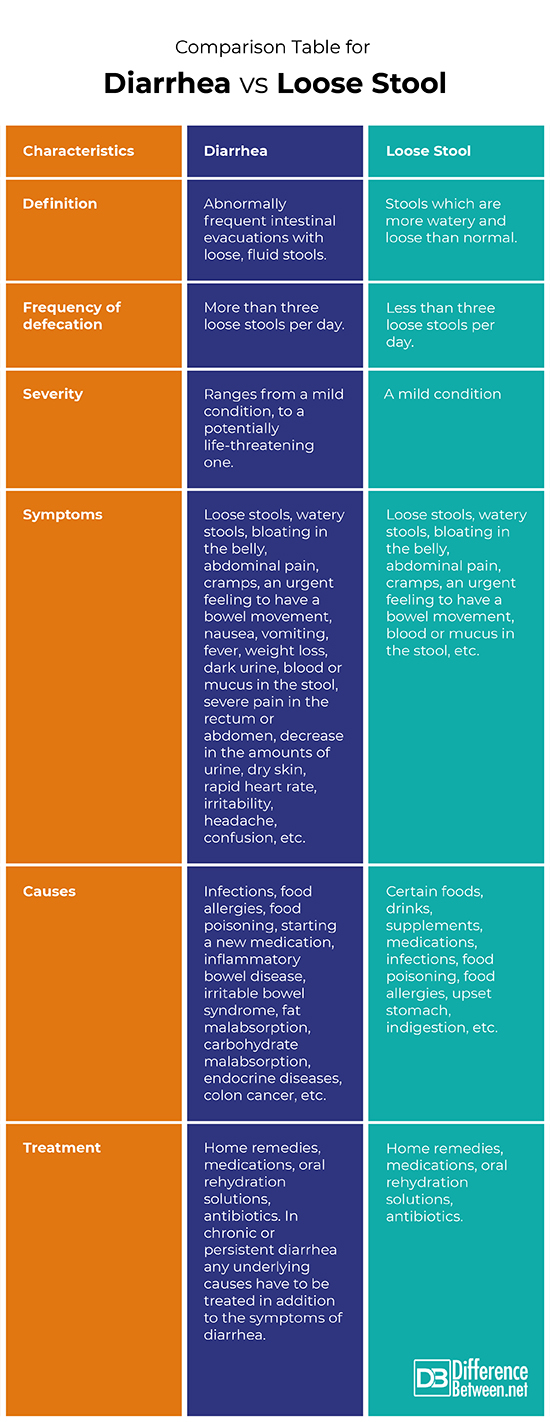
Definition
Diarrhea: Diarrhea is a condition of abnormally frequent intestinal evacuations with loose, fluid stools.
Loose Stool: Stools that are more watery and loose than normal are called loose stools.
Frequency of defecation
Diarrhea: In general, more than three loose stools per day are considered diarrhea.
Loose Stool: Less than three loose stools per day.
Severity
Diarrhea: Diarrhea can range from a temporary, mild condition, to a potentially life-threatening one.
Loose Stool: Usually, loose stools are not associated with significant health risks.
Symptoms
Diarrhea: The symptoms of diarrhea are loose stools, watery stools, bloating in the belly, abdominal pain, cramps, an urgent feeling to have a bowel movement, nausea, vomiting, fever, weight loss, dark urine, blood or mucus in the stool, severe pain in the rectum or abdomen, decrease in the amounts of urine, dry skin, rapid heart rate, irritability, headache, confusion, etc.
Loose Stool: The symptoms of loose stools are watery stools, bloating in the belly, abdominal pain, cramps, an urgent feeling to have a bowel movement, blood or mucus in the stool, etc.
Causes
Diarrhea: The diarrhea is caused by infections, food allergies, food poisoning, starting a new medication, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, fat malabsorption, carbohydrate malabsorption, endocrine diseases, colon cancer, etc.
Loose Stool: The loose stool can be caused by certain foods, drinks, supplements, medications, infections, food poisoning, food allergies, upset stomach, indigestion, etc.
Treatment
Diarrhea: The treatment of diarrhea may include different home remedies, medications, oral rehydration solutions, antibiotics. In chronic or persistent diarrhea any underlying causes have to be treated in addition to the symptoms of diarrhea.
Loose Stool: The treatment of loose stool may include different home remedies, medications, oral rehydration solutions, antibiotics.
Comparison table for Diarrhea Vs. Loose Stool
Summary of Diarrhea Vs. Loose Stool
- Diarrhea is a condition of abnormally frequent intestinal evacuations with loose, fluid stools.
- Stools that are more watery and loose than normal are called loose stools.
- Diarrhea and loose stools are two of the most common health complaints.
- In general, more than three loose stools per day are considered diarrhea.
- Diarrhea can range from a temporary, mild condition, to a potentially life-threatening one, while loose stools are usually not associated with significant health risks.
- The symptoms of diarrhea are loose stools, watery stools, bloating in the belly, abdominal pain, cramps, an urgent feeling to have a bowel movement, nausea, vomiting, fever, weight loss, dark urine, blood or mucus in the stool, severe pain in the rectum or abdomen, decrease in the amounts of urine, dry skin, rapid heart rate, irritability, headache, confusion, etc. The symptoms of loose stools are watery stools, bloating in the belly, abdominal pain, cramps, an urgent feeling to have a bowel movement, blood or mucus in the stool, etc.
- The diarrhea is caused by infections, food allergies, food poisoning, starting a new medication, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, fat malabsorption, carbohydrate malabsorption, endocrine diseases, colon cancer, etc. The loose stool can be caused by certain foods, drinks, supplements, medications, infections, food poisoning, food allergies, upset stomach, indigestion, etc.
- The treatment of diarrhea and loose stool may include different home remedies, medications, oral rehydration solutions, antibiotics. In chronic or persistent diarrhea any underlying causes have to be treated in addition to the symptoms of diarrhea.
- Drinking plenty of fluids is very important to avoid dehydration in case of diarrhea or loose stool.
- Difference Between Gallstones and Cholecystitis - September 5, 2021
- Difference Between Constipation and Cramping - August 4, 2021
- Difference Between Whole Genome Sequencing and Microarray - May 6, 2021
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/anatomy-bacteria-bacterium-bowels-160524/
[1]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e1/Symptoms-diarrhea-bloody.jpg/593px-Symptoms-diarrhea-bloody.jpg
[2]Donowotz, M, J. Fordtean (Eds.). What I Need to Know About Diarrhea. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2012. Print.
[3]Khurana, V. Demystifying Digestive Tract Symptoms: Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea and Constipation in the Language of Gut. 2015. Kindle Edition.
[4]Peikin, S. Gastrointestinal Health: The Proven Nutritional Program to Prevent, Cure, or Alleviate Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Ulcers, Gas, Constipation, Heartburn, and Many Other Digestive Disorders, Third Edition. New York: Harper Collins Publishing. 2005 Print.

Thanks for this. This helped me to define the difference between diarrhea and loose stool and helped me to figure out which one I was having.