Difference between Diabetes and Hypoglycemia
Diabetes is a disorder related to insulin in which blood sugar levels are too high. Hypoglycemia is a disorder in which blood sugar levels are too low.

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes Definition:
Diabetes is a disorder in which either the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin to break down blood sugar, or enough insulin is produced but the cells in the body become resistant to the insulin.
Causes of Diabetes:
There are three causes of diabetes and also three types. Diabetes type I is caused by an autoimmune reaction; type 2 diabetes is caused by unhealthy eating habits, being overweight and living a sedentary life. The third type of diabetes is a complication of pregnancy and is known as gestational diabetes.
Diagnosis for Diabetes:
Diabetes can be diagnosed using either a random blood sugar test, fasting sugar test or glucose tolerance testing. The random test ignores when you last ate. If you have 200mg/dL blood sugar of higher on this test, then diabetes is diagnosed. A fasting test is when blood sugar is measured after a night after fasting. A level above 100 mg/dL suggests diabetes. Glucose tolerance testing is a test where you drink a sugary solution and glucose levels are tested over the next two hours. If your sugar is greater than 200mg/dL at two hours then this indicates diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
Classic symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, polydipsia; increased hunger, polyphagia (increased hunger), and problems with vision. Additional symptoms include feeling exhausted, losing weight, feeling nauseated, and having a fruity breath odor. Skin can become dry and people can feel short of breath. People with poorly controlled diabetes can have symptoms of high blood sugar and low blood sugar (if on insulin).
Treatment and management of Diabetes:
Insulin medications and injections may be needed, especially in the case of type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be controlled by following a healthy diet, losing weight and exercising. A pregnant woman may be able to control their diabetic condition by diet and exercise. However, sometimes, type 2 diabetics and those with gestational diabetes may still require medications of injections. It is important that diabetics carefully monitor blood sugar levels and manage their diet carefully to avoid problems.
Diabetes Complications:
Diabetes is a dangerous condition since it leads to many complications, including death. High blood sugar damages nerves causing organ damage, including problems with the eyes, kidneys, and heart, and it can lead to loss of limbs. Often a person with uncontrolled diabetes does not feel if they have a sore on a foot or other extremity until it is too late. Often ulcers develop that become further infected leading to gangrene and requiring amputation. In addition, some diabetics can develop ketoacidosis which can lead to coma. This happens because they are not metabolizing sugar but instead, are breaking down fats. This leads to ketones being produced that can make them dehydrated and confused. Taking too much insulin can cause hypoglycemia and coma as well.
What is Hypoglycemia?
Definition of Hypoglycemia:
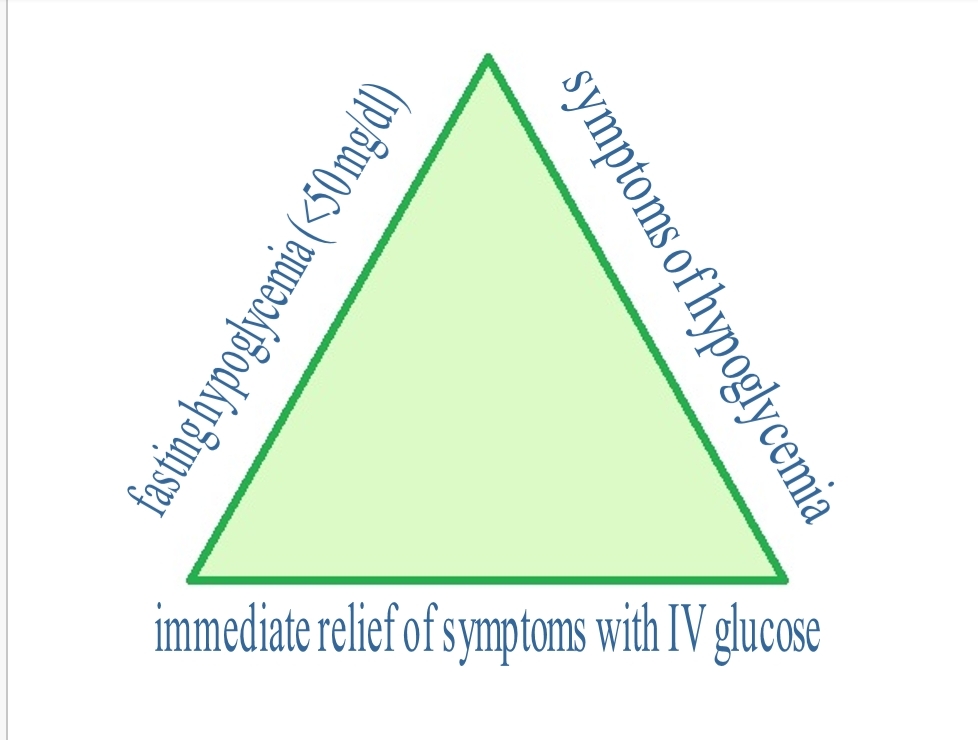
Hypoglycemia is the condition in which the blood sugar level drops too low, to less than about 50 mg/dL.
Causes of Hypoglycemia:
Most often hypoglycemia is caused when a diabetic takes too much insulin. However, there are other causes of the condition and it is found in non-diabetics. Certain drugs can cause hypoglycemia and it can also be triggered by an insulin-secreting tumor. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery can sometimes cause hypoglycemia.
Diagnosis of Hypoglycemia:
Doctors note a low blood plasma level of glucose of usually less than 60 or 50 mg/dL. Patients also respond when given dextrose. The condition can also be diagnosed after taking measurements after a patient has undergone a 48 hr and 72 hr fast in a controlled environment.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia:
Symptoms of low blood sugar include trembling, sweating, nausea, palpitations, and anxiety. People may also feel faint and have blurry vision and headaches. In severe cases, a person may be unable to speak properly, be mentally confused and fall into a coma.
Treatment and management:
Hypoglycemia is treated by giving the purpose glucose orally or by giving intravenous dextrose. If possible, the underlying condition causing the low blood sugar should be diagnosed and treated. Patients can learn to eat more often and eat foods that digest more slowly to try to prevent sudden drops in blood glucose.
Complications involved in Hypoglycemia:
The main complication of hypoglycemia is seizures, brain damage, coma and eventually death. The brain cannot function without glucose.
Difference between Hyperglycemia and Diabetes
-
Definition
Diabetes is a condition in which blood sugar is too high because either cells have stopped responding to insulin or not enough insulin is being secreted. Hypoglycemia is a condition in which blood glucose level is too low, usually less than 50mg/dL.
-
Causes
Diabetes can be caused by an autoimmune reaction, an unhealthy lifestyle or as a complication of pregnancy. Hypoglycemia can be caused by taking too much insulin, a tumor, a reaction to a drug or complication of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.
-
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of diabetes is based on a random blood test, fasting blood test or glucose tolerance test. Hypoglycemia is based on symptoms and results from a 48 hr to 72 hr fast.
-
Symptoms
Diabetics have symptoms such as extreme thirst, hunger, urinating often, being fatigued, problems with vision, nausea, dry skin, and a fruity breath odor. Hypoglycemics have symptoms like trembling, palpitations, blurred vision, sweating and mental confusion.
-
Treatment
Diabetes is treated with medicine, insulin injections, a change in diet, exercise and weight loss. Hypoglycemia is treated by giving oral glucose, IV dextrose and by eating small meals often and eating food that is slow to digest such as proteins.
-
Complications
Complications from diabetes include limb amputation, blindness, kidney and heart failure, ketoacidosis, coma, and death. Complications from hypoglycemia include seizures, brain damage, coma, and death.
Table comparing Diabetes and Hypoglycemia

Summary of Diabetes Vs. Hypoglycemia
- Diabetes and hypoglycemia both involve problems with blood sugar.
- Diabetics tend to have high blood sugar that causes damage to organs.
- Hypoglycemics have low blood sugar that can cause brain damage and coma.
- A healthy and carefully controlled diet can be helpful for both conditions.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Whipple%27s_triad.jpg
[1]Image credit: http://www.thebluediamondgallery.com/wooden-tile/images/diabetes.jpg
[2]Brutsaert, Erika F. “Diabetes.” Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/endocrine-and-metabolic-disorders/diabetes-mellitus-and-disorders-of-carbohydrate-metabolism/diabetes-mellitus-dm
[3]Brutsaert, Erika F. “Hypoglycemia.” Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”. Merck & Co, 2017, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/endocrine-and-metabolic-disorders/diabetes-mellitus-and-disorders-of-carbohydrate-metabolism/hypoglycemia
[4]Kellogg, Todd Andrew, et al. "Postgastric bypass hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia syndrome: characterization and response to a modified diet." Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases 4.4 (2008): 492-499.
