Difference Between DHEA and DHEAS

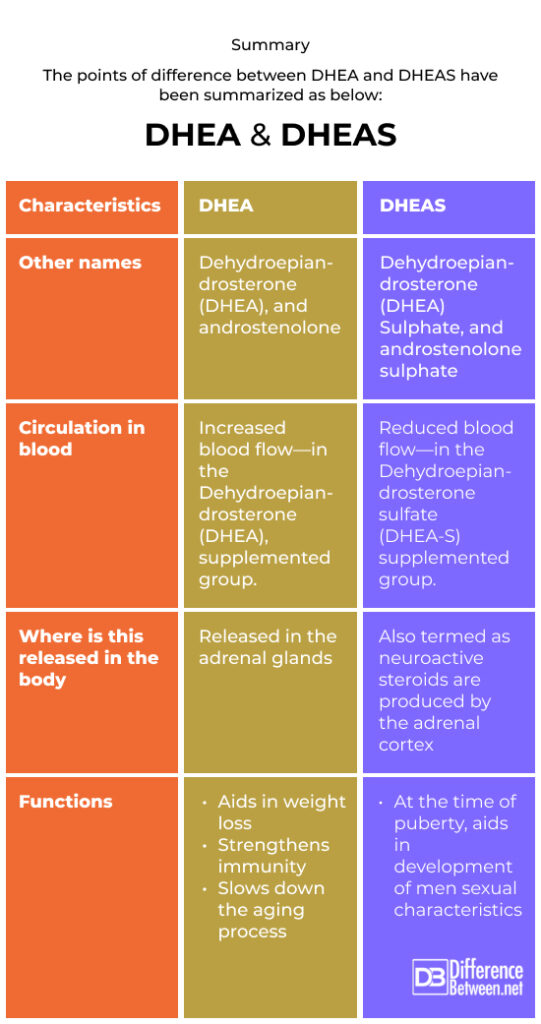
DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) contains an additional sulphate (SO2−4 S O 4 2 −) molecule connected to it, which is the key distinction between it and Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate – DHEA-S. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) is an androgen steroid (anabolic-androgenic steroids) that is present in both males and females. The ovaries (oval-shaped glands located in the uterus), testes (male reproductive gland or gonad), and adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) produce DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone). Using the enzyme steroid sulfatase (key enzymes in sulfate metabolism), the body converts DHEA sulphate to DHEA.

Similarity
- Both possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-glucocorticoid activity
- Both are released by the adrenal glands
- Both compounds serve as neurosteroids
DHEA
Both females and males naturally possess DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone), a mild androgen (hormone found in men), in their bodies. The adrenal glands zona reticularis (a site of steroid dysregulation) is where DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) is largely made from cholesterol. In females (oval shaped glands located in the uterus), the ovaries create a tiny quantity of it, which binds to androgen receptors (ligand-activated nuclear transcription factor) and supports a healthy ovarian environment. The nervous system (brain) also produces DHEA, which has been shown to interact with neurotrophin (a family of proteins that induce the survival of neurons) and neurotransmitter receptors (also known as a neuroreceptor).
DHEAS
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (androstenolone sulfate) is referred to as DHEAS. It is a male sexual hormone found in both males and females. DHEAS – Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate is important and plays a vital in the release of the sex hormones oestrogen (a group of hormones that that are critical in the normal sexual and reproductive development in females) and testosterone in both males and females. Also, it plays a role in the sexual maturation of men sexual features during puberty.
Difference between DHEA and DHEAS
Definition
DHEA
DHEA also known as dehydroepiandrosterone (androstenolone), which is a steroid hormone. Dehydroepiandrosterone serves as a precursor (compound that participates in a chemical reaction that produces another compound) to estrogens and testosterone while aiding to elevate follicular stimulation.
DHEAS
DHEAS also known as dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. It is a steroid hormone (group of hormones, derived from cholesterol) released by the adrenal glands (suprarenal glands), the gonads (glands that produce gametes) and the brain.
Levels during the day
DHEA
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), levels show reduced levels during different times of the day.
DHEAS
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) levels show no change throughout the day.
Summary
The points of difference between DHEA and DHEAS have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
Is DHEA and DHEAS the same?
The presence of a sulphate group (a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula SO2−4) distinguishes the two molecules structurally; Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulphate (DHEAS) is the sulfated version of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). The sulfated form of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) – Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEAS) makes up around ninety eight percent of the circulating amount in the bloodstream.
Does DHEA convert to DHEAS?
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is reversibly converted to Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulphate (DHEAS) and is the precursor (a compound that is involved in a chemical reaction that results in another compound) of several metabolites, also involves inclusion of sex steroid hormones.
What is DHEA and DHEAS function?
DHEA function – People with depression and anxiety, obesity (excessive weight), lupus, and adrenal insufficiency may benefit from Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) supplements. Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) may also aid in slowing down aging process, osteoporosis (bones becoming brittle), vaginal atrophy (atrophic vaginitis), erectile dysfunction (impotence), and various mental health issues.
DHEAS – Dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate is important and plays a vital in the release of the sex hormones oestrogen (a group of hormones that that are critical in the normal sexual and reproductive development in females) and testosterone in both males and females. Also, it plays a role in the sexual maturation of men sexual features during puberty.
What is the difference between DHEA and DHEAS test?
DHEA test helps to assess PCOS and DHEAS test is done to assess the working and functioning of adrenal glands.
What is the difference between DHEA and DHEA SR?
DHEA also known as dehydroepiandrosterone (androstenolone), which is a steroid hormone. Dehydroepiandrosterone serves as a precursor (compound that participates in a chemical reaction that produces another compound) to estrogens and testosterone while aiding to elevate follicular stimulation.
Nutrascriptives® DHEA-SR is a micronized (process of reducing diameter of a solid material’s particles) sustained release formula that has been created to maintain DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) levels throughout the day.
Is DHEA legal in Canada?
DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) is illegal in the Canadian market and has been banned in Canada.
What is the downside of DHEA?
High-density lipoprotein (HDL), or “good,” cholesterol levels may be decreased by DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone). Dehydroepiandrosterone use may potentially exacerbate psychiatric issues and raise the likelihood of mania (you feel abnormally extreme changes in emotions), in those with mood disorders. Dehydroepiandrosterone has the potential to make females develop hirsutism (unwanted men-pattern growing of hair on a female’s face, chest and back), greasy skin, acne (redness and lumps), and undesirable male-pattern hair growth.
Does DHEAS cause weight gain?
Yes, it could cause weight gain.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Baulieu, E. E., & Robel, P. (1998). Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) as neuroactive neurosteroids. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95(8), 4089-4091.
[1]Kroboth, P. D., Salek, F. S., Pittenger, A. L., Fabian, T. J., & Frye, R. F. (1999). DHEA and DHEA‐S: a review. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 39(4), 327-348.
[2]Maninger, N., Wolkowitz, O. M., Reus, V. I., Epel, E. S., & Mellon, S. H. (2009). Neurobiological and neuropsychiatric effects of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and DHEA sulfate (DHEAS). Frontiers in neuroendocrinology, 30(1), 65-91.
