Difference Between Covid Pneumonia and Bacterial Pneumonia
What is covid pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection of lungs. Any type of pneumonia is a frightening illness. It is either caused by viral agents or bacterial gents.
Covid pneumonia is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus strain.
Bacterial pneumonia is caused by Streptococcus (pneumococcus). However, other bacteria can cause it too.
Covid pneumonia is more severe in comparison to bacterial pneumonia.
Similarity
Common signs and symptoms in both pneumonias’ are;
- High temperature (may or may be high in either infections)
- Cough
- Difficulty in breathing
- Breath rate that has suddenly increased
In both the cases, lungs are examined by the provider using stethoscope for further diagnosis
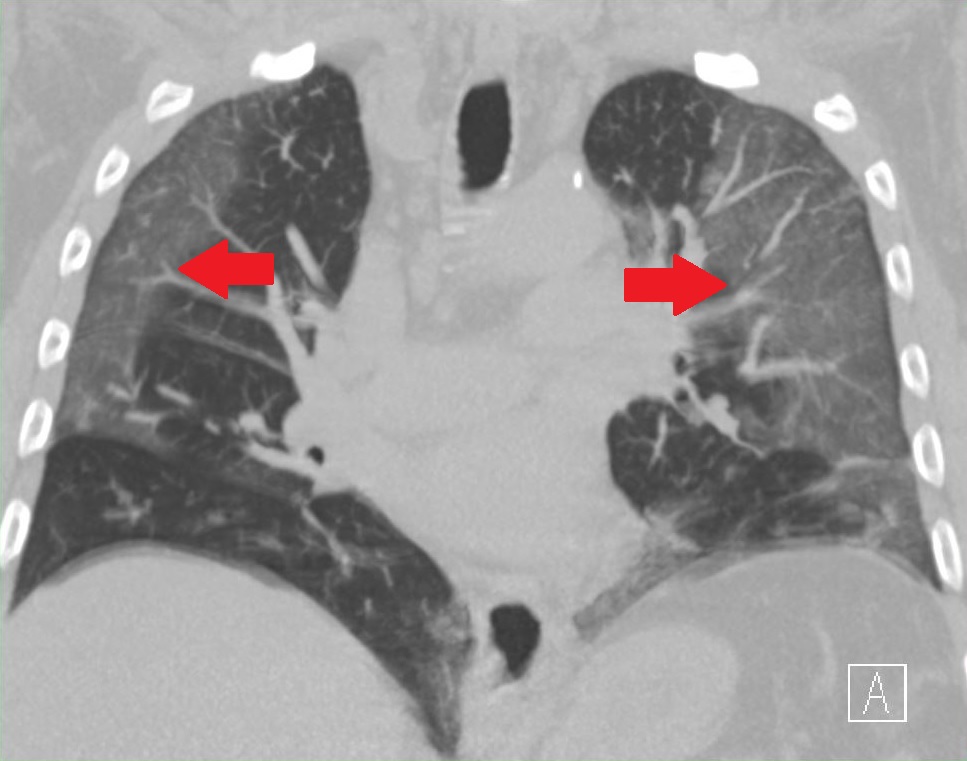
Covid Pneumonia
In covid pneumonia, viruses’ impact both sides of the lungs by triggering a more homogeneous (uniform composition) inflammatory reaction that results in elevating cellular debris (organic waste left over after the death of a cell) and mucus (slippery and stringy fluid substance) where previously open lung pockets were present.
Viral cases of pneumonia start with coughing and heaviness (congestion) with or without high body temperature (fever) in the first few days.
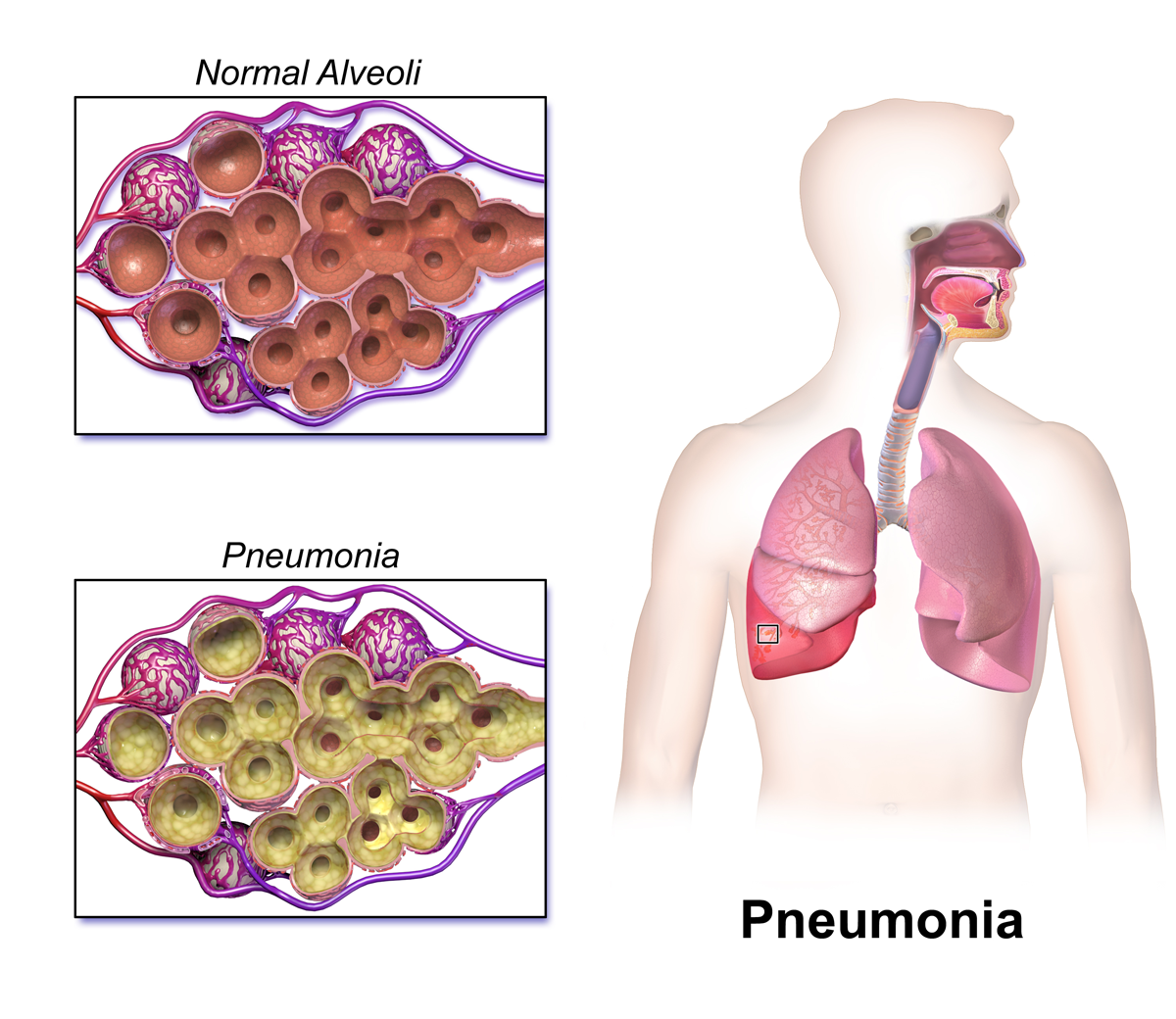
Bacterial Pneumonia
When the doctor hears some sounds in the pneumon (lungs) that seem normal on one side but not present on the other, it is a classic case of bacterial pneumonia.
Difference between covid pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia
Description
Covid pneumonia
Severe pneumonia (infection of lungs) caused by coronavirus infection itself
Bacterial pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia (infection of lungs) is caused by:
- Staphylococcusaureus
- Moraxellacatarrhalis
- Streptococcuspyogenes
- Neisseriameningitidis
- Klebsiellapneumoniae
Symptoms
Covid pneumonia
- Fever
- Chills
- Sore throat, cough
- Rise in temperature
- Headache
- Labored breathing
- Runny nose
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- Conjunctivitis
- Nausea
Severe symptoms:
Bacterial pneumonia
- Fever
- Sweating and shaking chills
- Cough with sputum – Yellow or greenish
- Labored breathing
- Body aches
- Chest pain
- Loss of appetite
- Low energy, and fatigue
- Fatigue, malaise
- Diarrhea
- Bluish skin
- Nausea and vomiting
Severe symptoms:
- Blood in mucus
- High fever of 102.5°F of higher
Association
Covid pneumonia
Viral pneumonia has been found to be associated with
- Lower serum creatinine
- Rhinorrhoea, multivariate
- GGO – (Ground-glass opacity) in radiology results
- Higher lymphocyte fraction in the WBCs – white blood cells
Bacterial pneumonia
The independent predictors for bacterial pneumonia were found to be associated with:
- Age > 65 or
- Comorbidity
- Leucocytosis or leukopenia
How the virus or the bacterial affects the lungs?
Covid pneumonia
Viruses in case of COVID-19 affect both sides of the Pneumon by releasing a more uniform kind of inflammatory response that results in an elevated cellular mucus and debris where earlier open pneumon (lungs) pockets were present.
Bacterial pneumonia
Bacteria affects or attacks only one part or lobe of the pneumon (lungs) resulting in a specific region of inflammation to take over the cellular particles that were filled with air.
Vaccine
Covid pneumonia
So many vaccines which have been rolled out globally by different providers have not been able to 100% safeguard from the virus infection. There are instances where people even after getting vaccinated are getting infected.
Bacterial pneumonia
Some types in this case can be prevented with vaccines, for example, the pneumococcal vaccine. However, the aggressive ones like the Strep pneumonia, vaccine utilization has not been 100% effective. The persistence of Strep pneumonia or pneumococcus, infections remain.
Treatment
Covid pneumonia
As of now, there is no approved 100% effective and curative treatment available for people suffering from covid pneumonia. Antibiotics do not work in this case
Bacterial pneumonia
Antibiotics may be prescribed.
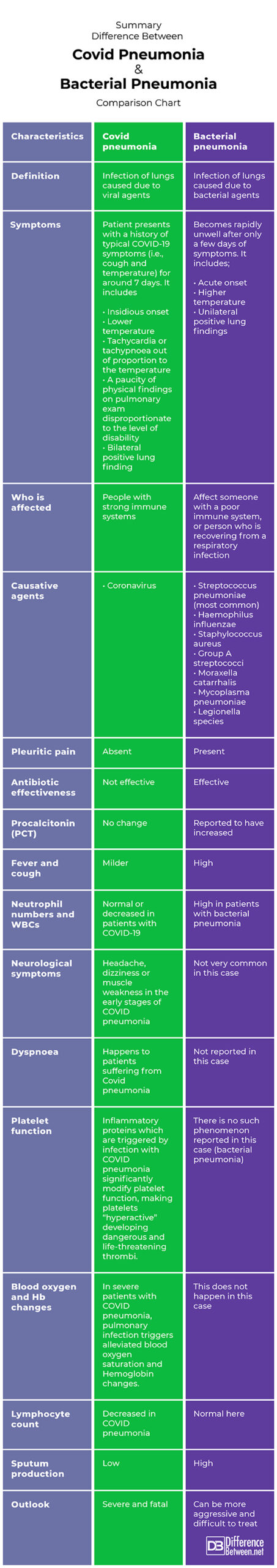
Summary
The points of difference between covid pneumonia and bacterial pneumonia have been summarized as below:
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Attaway, A. H., Scheraga, R. G., Bhimraj, A., Biehl, M., & Hatipoğlu, U. (2021). Severe covid-19 pneumonia: pathogenesis and clinical management. bmj, 372.
[1]Metersky, M. L., Masterton, R. G., Lode, H., File Jr, T. M., & Babinchak, T. (2012). Epidemiology, microbiology, and treatment considerations for bacterial pneumonia complicating influenza. International Journal of Infectious Diseases, 16(5), e321-e331.
[2]Schneider, R. F. (1999, December). Bacterial pneumonia. In Seminars in respiratory infections (Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 327-332).
[3]Zhao, D., Yao, F., Wang, L., Zheng, L., Gao, Y., Ye, J., ... & Gao, R. (2020). A comparative study on the clinical features of coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia with other pneumonias. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 71(15), 756-761.
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0994_Pneumonia.png
[5]Image rcedit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:COVID-19-Longontsteking.jpg
