Difference Between Convalescent Plasma and IVIG
Ever since the COVID-19 pandemic hit the world’s population, the proportion of the critically ill patients has only increased, collapsing the hospital care worldwide. The virus first emerged in China in December 2020 and rapidly spread worldwide. Soon, it was declared an ongoing outbreak as a global public health emergency by the World Health Organization (WHO). The health authorities of the world are currently focused on rapid diagnosis and isolation of patients as well as the search for alternative therapies for the critically ill patients. This article compares the safety and efficacy of convalescent plasma with human immunoglobulin (IVIG).
What is convalescent plasma therapy?
Though vaccines are now available for many infections or diseases, it takes a very long time to develop a vaccine for novel viruses like the COVID-19 outbreak. This new strain of virus from the family of “Coronaviridae” has brought the world’s economy at a stand-still, affecting the lives of people across the globe. Convalescent plasma (or Covid plasma therapy) is an experimental procedure used to treat COVID-19 infection. This treatment is administered to patients if all the principal treatments failed to improve the survival of patients suffering from SARS-CoV-2.
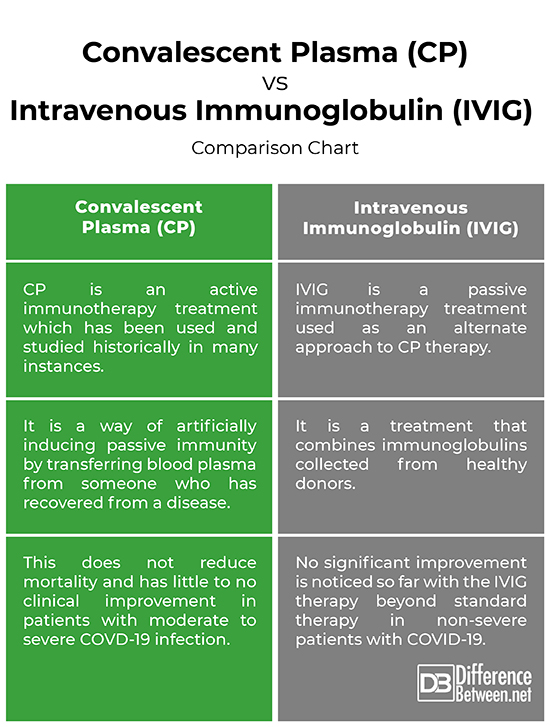
It is a way of artificially inducing passive immunity by transferring blood plasma from someone who has recovered from a disease, whose blood is presumed to already have antibodies for that disease. Plasma is the liquid part of blood which may contain antibodies against the virus. Ever since COVID-19 has become a major global concern, no treatment has been proved efficacious against the infection. In this situation, convalescent plasma therapy has showed positive results against the infection. This procedure isn’t new. This has been used and studied historically in many instances.
What is IVIG?
Immunoglobulins are the antibodies that your immune system produces naturally to help fight infections and diseases. It is part of your blood’s plasma. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is a treatment that combines immunoglobulins collected from different people to decrease the impacts of some inflammatory conditions that entail the immune system (autoimmune diseases). IVIG is prepared from large plasma pools of healthy donors. IVIG thus contains the wide spectrum of IgG antibodies present in normal human plasma.
IVIG has been used as substitutive therapy in primary humoral immunodeficiencies for many years. The beneficial effect of IVIG therapy has been documented in a large number of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, although definitive evidence for its efficacy has been established only in few diseases in controlled and randomized studies. The main component of IVIG preparations is the serum IgG fraction consisting mainly of IgG1 and IgG2 subclasses. Its use in COVID-19 related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is not well established.
Difference between Convalescent Plasma and IVIG
Procedure
– Convalescent plasma (or Covid plasma therapy) is an experimental procedure, a way of artificially inducing passive immunity by transferring blood plasma from someone who has recovered from a disease, whose blood is presumed to already have antibodies for that disease.
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is a treatment that combines immunoglobulins collected from different people decrease the impacts of some inflammatory conditions that affect the immune system. IVIG is prepared from large plasma pools of healthy donors.
Efficacy
– Although Convalescent plasma shows promising results, it has not yet been proven to help as a treatment for COVID-19 infection all the time. The use of this treatment is based on complex logistics and requires an assured level of antibodies if used therapeutically. This method has been tried in a very few people during initial studies, and some of them showed signs of improvement. The CP therapy does not reduce mortality and has little to no clinical improvement in patients with moderate to severe COVD-19 infection.
The effectiveness of IVIG is mainly based on clinical conditions and safety of administration. Initial clinical trials suggested no significant improvement with the IVIG therapy beyond standard therapy in non-severe patients with COVID-19. No significant difference was noticed in the IVIG patients and non-IVIG patients in terms of length of hospital stay, fever duration, or the use of antibiotics.
Convalescent Plasma (CP) vs. Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): Comparison Chart
Summary
Convalescent plasma therapy is an experimental procedure administered to patients if all the principal treatments failed to improve the survival of patients suffering from COVID-19. IVIG is a passive immunotherapy treatment used as an alternate approach to CP therapy. Randomized clinical trials were conducted by health authorities all over the world to evaluate the efficacy and safety of convalescent plasma therapy and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) for COVID-19 regardless of the severity of infection, gender, age, or ethnicity. Trials suggested CP therapy does not reduce mortality and has little or no significant impact on clinical improvement of patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection. The effectiveness of IVIG is mainly based on clinical conditions and safety of administration.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Kumar, Anoop. COVID-19 Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Sharjah, United Arab Emirates: Bentham Science Publishers, 2021. Print
[1]Khardori, Nancy and Romesh Khardori. Immunotherapy in Clinical Medicine, An Issue of Medical Clinics. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences, 2012. Print
[2]Imbach, Paul. Immunotherapy with Intravenous Immunoglobulins. Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press, 2012. Print
[3]Kazatchkine, Michael. Intravenous Immunoglobulins: Clinical Benefits and Future Prospects. Florida, United States: CRC Press, 1994. Print
