Difference Between Communicable and Noncommunicable Disease
A communicable disease is an illness that is transmittable from one person to other people. A noncommunicable disease is a disease that is not transmittable to other people.
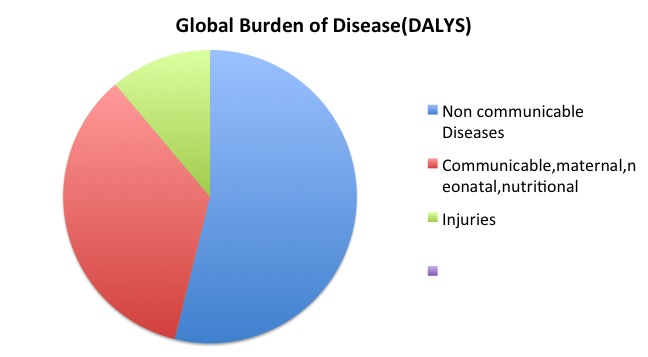
What is Communicable?
Definition:
A communicable disease is one that is able to be transmitted from one person to another. This can be via various ways such as body fluids or indirectly via vectors such as insects. Communicable diseases, in general, cause fewer deaths worldwide compared with noncommunicable diseases.
Duration and symptoms:
In general, a communicable disease is acute and does not last for very long. The pathogen can spread to other people and a sick person is thus contagious to others. Symptoms usually involve the respiratory or gastrointestinal systems where pathogens first make entry into the body.
Causes:
Some microbes such as bacteria, as well as viruses can spread among people, causing communicable disease. The causes of communicable diseases are often pathogens that may have originally been transmitted via vectors such as insects, which then spread to people. Often such illnesses are called zoonoses because animals carry the pathogen, which then inadvertently spreads to humans; shortly after, human to human transmission occurs. Although communicable illness can be confused with noncommunicable illness, it should be remembered that in communicable diseases genetics and lifestyle factors are not significant.
Prevention:
Communicable diseases can be prevented by improved hygiene practices and avoiding contact with ill individuals. Vaccination also works well in some cases to prevent illnesses such as measles, mumps, and influenza. Good sanitary practices and a clean environment also help stop bacterial infections from occurring or spreading through a population.
Examples:
Tuberculosis and cholera are both communicable diseases caused by a bacterium in each case. Influenza, HIV, hepatitis chickenpox, COVID-19, and measles are all contagious illnesses caused by viruses.
Treatment:
Antibiotics can be used for bacterial infections but this does not work for viruses, because antibiotics only attack bacterial cells. Viral infections are difficult to treat and most often, the infection runs its course and the person recovers. Treatment of viral infection is often supportive.

What is Noncommunicable disease?
Definition:
A noncommunicable disease is a disease that is not spread to other people; the illness is usually not due to a virus or bacterial agent. These diseases cause much mortality every year; in fact, in 2016 they caused an estimated 71 percent of deaths.
Duration and symptoms:
Noncommunicable diseases are not usually acute, but tend to be long-lasting chronic problems that worsen with time. Such illnesses can be confused with communicable disease when symptoms are similar, e.g. wheezing and difficulty breathing can be due to asthma, which is not contagious, but also due to tuberculosis, which is contagious.
Causes:
Many noncommunicable diseases are due to bad lifestyle choices people make, or in some instances, can be a result of a genetic mutation. Lifestyles in which people eat incorrectly and do not exercise often lead to metabolic syndrome that also then causes type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Both conditions can be deadly, particularly if not diagnosed soon enough. Illnesses caused by genetic mutations include cystic fibrosis and certain types of cancers. Although most often pathogens are not important in causing noncommunicable diseases there may be a link, in a few cases, between viruses and certain cancers.
Prevention:
It can be difficult to prevent noncommunicable diseases that are inherited as genetic mutations. However, many other illnesses are due more to lifestyle factors such as bad eating habits and lack of exercise.
Examples:
Cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cystic fibrosis and many types of cancer are noncommunicable diseases. Asthma and emphysema are also not contagious conditions, but are chronic problems.
Treatment:
Noncommunicable diseases due to lifestyle factors can sometimes be reversed with changes in diet and exercise. Type 2 diabetes can be managed through such changes; in other cases, such as type 1 diabetes, insulin is needed as this is an autoimmune disease not caused by lifestyle. Heart disease is treated most often by medication, in cases where coronary arteries are blocked, surgical intervention is needed. Cancer is treated by a combination of methods including chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery; the choice of treatment differs according to the type and stage of cancer.
Difference between Communicable and Noncommunicable disease?
Definition
Communicable diseases are illnesses that are contagious and can be spread to other people. Noncommunicable diseases are illnesses that are not contagious.
Often acute
With communicable disease, the illness is usually acute and short-lived. With noncommunicable disease, the illness is a chronic condition that lasts many years and often cannot be cured but managed.
Zoonoses
In the case of some communicable diseases, the illness originated as a zoonosis, which then spread into people. In the case of noncommunicable disease, the illness never arose as a zoonosis.
Pathogens
Communicable diseases are caused by microbes such as bacteria and viruses. Noncommunicable diseases are generally not caused by pathogens.
Examples
Examples of communicable diseases include West Nile Virus, Ebola, HIV, hepatitis, COVID-19, and influenza. Examples of noncommunicable diseases include cardiovascular disease, diabetes, lupus and arthritis.
Table comparing Communicable and Noncommunicable disease

Summary of Communicable Vs. Noncommunicable disease
- Communicable diseases are those that are contagious but generally short-lived.
- Noncommunicable diseases are not contagious and can’t spread to other people; these are chronic illnesses.
- While communicable diseases are caused by pathogens such as bacteria and viruses, noncommunicable diseases are generally due to genetics and lifestyle.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bush, Larry M. “Introduction to the Biology of Infectious Diseases”. Merckmanuals, Merck & Co., 2020, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/biology-of-infectious disease/introduction-to-the-biology-of-infectious-diseases?query=infectious%20diseases
[1]Healthday News. “Many Countries Failing on Non-Communicable Dz Death Targets ”. Merckmanuals, Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/news/external/2018/09/26/19/34/many-countries-failing-on-non-communicable-dz-death-targets
[2]Rivera, Juan A., et al. "Epidemiological and nutritional transition in Mexico: rapid increase of non-communicable chronic diseases and obesity." Public health nutrition 5.1a (2002): 113-122.
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Global_burden_of_disease(Dalys).jpg
[4]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e7/Age-standardized_death_rate_from_non-communicable_diseases%2C_OWID.svg/500px-Age-standardized_death_rate_from_non-communicable_diseases%2C_OWID.svg.png
