Difference Between Cataplexy and Catalepsy
Cataplexy is when muscles suddenly feel weak. Catalepsy is when muscles become rigid and the person has a loss of sensation to painful stimuli.
What is Cataplexy?
Definition:
Cataplexy is an instantaneous and unexpected loss of muscle strength.
Causes:
One of the causes of cataplexy is strong emotion such as sudden joy and laughter or anger or fear. It is also commonly associated with the sleep disorder narcolepsy. There are other causes of cataplexy, though, including having certain genetic conditions such as Angelman syndrome or Prader-Willi syndrome. Brain tumors and strokes can cause brain damage leading to cataplexy.
Symptoms and complications:
Symptoms usually vary from very mild to severe and include the following: a feeling that the muscles are weak. Most often muscles in the face, neck, and arms are affected. In severe cases, the person may collapse. In a child the facial expression may change, their eyes close a bit and the tongue may protrude. The person may injure themselves in severe cases where they totally collapse and fall to the ground.
Diagnosis:
A doctor can diagnose a patient by asking about their history and the types of episodes they have had. Recently, a computer-aided system has been suggested as a way to diagnose the condition by recording patient behavior after strong emotional responses. Diagnosis can also be suspected in people who have Prader-Willi or Angelman syndrome who show the symptoms of cataplexy.
Treatment:
Medication including antidepressants such as Tofranil can help in treating this condition. Another effective medication for treating cataplexy is Xyrem, a central nervous system (CNS) depressant.

What is Catalepsy?
Definition:
This is a disorder in which muscles become stiff and the person has a seizure or is in a type of trance regardless of what is going on around them and they are also not as sensitive to pain as they would normally be.
Causes:
There are many causes of catalepsy including seizures, Parkinson’s disease, substance abuse, and schizophrenia. It can also be a result of some medications such as haloperidol. Establishing the cause of the condition is necessary so that the correct management and treatment of the catalepsy can begin.
Symptoms and complications:
The most noticeable symptom is a stiff body posture. The person also is not as aware of pain and muscle control is greatly reduced or lost. A person is less aware of any pain and could possibly harm themselves accidentally while in a cataleptic state.
Diagnosis:
Catalepsy is difficult to diagnose because the signs are quite vague, but often the physical symptoms in conjunction with a condition that generally causes the problem can lead doctors to suspect and diagnose the disorder. The condition also needs to be separated from catatonia which has additional signs associated with it such as problems in communication.
Treatment:
Treatment may include the use of muscle relaxant medication. In the case of mental illness, antipsychotics are useful to treat problems like schizophrenia.
Difference between Cataplexy and Catalepsy?
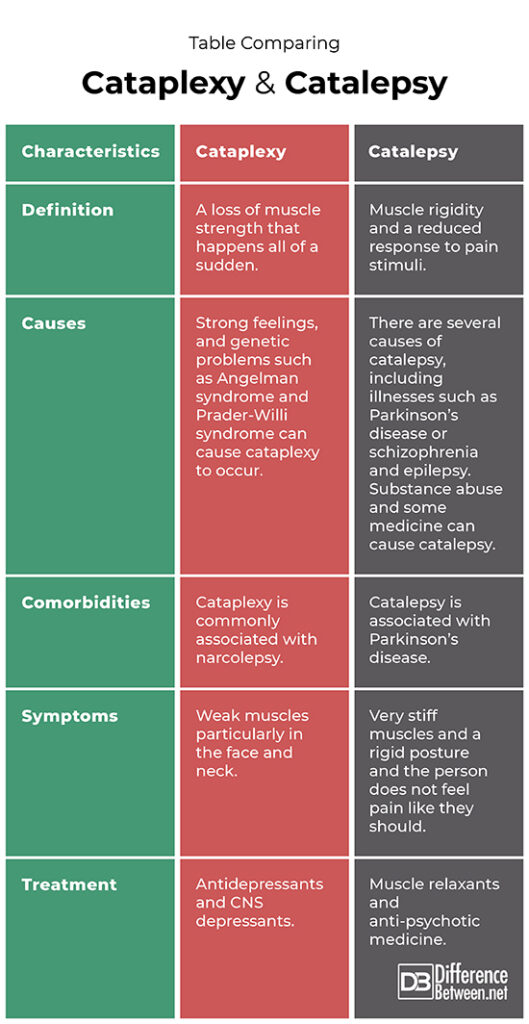
Definition
Cataplexy is when there is a loss of muscle strength that happens suddenly and unexpectedly. Catalepsy is when a person experiences a type of muscle rigidity and a reduced response to painful stimuli.
Causes
Sudden emotions and certain genetic problems like Angelman Syndrome or Prader-Willi Syndrome can cause cataplexy. Catalepsy can be triggered by certain diseases like epilepsy or Parkinson’s and certain medicines.
Comorbidities
The comorbidity of cataplexy is narcolepsy with many people having both problems together. The comorbidity of catalepsy is Parkinson’s disease.
Symptoms
In cataplexy, there are weak muscles, particularly in the neck and face and the person can collapse to the ground. In catalepsy, the muscles become stiff and the person doesn’t feel pain like they used to.
Treatment
Antidepressants and CNS depressants are used for treating cataplexy. Antipsychotics and muscle relaxant medications are used for treating catalepsy.
Table comparing Cataplexy and Catalepsy
Summary of Cataplexy Vs. Catalepsy
- Cataplexy and Catalepsy are both conditions that involve changes in muscular tone.
- Cataplexy can be a result of genetic problems like Prada-Willi syndrome or from strong emotions.
- Catalepsy is related to disorders such as Parkinson’s and seizures.
- Different types of medications can be helpful in treating cataplexy and catalepsy.
FAQ
What is the difference between catalepsy and narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is when people fall asleep at odd times. Catalepsy is when muscles become stiff and the sensation of pain is decreased.
What is the difference between catatonia and catalepsy?
Catatonia includes more than the symptoms of catalepsy. Catalepsy is only one of the many symptoms of catatonia and such patients usually also show additional symptoms such as having mutism, grimacing, or repeating words.
What are the symptoms of catalepsy?
The symptoms of catalepsy are that the muscles become stiff and immoveable and the person does not feel pain like they used to.
What mimics cataplexy?
Epilepsy and fainting can both appear to be cataplexy. A proper diagnosis is important to determine if symptoms are from cataplexy or some other condition that appears similar to cataplexy.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
References :
[0]Bartolini, Ilaria, and Andrea Di Luzio. "CAT-CAD: A Computer-Aided Diagnosis Tool for Cataplexy." Computers 10.4 (2021): 51.
[1]Dauvilliers, Yves, et al. "Cataplexy—clinical aspects, pathophysiology and management strategy." Nature Reviews Neurology 10.7 (2014): 386-395.
[2]Waku, Isabelle, et al. "Haloperidol‐induced catalepsy as an animal model for parkinsonism: A systematic review of experimental studies." European Journal of Neuroscience 53.11 (2021): 3743-3767.
