Difference Between Bronchitis and Acute Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes and trachea that can last for a short or long time depending on the form of the disease. Acute bronchitis is tracheobronchial inflammation that lasts a short time, not more than a few weeks.
What is Bronchitis?
Definition of Bronchitis:
Bronchitis is a disorder where the windpipe and tubes (bronchi) become inflamed. The condition can take the form of a chronic or acute disorder.
Symptoms and prevention for Bronchitis:
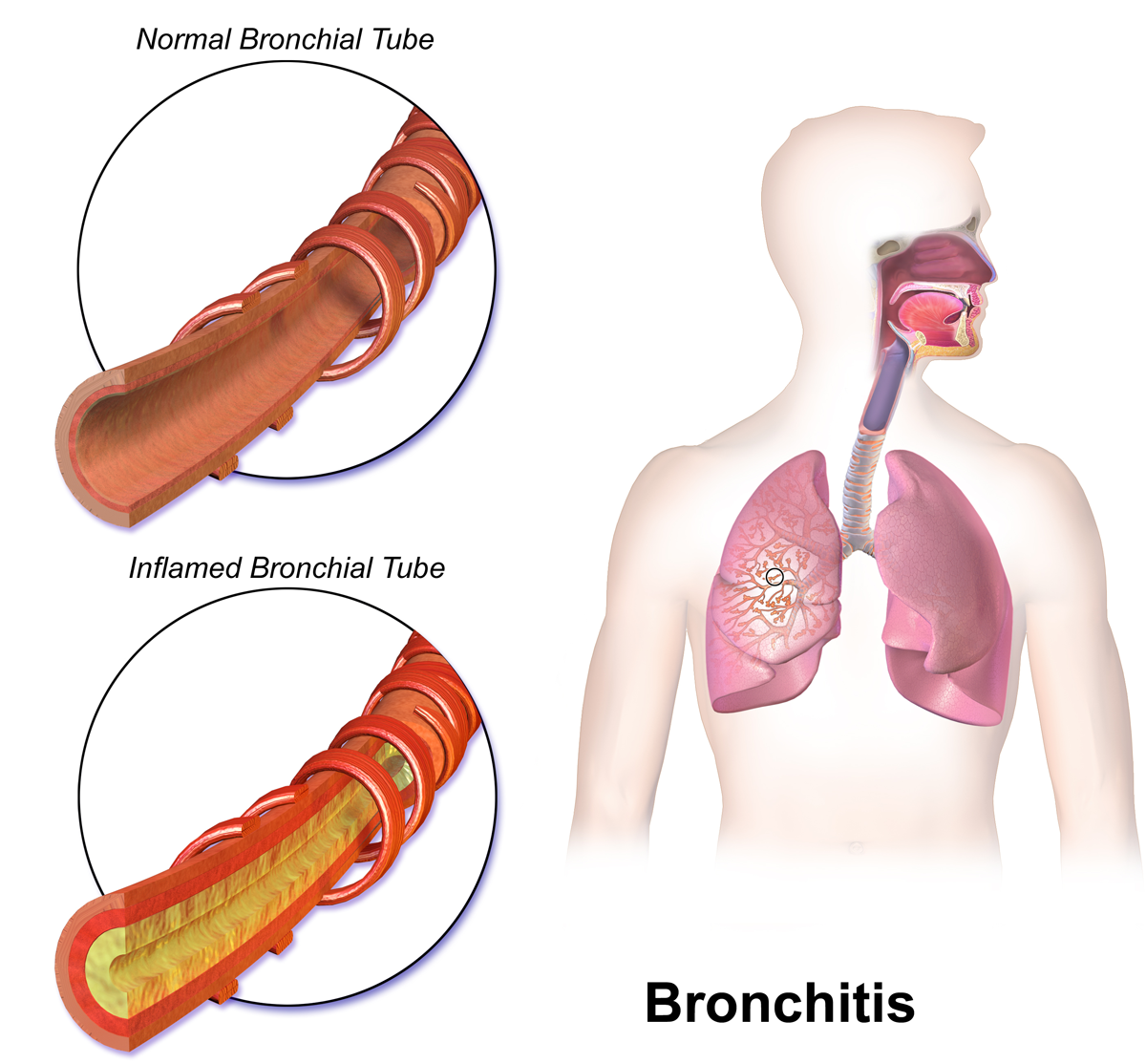
Symptoms of bronchitis include pain in the chest, a feeling of congestion and tightness, especially of the chest area. People also often have a cough that may produce thick sputum. A cough and a sense of difficulty in breathing are the symptoms that are the most common and can last for months if it is chronic bronchitis. Symptoms may last from just under a week to 3 weeks if it is the acute form. The chronic form of bronchitis includes the usual symptoms but keeps recurring and does not go away easily. Chronic bronchitis may be prevented by avoiding smoking or exposure to harmful chemicals. Getting a flu vaccine may help decrease the odds of developing acute bronchitis.
Diagnosis and causes of Bronchitis:
Bronchitis is generally diagnosed by a doctor completing a physical exam and then excluding other possible conditions by looking at a chest x-ray. The cause of bronchitis can be viral, but this more for the acute form. Chronic bronchitis is commonly caused by cigarette smoking of people who have chronic respiratory illnesses such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or the inherited disease, cystic fibrosis.
Risk factors and treatment for Bronchitis:
The risk of developing chronic bronchitis is high if you are a person who smokes cigarettes. The genetic disorder cystic fibrosis also significantly increases the risk of developing the disorder. People who have COPD are also likely to end up with chronic bronchitis. People who smoke should stop. Mostly the condition is treated symptomatically using anti-inflammatory medications and beta2-antagonists. The latter can help to open up the airways.
What is Acute bronchitis?
Definition of Acute bronchitis:
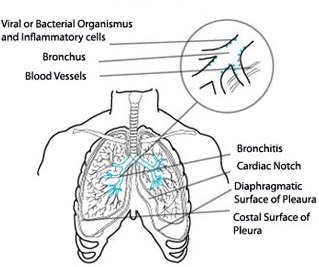
Acute bronchitis is inflammation of the trachea and bronchial tubes due to an infection of the upper respiratory tract. The condition is short-lasting with the worst symptoms occurring for about 5 days. A cough may take as long as three weeks to completely go away.
Symptoms and prevention for Acute bronchitis:
The most obvious symptom is a cough which may or may not result in sputum being produced. Individuals may also have a fever, have some difficulty in breathing and feel that their chests are tight and congested. Getting a flu vaccine every year may help prevent you from getting acute bronchitis. It is also advisable to avoid contact with people who have a respiratory infection that you may catch.
Diagnosis and causes of Acute bronchitis:
A physical exam is done and chest X-rays. The chest X-rays are used to exclude all other conditions that could be causing the symptoms. The most frequent cause of acute bronchitis is a viral infection particularly, viruses such as influenza A or B, parainfluenza virus or respiratory syncytial virus.
Risk factors and treatment:
The main risk factor for acute bronchitis is having an upper respiratory tract infection that is caused by a virus, such as the flu. It is also more common in young children who are less than 5 years old and in people with a compromised immune system. Painkilling medications that are anti-inflammatories are recommended as are beta2-antagonists. The use of antibiotics is recommended by some physicians; however, there are risks to this. Studies have shown it may help when symptoms last more than 5 days.
Difference between Bronchitis and Acute Bronchitis?
-
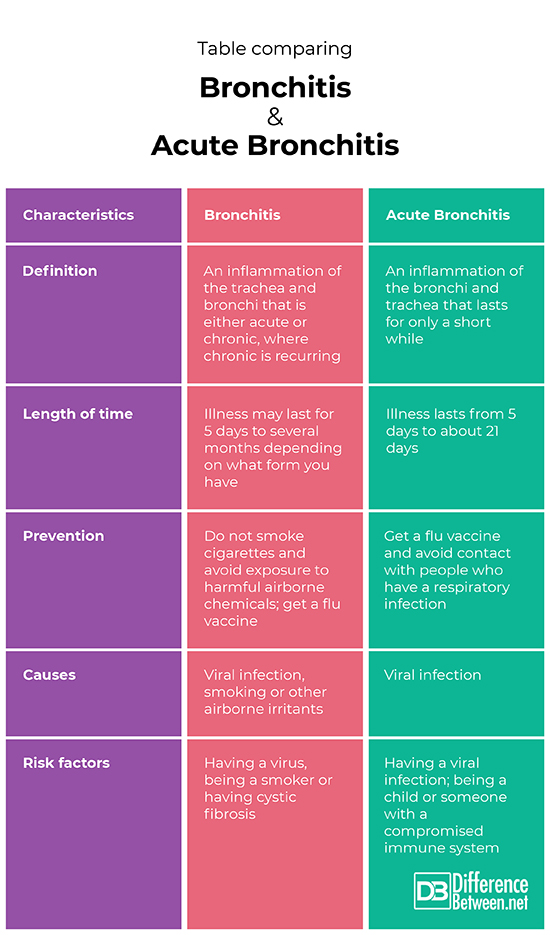
Definition
Bronchitis is defined as inflammation of the trachea and windpipe. Acute bronchitis is tracheobronchial inflammation which lasts a short time.
-
Length of time
Bronchitis can last anywhere from about a week to several months depending on what form you have. Acute bronchitis only lasts about 5 days to 21 days.
-
Prevention
The condition of bronchitis can be prevented by not smoking cigarettes and avoiding being exposed to airborne irritants, and getting a flu vaccine. Acute bronchitis can be prevented by avoiding contact with people sick with a respiratory infection, and by getting a flu vaccine every year.
-
Causes
Causes of bronchitis include having a disease such as cystic fibrosis, having a viral respiratory infection, smoking cigarettes. Causes of acute bronchitis include various viruses such as influenza and parainfluenza.
-
Risk factors
The major risk factor for bronchitis in most people is cigarette smoking or viral infections. Cystic fibrosis and COPD can also increase the risk of the chronic form of bronchitis. Acute bronchitis risk factors include being a child, having a weak immune system and having a respiratory viral infection like the flu.
Table comparing Bronchitis and Acute Bronchitis
Summary of Bronchitis Vs. Acute bronchitis
- Bronchitis is the condition when the bronchial tubes and the windpipe become inflamed for some reason.
- Acute bronchitis is the form of bronchitis which is caused by a virus and lasts only about 3 weeks.
- Bronchitis and acute bronchitis have similar symptoms such as a cough, difficulty breathing, tight chest, and chest congestion.
- Both conditions are diagnosed mainly by physical symptoms.
- Treatment of both conditions is usually symptomatic and includes using anti-inflammatory medications and beta2-antagonist medications.
- Not smoking and avoiding airborne irritants can help to prevent the chronic form of bronchitis.
- Receiving a flu vaccine every year can help to prevent acute bronchitis that is caused by having influenza.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Kinsman, Robert A., et al. "Symptoms and experiences in chronic bronchitis and emphysema." Chest 83.5 (1983): 755-761.
[1]Sethi, Sanjay. “Acute bronchitis”. Merckmanuals. Merck & Co., 2018, https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/pulmonary-disorders/acute-bronchitis/acute-bronchitis
[2]Smucny, John, et al. "Antibiotics for acute bronchitis." Cochrane database of systematic reviews 3 (2000).
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bronchitis.png
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acute-bronchitis.jpg

not until I found totalcureherbsfoundation com their supplement are 100% guaranteed.