Difference Between Blepharitis Anterior and Blepharitis Posterior
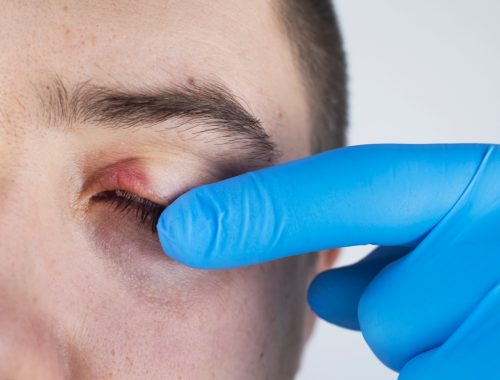
Both seborrheic (dandruff of the scalp and eyebrows) and staphylococcal blepharitis (a type of blepharitis caused by staphylococcus (or “staph”) bacteria) are considered to be anterior blepharitis, which affects the lash margin, while meibomian gland (oil producing glands present on both the top and bottom eyelid margin) involvement is considered to be posterior to the lash margin. There are several treatment options that are used to treat blepharitis. These include eye drops that are usually steroid eye drops that reduce inflammation, pain, irritation, discomfort and redness. These drops are available as over the counter medicines and can be obtained without a prescription. Other treatment options include ointments, pills and topical antibiotics.
Similarity
Both Blepharitis anterior and Blepharitis posterior are the infections of the eyes
Blepharitis Anterior
Where your eyelashes (cilium) join your eyelid (two pieces of skin which cover your eyes when they are closed), on the exterior of your eye, is where anterior blepharitis (an inflammatory condition of the eyelid margin) manifests. Usually, skin microorganisms or dandruff (flaking) from the scalp or eyebrows are the primary culprits. Although uncommon, allergies (when immune system reacts abnormally to a foreign substance) or mites (tiny parasites) can also induce anterior blepharitis.
Blepharitis Posterior
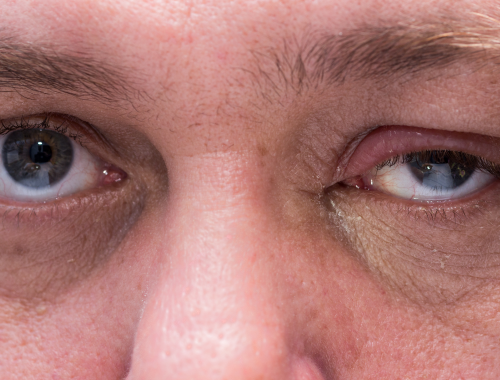
Posterior blepharitis is the eye condition/infection of the inner edge of the eyelid (two pieces of skin which cover your eyes when they are closed) that is linked to the eyeball.
Difference between Blepharitis Anterior and Blepharitis Posterior
Definition
Blepharitis Anterior
It is the infection of the eyelashes. Usually, skin microorganisms (very small organisms not visible to naked eyes) or dandruff (flaking on the scalp) from the scalp or eyebrows are the key culprits. Although not common, allergies or mites (tiny arthropods) infestation can also induce anterior blepharitis.
Blepharitis Posterior
Posterior blepharitis is the eye condition/infection of the inner edge of the eyelid (two pieces of skin which cover your eyes when they are closed) that is linked to the eyeball.
Symptoms
Blepharitis Anterior
Inflammation of the base of the eyelashes
Grey scales on lid margins
Blepharitis Posterior
- Inflammation of the inner portion of the eyelid at the level of the meibomian glands.
- Fluctuations in vision
- Dry eyes
- Foam thick meibum, meibomian gland dropout, pouting meibomian glands, inspissated glands
Causes
Blepharitis Anterior
- Allergies – which could be triggered by eye drops, several synthetic cosmetic products, contact lens solution
- Acne rosacea: can causes irritation and itching on the skin of your face, eventually affecting the eyelids
- Seborrheic dermatitis (Dandruff)- Flaking on the scalp skin can eventually affect eyelids and cause swelling and irritation of the eyelids
- Dry eyes which could modify and impact bacteria resistance (immunity to endure bacterial infections) resulting in infection.
- Demodex mites or lice (mites that live in human hair follicles) in the eyelashes can impede the glands and follicles that create eyelashes (demodicosis).
Blepharitis Posterior
- Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD
- Acne rosacea
- Dandruff
Types
Blepharitis Anterior
- Seborrheic Blepharitis (dandruff)
- Ulcerative Blepharitis (bacteria)
- Demodex Blepharitis (mites)
Blepharitis Posterior
- Meibomian glands
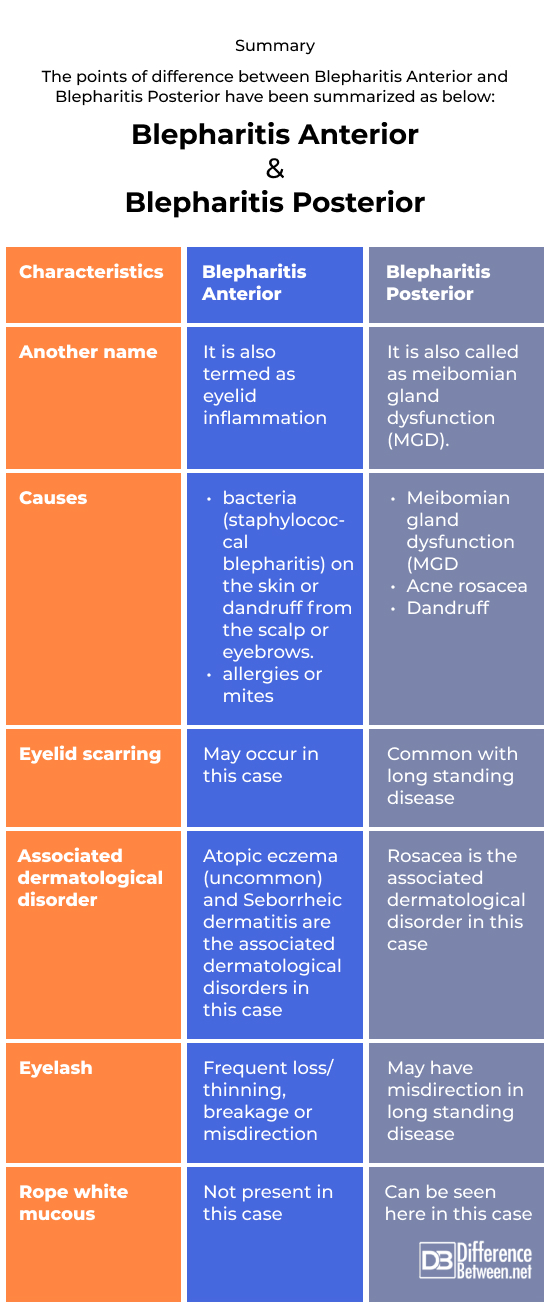
Summary
The points of difference between Blepharitis Anterior and Blepharitis Posterior have been summarized as below:
FAQ:
How can you tell the difference between anterior and posterior blepharitis?
Anterior blepharitis is the infection of the outer side of the eyes where the eyelashes (any of the short hairs that grow along the edges of the eye) attach to your eyelid.
Posterior blepharitis is the infection of the outer side of the inner edge (inner aspect of the eyelid) of the eyelid.
What are the two types of blepharitis?
Anterior Blepharitis and Posterior Blepharitis are two main types of blepharitis.
What is anterior blepharitis?
Anterior blepharitis is commonly caused by bacteria or scalp dandruff (flaking) and affects the outer side of the eyelid (two pieces of skin which cover your eyes when they are closed), where the eyelashes attach.
Is anterior or posterior blepharitis more common?
Posterior blepharitis is more common in comparison to the anterior blepharitis.
What are the signs of anterior blepharitis?
Superficial discomfort, scales and collarettes base of lashes, itchy eyelids, red and swollen eyelids, trichiasis and lid notching.
What is the best eye drop for posterior blepharitis?
Topical cyclosporine (Restasis) is the best eye drop to give some relief from the symptoms of posterior blepharitis.
What is the first treatment for anterior blepharitis?
Use of ointment or gel formulations and topical antibiotics (bacitracin or erythromycin for two to eight weeks) is the first treatment for anterior blepharitis
How do you diagnose posterior blepharitis?
A thorough eye examination can be used to confirm and diagnose posterior blepharitis.
Does posterior blepharitis cause dry eyes?
Yes, posterior blepharitis causes dry eyes.
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Bernardes, T. F., & Bonfioli, A. A. (2010, May). Blepharitis. In Seminars in ophthalmology (Vol. 25, No. 3, pp. 79-83). Taylor & Francis.
[1]Duncan, K., & Jeng, B. H. (2015). Medical management of blepharitis. Current opinion in ophthalmology, 26(4), 289-294.
[2]Guillon, M., Maissa, C., & Wong, S. (2012). Symptomatic relief associated with eyelid hygiene in anterior blepharitis and MGD. Eye & contact lens, 38(5), 306-312.
[3]Kyei, S., Asiedu, K., Ephraim, R. K., & Adanusa, M. (2022). Posterior blepharitis and associated potential factors: a study among pregnant women. Ocular Immunology and Inflammation, 30(6), 1475-1481.
