Difference Between Anticoagulants and Fibrinolytics
Anticoagulants are substances that stop clots from being made while the fibrinolytics work to break down clots that have already been formed.

What is Anticoagulants?
Definition:
Anticoagulants are chemical substances that help prevent blood clots from being produced in the blood.
How anticoagulants work:
Some anticoagulants work by binding to cofactors of enzymes that are involved in clotting. For example, heparin binds to a cofactor called antithrombin, which in turn binds to coagulation proteases and reduces blood clotting in the process. Other anticoagulants such as the medicine warfarin function by impeding the process by which vitamin K is involved in making clots. By interfering with vitamin K, the anticoagulant warfarin ensures that it takes a much longer time for a clot to form.
Advantages:
Taking anticoagulants is helpful for people who have a history of myocardial infarction (MI), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism). The idea is that anticoagulants aid by stopping clots from forming in the future in people who are susceptible to this problem.
Disadvantages
There are risks associated with anticoagulant therapy such as a higher chance of bleeding leading to anemia or even uncontrolled hemorrhage.
Examples:
Heparin and warfarin are two types of anticoagulants that work in different ways to prevent blood clotting. Edoxaban is a newer anticoagulant used by people with particular heart issues.
What is Fibrinolytics?
Definition:
Fibrinolytics are substances that are used to help break down blood clots in the bloodstream.
How fibrinolytics work:
Fibrinolytic medications are designed to stimulate the natural fibrinolytic system involved in the process of removing blood clots from the bloodstream. TNKase is one type of fibrinolytic that increases the production of the plasmin that dissolves clots. Fibrinolytics also break up the substance fibrin, which is involved in forming clots. Alteplase is a medicine that stimulates plasminogen to form into the plasmin that dissolves clots. Plasmin actually cleaves the molecule fibrin, thus causing the dissolution of a clot.
Advantages:
Fibrinolytics are a very useful treatment for life-threatening clots that have formed such as those that could be causing an acute heart attack (also called an MI) and stroke. If given in time, a fibrinolytic medication can dissolve such clots. This is especially important in the cases of ischemic stroke where timely administration of such medicine can reverse the stroke and its associated symptoms.
Disadvantages:
Some disadvantages of fibrinolytic therapy include a chance of allergic reactions such as angioedema. It can also cause low blood pressure and bleeding. Fibrinolytics are also contraindicated for people having a hemorrhagic stroke where further bleeding would be dangerous.
Examples:
Examples of fibrinolytics include the medications streptokinase, TNKase, and eminase.
Difference between Anticoagulants and Fibrinolytics?
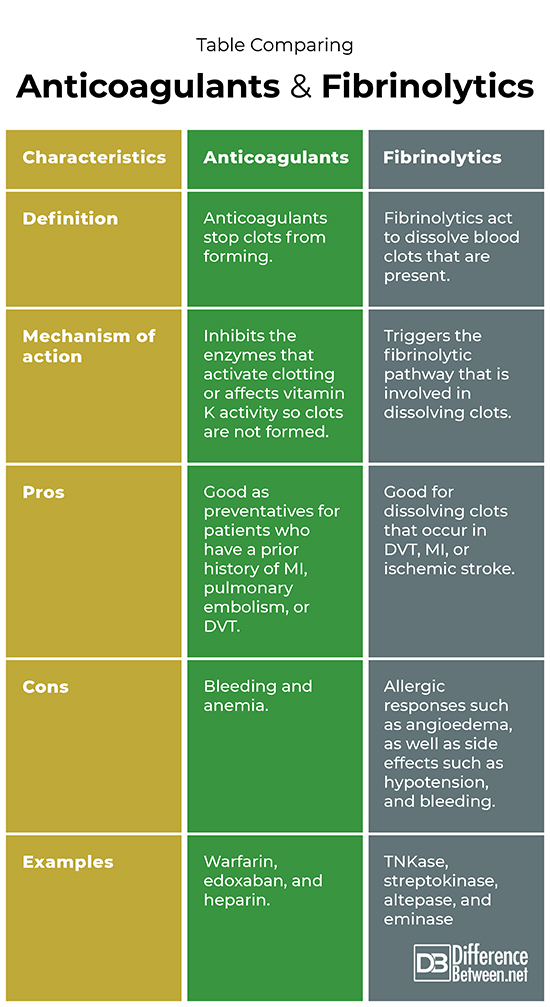
Definition
Anticoagulants are substances that prevent clots from being created. Fibrinolytics are substances that work to break down pre-existing clots.
Mechanism of action
The way that anticoagulants function is that they inhibit the enzymes that activate clotting or else they affect vitamin K activity so that clots are not formed. The way that fibrinolytics function is that they trigger the fibrinolytic pathway that is involved in dissolving clots; this often involves activating plasminogen.
Pros
The benefits of anticoagulants are that these substances are good as preventatives to stop clots from forming in patients who have a prior history of MI, pulmonary embolism, or DVT. The benefit of fibrinolytics is that they are very useful and effective in dissolving clots that form when a person has DVT, MI, or ischemic stroke.
Cons
A disadvantage of using anticoagulants is that they can cause bleeding and anemia. Disadvantages of using fibrinolytics are that there can sometimes be an allergic reaction or the person can have bleeding and hypotension.
Table comparing Anticoagulants and Fibrinolytics
Summary of Anticoagulants Vs. Fibrinolytics
- Anticoagulants and fibrinolytics are helpful medications used for certain blood clotting problems.
- Fibrinolytics interfere with clotting by impacting the chemicals that break down clots.
- Anticoagulants stop a clot from forming by influencing the enzymes involved in the process.
- The mechanism of action of fibrinolytics and anticoagulants is different.
- Both types of medications can cause bleeding due to affecting the ability of the blood to form clots.
FAQ
How are anticoagulants different from thrombolytics?
The mechanism of action is different between the medications that are classified as thrombolytics versus those that are classified as anticoagulants. In fact, the anticoagulant mechanism involves stopping clot production while thrombolytics work to break down clots that have already been formed.
What is the difference between fibrinolytics and thrombolytics?
Fibrinolytics and thrombolytics are the same medications that work to activate plasminogen to break down fibrin (a protein involved in clotting) to help dissolve clots. The terms are used interchangeably to refer to medicine that helps break down clots that have been made in the body.
What is the difference between fibrinolytic and antiplatelet drugs?
Both types of drugs affect blood clotting. However, antiplatelet drugs, unlike fibrinolytic drugs, work specifically to decrease blood platelet formation. This is important because blood platelets are an important component of a blood clot.
What is the difference between antithrombotic and anticoagulant?
Antithrombotic is a general term to describe drugs used to reduce blood clots in some manner. Anticoagulant is a specific type of antithrombotic drug that acts on enzyme cofactors to reduce blood clot formation.
- Difference Between Rumination and Regurgitation - June 13, 2024
- Difference Between Pyelectasis and Hydronephrosis - June 4, 2024
- Difference Between Cellulitis and Erysipelas - June 1, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Björk, I., and U. Lindahl. "Mechanism of the anticoagulant action of heparin." Molecular and cellular biochemistry 48.3 (1982): 161-182.
[1]Fedan, J.S. “Fibrinolytics.” Encyclopedia Britannica, 2022, https://www.britannica.com/science/fibrinolytic-drug
[2]Melandri, Giovanni, et al. "Review of tenecteplase (TNKase) in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction." Vascular health and risk management 5 (2009): 249.
