Difference Between Agglutination and Coagulation

Agglutination and coagulation might be on different teams, but they certainly are part of the same sport.
Platelet agglutination is either artificially done as a diagnostic tool or it refers to a part of the coagulation process. Coagulation on the other hand, is a broader process and mechanism whereby the body is kept in a steady state.
Both aspects have various disorders and treatments associated with them and treating them correctly is nothing short of crucial!

Definition and Physiology
Agglutination
Platelet agglutination is the clumping together of particles due to agglutinins and occurs in a test tube, which is a useful diagnostic tool in medicine.
Agglutinin is an antibody or sugar-binding protein found in the blood. This substance is the mechanism behind particles’ ability to both aggregate and coagulate.
When agglutinin is added to suspended blood or bacteria sample inside a test tube, it is been observed that the agglutinin binds to an agglutinin-specific structure on one of the particles. This ultimately results in states of both aggregation and separation.
This process is a ground-breaking too for medical diagnoses. This includes differentiating what blood type a patient is. Another example is the process of accurately identifying blood transfusion cross matches in patients to avoid a negative reaction and even death. Finally, agglutination shows past or present exposure of a patient’s blood to pathogen infection or finding new bacterial cells.
Coagulation
Coagulation is a mechanism of the body to maintain homeostasis (or a regulatory steady state). This happens in three main steps referred to as platelet plugging, intrinsic and extrinsic pathways, and the common pathway to ultimately stop bleeding.
The platelet plugging, or aggregation is the first step. This is also referred to as primary homeostasis. When there is a damaged site in the body where endothelial cells are exposed, platelets come together to form a plug over the area.
Then comes secondary homeostasis, which involves the coagulation pathways. The intrinsic pathway is activated when damage or trauma has occurred to an area where endothelial collagen is exposed. The extrinsic pathway is activated when damage occurs to an area involving blood vessels. Which ever one is active will then connect to the common pathway, which begins once factor X is produced to factor Xa.
To stop the process of too much clotting, there is a negative feedback process that the body follows. The thrombin substance found in the blood activates plasminogen into plasmin which then produces antithrombin. Antithrombin lowers the level of activated factor X. In addition, protein C and S and also responsible to stop over-clotting and do so by preventing the activation of factor V and VIII.
Disorders
Agglutination
Cold agglutinin disease is an agglutination disorder characterized by a high concentration of cold sensitive antibodies circulating in the blood stream of the body.
Cold agglutination disease is also a rarely occurring disorder of the body’s autoimmune system. Primary, this autoimmune disorder works by early (or premature) destruction of the red blood cells. This disease is specifically categorized as a subtype of autoimmune haemolytic anaemia.
An autoimmune disease is characterized by the body destroying its own tissue or cells and this is exactly the case in cold agglutination disease.
An agglutination related response that can occur in the body is one brought on by the venom of Formosan Pit Viper. This response causes clumping due to the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib agonist found in the venom.
Coagulation
Coagulation disorders include Hemophilia A and B (which are inherited disorders), and Hemophilia C (which is due to a deficiency of factor XI).
Factor V Leiden is a disorder caused by a genetic mutation which results in a defect of factor V to the extent that protein C is unable to activate is.
When protein C and S deficiencies are present, disorders that lead to over clotting can occur and leave the body in a state where it is unable to stop factor V and VIII.
Treatment
Agglutination Disorders
Generally speaking, avoiding exposure to cold is the standard treatment for everyday life. This is especially true for the head, face, arms, and legs.
Medical treatment includes an artificially generated antibody called Rituximab. This medication targets specific white blood cells that are responsible for creating the red blood cell destroying antibody.
In cases where the condition is so severe that the patient becomes severely anaemic, the patient can be treated with blood transfusions or plasma transfusions. This is only a temporary solution though!
Coagulation Disorders
Treatment for coagulation disorders include plasma transfusions and other blood clotting medications including Vit
If the coagulation disorder is one that causes over clotting, then patients are treated with anticoagulation medication such as Warfarin and Heparin. This is crucial to keep in balance, as giving too little can increase the risk of a stroke occurring.
Table of comparison between agglutination and coagulation
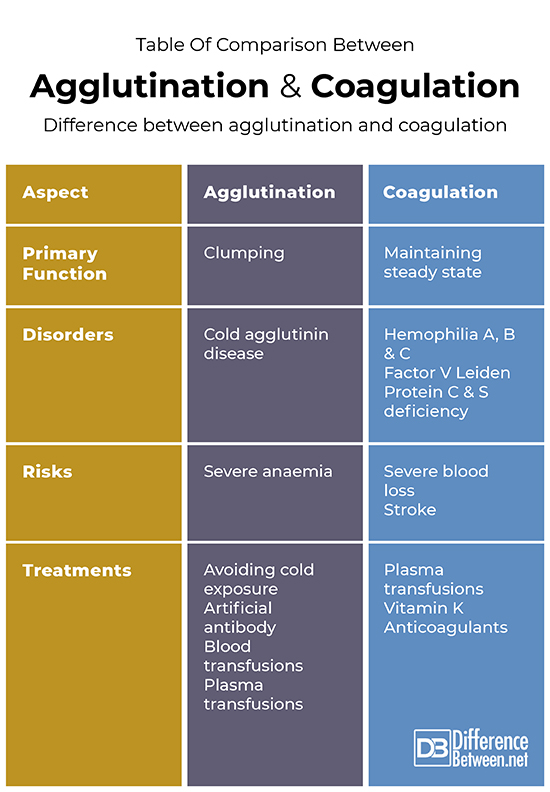
Summary
Agglutination and coagulation are both important mechanisms and aspects of the body’s circulatory system.
Although they both have differences in their disorders, the treatments are both aimed at correcting the compromised component of the blood.
FAQ
What is the difference between agglutination and aggregation?
Platelet agglutination and aggregation are both processes primarily involving the clumping of blood cells. Platelet agglutination includes the presence of agglutin and is usually used as a diagnostic tool, where platelet aggregation is part of the body’s normal clotting process or occurs during agglutination processes as diagnostic tool. Although the processes have similarity in terms of cell clumping, each has unique uses and functions, and presents with specific associated disorders.
Platelet agglutination is the clumping together of particles due to agglutinins and occurs in a test tube, which is a useful diagnostic tool in medicine.
Platelet aggregation is the platelet-to-platelet adhesion for clumping and plays a vital role in the formation of a blood clot to attach to an area in the body or can form part of the diagnostic process in medicine.
Is clotting and coagulation the same?
Yes. Coagulation is another way of saying clotting.
What is the difference between agglutination and hemolysis?
Hemolysis involves breaking down clumps where agglutination is the formation of clumps.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]National Organization for Rare Disorders. Rare Disease Database: Cold Agglutinin Disease. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/cold-agglutinin-disease/
[1]Periayah, M.H., Halim, A.S and Mat, Saad A.Z. Mechanism Action of Platelets and Crucial Blood Coagulation Pathways in Hemostasis. International Journal of Hematology, Oncology and Stem Cell Research. 2017, vol. 11, no. 4, pp:319-327.
[2]Rumbaut, R.E and Thiagarajan, P. Platelet-Vessel Wall Interactions in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. San Rafael (CA): Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences. 2010. Chapter 4, Platelet Aggregation. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK53449/
[3]Shih, C.H., Chiang, T.B and Wang, W.J. A critical role for the regulation of Syk from agglutination to aggregation in human platelets. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2014, vol. 443, no. 2, pp:580-585.
