Difference Between Fat Burning and Cardio
Many people struggle to maintain a healthy lifestyle, maybe because of their busy, hefty routine. But it’s important to stay in shape and stay fit in today’s fast paced lifestyle. Well, not everybody is a fitness fanatic. But, like they say, it’s never too late to start exercising or to change the way you look and eat. Nobody likes to carry extra fat around. If you want to change that, you must push yourself out of your comfort zone and start doing workouts. For one, aerobic exercises are a great way to burn some calories along with fat burning and cardio workouts.
When personal trainers talk about cardio exercises, they often refer to performing that aerobic exercise in one of the two zones. One is the fat-burning zone and the other is the cardiovascular training zone (cardio training zone). Over the years, much discussion has been followed around the topic that which zone is the best to lose weight and why one is better than the other. Each one has its benefits and drawbacks. Let’s take a look at the two activities to comprehend how they differ in terms of intensity and effectiveness.

What is a Fat-Burning Workout?
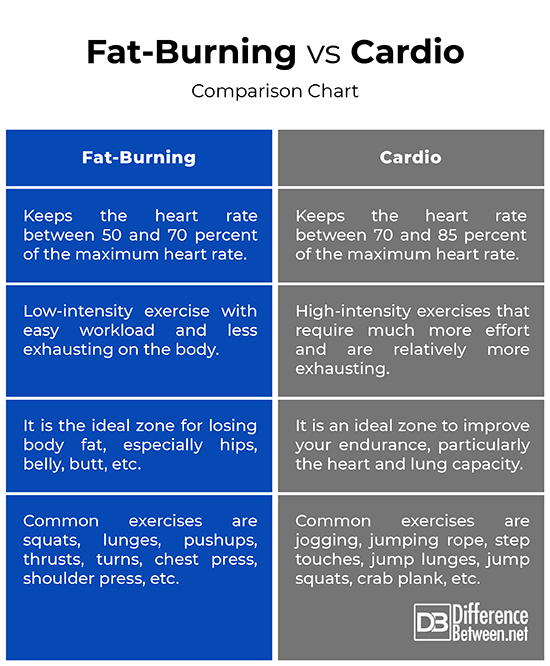
Fat-burning, as the name suggests, exercises refer to the fitness regime aimed towards burning fat by keeping your heart rate in the fat burning zone. It is typically a low-intensity cardio workout that keeps the heart rate between 50 and 70 percent of your maximum heart rate (MHR). The intensity of these types of exercises is low and the workload is not too difficult. This is a zone for beginners looking to lose some body fat because it is intense enough to have a positive impact on your body and hard enough to burn a significant amount of calories. In addition, fat-burning exercises are less exhausting meaning most people can do it without pushing themselves to the edge. In this zone, you tend to burn a higher percentage of fat, hence the name. The most common and widespread fat burning exercises are squats, lunges, pushups, thrusts, turns, chest press, shoulder press, seated row, and so on.

What is a Cardio Workout?
Cardio zone, also known as the aerobic zone, is a high-intensity aerobic workout that keeps the heart rate between 70 and 85 percent of your maximum heart rate. These exercises are usually more intensive meaning they would require much more effort than with fat-burning workout. Cardio workout is designed to complement the aerobic fitness and is fueled typically through 50 percent fat and 50 percent carbohydrate. At lower-intensity cardio, as measured by heart rate, a significantly higher percentage of fat is burned, whereas, at higher-intensity cardio, a lower percentage of glucose is burned. The heart is being vigorously exercised in the cardio zone and the body burns fat as well. The higher the intensity you train at, the greater the number of calories is burned and the less lactic acid is produced. Common cardio exercises are jogging, jumping rope, step touches, jump lunges, jump squats, crab plank, speed skater lunge, and so on.
Difference between Fat-Burning and Cardio
MHR -Maximum Heart Rate
– Cardiovascular training exercises fall typically into two zones: the fat-burning zone and the cardio zone. The fat-burning zone is a low-intensity training exercise plan aimed at burning body fat by keeping your heart rate between 50 and 70 percent of your maximum heart rate (MHR). The cardio zone, on the other hand, is also known as the aerobic zone and is a high-intensity aerobic workout that keeps the heart rate between 70 and 85 percent of your maximum heart rate.
Intensity
– Fat- burning exercises are low-intensity cardio exercises that are less exhausting on the body and the workload is not too difficult. The activities in this zone feel fairly easy and easy exercises can be combined with tough ones and you can exercise longer to burn the same amount of calories as you would with high-intensity workout. Cardio exercises, on the contrary, are higher-intensity training exercises that require much more effort and are done without breaks. Cardio exercises would require at least 30 minutes of exercising for best results.
Goal
– The purpose of fat-burning exercises is to keep the heart rate in the fat-burning zone in order to burn a greater amount of fat at lower-intensity training exercises than with higher-intensity workout. It is the ideal zone for fat loss in the body, especially hips, belly, butt, etc. The purpose of cardio workout, on the other hand, is not solely to reduce body fat but to improve the overall body function in general. It is an ideal zone if you wish to improve your endurance, particularly the heart and lung capacity.
Exercise
– Fat-burning exercises can be performed with or without special fitness equipment and are ideal for those who are overweight. The most common fat-burning exercises in widespread use are squats, lunges, pushups, thrusts, turns, chest press, shoulder press, seated row, and so on. Cardio exercises may result in increased anaerobic threshold and the workouts are typically fueled through 50 percent fat and 50 percent carbohydrate. The common cardio exercises are jogging, jumping rope, step touches, jump lunges, jump squats, crab plank, speed skater lunge, etc.
Fat-Burning vs. Cardio: Comparison Chart
Summary
In a nutshell, both fat-burning and cardio exercises result in weight loss. However, many people mistakenly think that performing higher-intensity cardio workouts every time give the best results. To lose bodyweight, the key is to burn more calories than you consume. Fat-burning exercises are for those who want to get rid of that extra fat that’s accumulated over time. But cardio exercises can improve your endurance, particularly your heart and lung capacity. So, for most fitness enthusiasts, staying in the cardio zone might just be the best bang for the buck, while for the beginners, fat-burning workout might just be great.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Buckley, Julia. The Fat Burn Revolution: Boost Your Metabolism and Burn Fat Fast. London, United Kingdom: A & C Black, 2014. Print
[1]Henriques, Tim. NPTI’s Fundamentals of Fitness and Personal Training. Illinois, United States: Human Kinetics, 2014. Print
[2]Roschinsky, Johannes. Fat Burning: Exercise & Diet. Aachen, Germany: Meyer & Meyer Verlag, 2004. Print
[3]McFedries, Paul. Fitbit for Dummies. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2019. Print
[4]Clark, Michael, et al. NASM's Essentials of Sports Performance Training. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2010. Print
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4028/4425914966_53ff61c8d9_z.jpg
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gym_Cardio_Area.jpg
