Difference Between Strong and Weak Acid
Acids are chemical substances that donate hydrogen ions or protons when mixed in solutions. The number of protons given off by a particular acid actually determines the strength of the acid – whether it is a strong acid or a weak acid. In order to understand the strength of the acids, one need to compare their tendency to donate protons to the similar base (mostly water). The strength is denoted by a number called pKA.

What is a Strong acid?
An acid is said to be strong if it dissociates or ionizes completely in a solution. That means, it is able to give the largest number of H+ ions or protons when mixed in a solution. These ions are the charged particles. Since a strong acid donates a greater number of ions as it breaks down, or ionizes, that means a strong acid is a conductor of electricity.
When an acid mixes in H2O, a proton (H+ ion) is carried to a H2O molecule to generate a H3O+ (Hydroxonium ion) and a – ion based on which acid is involved to begin with.
In a general scenario,

Such chemical reactions can be revered, but in few cases, the acid is gives away H+ ion quite easily and the reaction looks like being one-way. And the acid is complete dissociated.
For e.g., when hydrogen chloride dissolves in H2O to make HCl, so little of the reverse reaction happens that we can write:

At one time, hundred percent virtual reaction will take place wherein hydrogen chloride will show reaction with H3O+ (Hydroxonium ion) and Cl– ions. Here, the strong acid is Hydrogen Chloride.
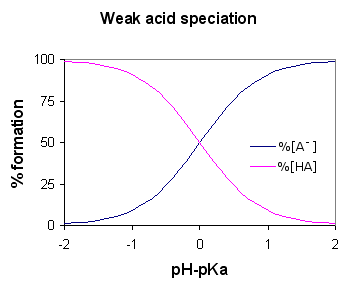
What is a Weak acid?
An acid is said to be weak if it ionizes partially or incompletely, giving off only some of its hydrogen atoms into the solution. Hence, it is less capable as compared to a strong acid in giving off protons. Weak acids have higher pKa than strong acids.
Ethanoic acid is a good example of a weak acid. It shows reaction with H2O for producing H3O+ (Hydroxonium ions) and CH3COOH (ethanoate ions), but the reverse reaction shows more success than the forward one. The molecules react quite easily to ameliorate the acid and the H2O.

At any one time, only about one percent of the CH3COOH acid molecules show conversion into ions. Whatever is left is the simple acetic acid (systematically called ethanoic acid) molecules.
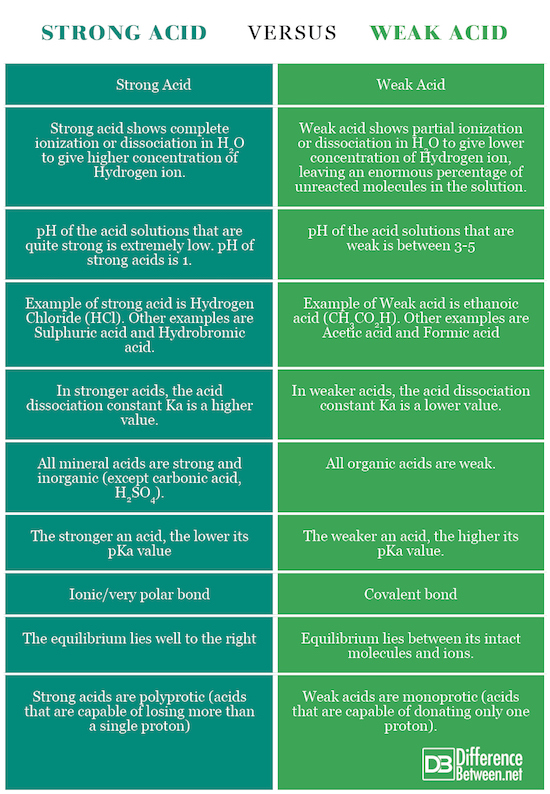
Difference between Strong acid and Weak acid
-
Definition
Strong acid
A strong acid is an acid that ionizes completely in an aqueous solution. A strong acid will always loose a proton (A H+) when dissolved in H2O. In other words, a strong acid is always on its toes and quite efficient in giving off protons.
Weak acid
A weak acid is one that ionizes partially in a solution. It gives off only few of its hydrogen atoms in to the solution. Hence it is less capable than a strong acid.
-
Electrical conductivity
Strong acid
Strong acids will always show strong conductivity. Strong acids usually pass more current as compared to the weak acids for the same voltage and concentration.
Weak acid
Weak acids have a low conductivity. They are poor conductors and show a low value for current passing
-
Rate of reaction
Strong acid
Rate of reaction is faster in the strong acids
Weak acid
Rate of reaction is slower in weak acids
-
Examples
Strong acid
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Nitric acid (HNO3), Perchloric acid (HClO4), Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), Hydroiodic acid (HI), Hydrobromic acid (HBr), Chloric acid (HClO3).
Weak acid
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3), Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Phosphoric acid (H3PO4), Benzoic acid (C6H5COOH), Hydrofluoric acid (HF), Formic acid (HCOOH), Nitrous acid (HNO2).
-
pH
Strong acid
In a strong acid, the pH is lower than, generally 3. Strong acids possess a very high concentration of H+ ions (an acid having a pH of 3 has 0.001 moles per liter of Hydrogen ions).
Weak acid
A weak acid has a pH ranging between 3-7.
-
Value of pKa
Strong acid
In a strong acid, the value of pKa is quite low.
Weak acid
In a weak acid, the value of pKa is quite high.
-
Dissociation
Strong acid
HCl(g) + H2O(l) ≈ H3O+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
Weak acid
CH3COOH(l) + H2O(l) ≈ H3O+(aq) + CH3COO−(aq)
Summary of Strong acid Vs. Weak acid
The points of difference between Strong and Weak Acids have been summarized below: Comparison chart
- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Kelly, R. M., & Akaygun, S. (2016). Insights into how students learn the difference between a weak acid and a strong acid from cartoon tutorials employing visualizations. Journal of Chemical Education, 93(6), 1010-1019.
[1]Ring, T., & Kellum, J. A. (2016). Strong Relationships in Acid-Base Chemistry–Modeling Protons Based on Predictable Concentrations of Strong Ions, Total Weak Acid Concentrations, and pCO2. PloS one, 11(9), e0162872.
[2]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/15/Weak_acid_pfe.png
[3]Image credit: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/7/71/Weak_acid_speciation.png

I’m a student of a important school, this succs