Difference Between Spirometry and Incentive Spirometry
Spirometry is a set of tests that measures the quantity of air inspired or expired. It helps in identifying several lung conditions. Incentive spirometry is a breathing exercise that is advised postoperatively to patients to ensure good breathing.
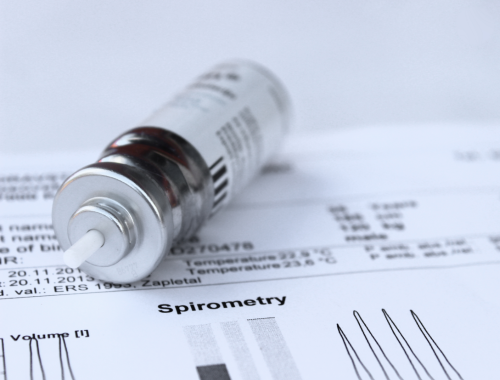
What is spirometry?
Definition:
Spirometry is a set of tests that measures the quantity of air inspired or expired. Three modalities that this procedure assesses include volume, time, and flow.
Procedure:
A spirometry test is a noninvasive procedure. It takes about 45 minutes and is an outpatient investigation carried out by a respiratory therapist or technician.
Uses:
Spirometry determines important lung volumes that aid in assessing lung function. It helps to identify lung pathologies, quantify lung damage, assess lung function after long-term occupational dirt exposure, and determine drug efficacy.
Interpretation:
Spirometry measures several important lung volumes. It measures forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), the maximum forced amount of air that can be exhaled after maximum inhalation, and Vital capacity (VC), the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled, at a relaxed pace, after maximum inhalation. Spirometry also measures peak expiratory flow (PEF), forced expiratory flow, and inspiratory vital capacity (IVC) which is the maximum inspiration after a full expiration. The most important relation that can be evaluated via spirometry is the ratio of FEV1/FVC.
Contraindications:
Any of these recent events contraindicate the use of spirometry: pneumothorax, history of myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolism, aneurysms of any kind, hemoptysis, complaints of nausea or vomiting, recent surgeries especially eye surgery or abdominal surgery.

What is incentive spirometry?
Definition:
An incentive spirometer is a handheld device that is used by patients post-surgery to encourage breathing and increase lung capacity after an operation.
Procedure:
An incentive spirometer is prescribed by doctors as a post-operative measure. The device can easily be operated at home. The procedure involves holding the device upright, sealing the mouthpiece with your lips, and inspiring slowly and as much as one can. The piston or the balls are supposed to rise more and more with practice. The breathing exercises are to be repeated 10 to 12 times per hour or as advised.
Uses:
Incentive spirometry helps to build lung capacity. It also helps with conditions like postoperative pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema.
Interpretation:
The doctor will explain to you the goal that you should be aiming for while using an incentive spirometer. Incentive spirometry is not a part of pulmonary function tests.
Contraindications:
Incentive spirometry is contraindicated in people with recent eye surgery, those with a collapsed lung, and those with aneurysms in the brain, chest, or abdomen.
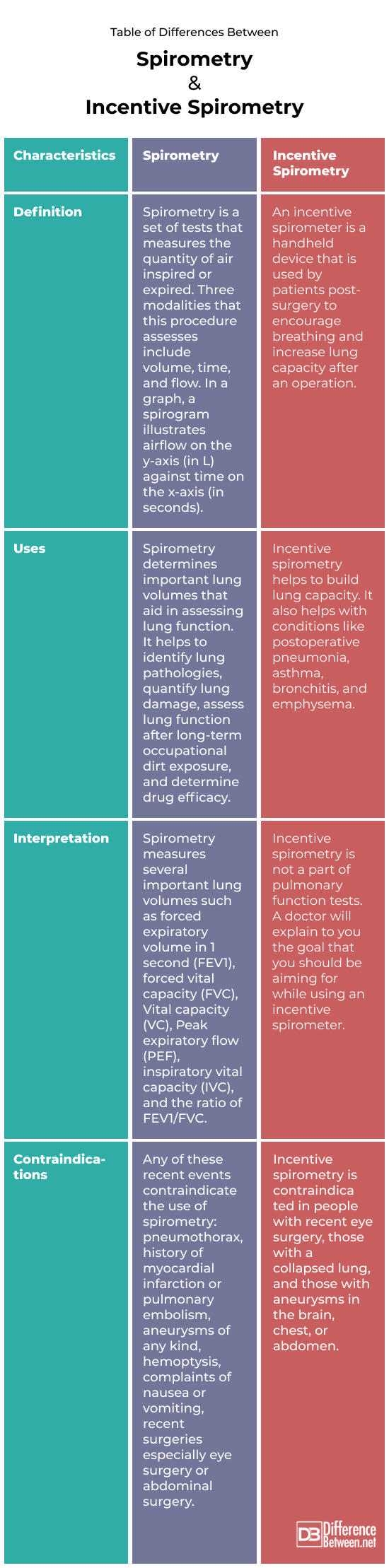
Difference between spirometry and incentive spirometry
Definition:
Spirometry is a set of tests that measures the quantity of air inspired or expired. Three modalities that this procedure assesses include volume, time, and flow. An incentive spirometer is a handheld device that is used by patients post-surgery to encourage breathing and increase lung capacity after an operation.
Procedure:
A spirometry test is a noninvasive procedure. It takes about 45 minutes and is an outpatient investigation carried out by a respiratory therapist or technician. An incentive spirometer is prescribed by doctors as a post-operative measure. The device can easily be operated at home. The procedure involves holding the device upright, sealing the mouthpiece with your lips, and inspiring slowly and as much as one can. The piston or the balls are supposed to rise more and more with practice. The breathing exercises are to be repeated 10 to 12 times per hour or as advised.
Uses:
Spirometry determines important lung volumes that aid in assessing lung function. It helps to identify lung pathologies, quantify lung damage, assess lung function after long-term occupational dirt exposure, and determine drug efficacy. Incentive spirometry helps to build lung capacity. It also helps with conditions like postoperative pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema.
Interpretation:
Spirometry measures several important lung volumes. It measures forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), Vital capacity (VC), peak expiratory flow (PEF), forced expiratory flow, and inspiratory vital capacity (IVC). The most important relation that can be evaluated via spirometry is the ratio of FEV1/FVC. On the other hand, incentive spirometry is not a part of pulmonary function tests. A doctor will explain to you the goal that you should be aiming for while using an incentive spirometer.
Contraindications:
Any of these recent events contraindicate the use of spirometry: pneumothorax, history of myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolism, aneurysms of any kind, hemoptysis, complaints of nausea or vomiting, recent surgeries especially eye surgery or abdominal surgery. Incentive spirometry is contraindicated in people with recent eye surgery, those with a collapsed lung, and those with aneurysms in the brain, chest, or abdomen.
Table of differences between spirometry and incentive spirometry
FAQs
What are the two types of spirometry?
Peak flow meters or digital spirometer and incentive spirometry.
Why is a spirometer called an incentive spirometer?
Incentive spirometry provides visual incentives or cues that show that the breathing exercise is adequately being done.
What are the two types of incentive spirometers?
Flow-oriented incentive spirometer and volume-oriented incentive spirometer.
What is incentive spirometry?
Incentive spirometry is a breathing exercise that is advised postoperatively to patients to ensure good breathing.
What is the second name for spirometry?
Lung function test.
What is the difference between a peak flow meter and an incentive spirometer?
The peak flow meter measures the ability of exhalation whereas incentive spirometry assesses inhalation.
- Differences Between Reptiles and Amphibians - May 17, 2024
- Difference Between Ophthalmology and Optometry - May 15, 2024
- Difference Between Fear and Anxiety - April 2, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Derom, Eric, et al. "Primary care spirometry." European Respiratory Journal 31.1 (2008): 197-203.
[1]Derom, Eric, et al. "Primary care spirometry." European Respiratory Journal 31.1 (2008): 197-203.
[2]Barreiro, Timothy, and Irene Perillo. "An approach to interpreting spirometry." American family physician 69.5 (2004): 1107-1114.
[3]Restrepo, Ruben D., et al. "Incentive spirometry: 2011." Respiratory care 56.10 (2011): 1600-1604.
