 Oxidation vs Combustion
Oxidation vs Combustion
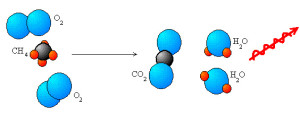
We have heard of the process of combustion and oxidation in our school. But only a few know about the main differences between them. In combustion organic compounds are completely burnt and get oxidized to CO2 and water. The process needs oxygen to occur. However in oxidation, oxygen is added to the compound. In case of oxidizing the element, we can say that an ion of negative charge has been lost or an atom is lost from the element.
Whenever combustion takes place oxidation is the end result, but it is not the same for oxidation. Combustion is accompanied with exothermic reactions which happen after a series of complex chemical reactions. It involves an oxidant that is required to catapult the experiment. Heat and light are also produced during the reaction. On the other hand in oxidation, oxygen is gained and hydrogen molecules or the electrons are lost thereby giving the element or the compound an oxidized form.
What happens in combustion? In this process the compound reacts with the element that acts like an oxidizing element (for example oxygen or fluorine). The end substance obtained consists of compounds which also have the oxidizing element as part of their chemistry. What is the procedure of oxidation? In oxidation the oxidation state of the compound is changed by two processes:
Redox process: For example oxidation of carbon to CO2.
Reducing the element of carbon to obtain CH4, also known as methane by the help of hydrogen.
This can also be represented by the example of sugar oxidation that takes place within the human body. This process involves a series of very complex process that includes electron transfers within the cell structure.
There may be different types of combustion processes like rapid combustion, complete combustion and incomplete combustion. We can define oxidation as a process in which oxygen reacts with the substances that come in its contact and form substances which have different properties. For example, iron or Fe gets converted to Fe3O4 when oxygen reacts with it. This is also termed as rusting that occurs in our day to day life. Oxidation can take place in case of living organisms too.
Combustion takes place in the liquid fuels that you burn in your vehicles. This process takes place in an atmosphere where oxygen is available and the entire reaction takes place in a gas phase.
Summary:
1. In combustion process organic compounds are oxidized in carbon and H2O molecules. The process requires oxygen participation. Whereas in oxidation, an ion is lost by the addition of oxygen.
2. In combustion, oxidation is the end process but same is not true for the oxidation process.
3. In combustion heat and light are produced but this is not the same with the oxidation.
- Difference Between Schizophrenia and Psychosis - March 7, 2024
- Difference Between African and Asian Elephants - March 7, 2024
- Difference Between Sunscreen and Sunblock - February 15, 2024

There are a number of factual errors in this entry attempting to illustrate the difference between the combustion of fossil fuels to obtain useful energy and the oxidation of hydrogen fuel to obtain useful energy. It is a little confusing because both methods of converting stored chemical energy into useful mechanical energy (to drive cars or to turn turbines & generate electricity) are redox (REDuction-OXidation) reactions. Here is a shorter, but more accurate & factually correct version of the differences.
Combustion of carbon-based fossil fuels (oil, gas, coal) is what we normally use today to generate energy. Gasoline in the car undergoes combustion in an internal combustion engine (ICE) which turns the chemical energy stored in the gasoline into mechanical energy driving the crankshaft. Combustion is a complex oxidation reaction of a gas, liquid, or solid fuel that occurs at very high temperatures generating heat and light we call a flame. During combustion of a hydrocarbon (like those found in gas & diesel) oxygen oxidizes the carbon in the fuel to carbon dioxide and is itself reduced to water. There is a net transfer of electrons and hydrogen from the hydrocarbon to the oxygen and this exchange liberates the stored chemical energy as light, heat & a small explosion that drives the piston down & turns the crankshaft.
Combustion is rarely a perfectly coordinated reaction and incomplete oxidation of the hydrocarbon releases not only carbon dioxide but also carbon monoxide (a deadly poison gas). Also due to the high temperatures generated oxides of nitrogen gas which can lead to air pollution (i.e.smog) in our cities. Nitrogen gas (N2) is present along with oxygen gas (O2) in our atmosphere, in fact the atmosphere is approximately 80% N2 and 20% O2!
Oxidation of hydrogen is where we hope our fuel economy is headed in the near future. Instead of putting liquid gasoline in the gas tank of your car, you will fill up your onboard hydrogen storage device (a technical challenge being worked on) with condensed hydrogen gas. The reaction here is between hydrogen and oxygen without any carbon and the reaction is carried out in a controlled, low temperature way by physically separating the two half-reactions that make up a single redox reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell. The oxidation side is where hydrogen gas releases its electrons and becomes a hydrogen ion, H+. The electrons are carried by a wire (electrons traveling along a wire is what we call electricity) to the reduction side and along the way the electricity can be used to do work (i.e. turn the crankshaft of the hydrogen car)! When they reach reduction side they are passed to the oxygen as are the hydrogen ions that came along a separate path in the fuel cell. The electrons, the hydrogen ions, and the oxygen combine to make water (H2O) and complete the whole redox reaction and the electrical circuit.
The great thing about hydrogen fuel technology vs. fossil fuel combustion for generating our energy is that there is no carbon involved! Therefore, no carbon dioxide & no carbon monoxide are generated – the first contributes greatly to global warming and the second is poisonous. Also since it is carried out a low temperatures, there is no side reaction oxidation of nitrogen to smog-generating NO compounds!
Transportation alone is responsible for a monumental amount of gaseous carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides on our planet. These harmful gases daily generated on a vast scale planet-wide contribute directly and indirectly to global warming, ozone depletion, acidification of atmosphere & hydrosphere, ecological problems through pollution or loss of habitat, respiratory disease, cancer, etc. The negative effects & impact of these pollutants on our environment & climate endanger not only our own health, but the health of the flora & fauna with whom we share the Earth. The health of our very planet is imperiled if we do not begin to adopt & embrace alternative fuels & alternative strategies to address our ever-expanding energy needs.
Reply
Thanks for your wonderful information.
Reply
no.
Reply
Oxidation vs Combustion
We have heard of the process of
combustion and oxidation in our
school. But only a few know about the
main differences between them. In
combustion organic compounds are
completely burnt and get oxidized to
CO2 and water. The process needs
oxygen to occur. However in
oxidation, oxygen is added to the
compound. In case of oxidizing the
element, we can say that an ion of
negative charge has been lost or an
atom is lost from the element.
Whenever combustion takes place
oxidation is the end result, but it is not
the same for oxidation. Combustion is
accompanied with exothermic
reactions which happen after a series
of complex chemical reactions. It
involves an oxidant that is required to
catapult the experiment. Heat and light
are also produced during the reaction.
On the other hand in oxidation, oxygen
is gained and hydrogen molecules or
the electrons are lost thereby giving
the element or the compound an
oxidized form.
What happens in combustion? In this
process the compound reacts with the
element that acts like an oxidizing
element (for example oxygen or
fluorine). The end substance obtained
consists of compounds which also
have the oxidizing element as part of
their chemistry. What is the procedure
of oxidation? In oxidation the oxidation
state of the compound is changed by
two processes:
Redox process: For example oxidation
of carbon to CO2.
Reducing the element of carbon to
obtain CH4, also known as methane by
the help of hydrogen.
This can also be represented by the
example of sugar oxidation that takes
place within the human body. This
process involves a series of very
complex process that includes
electron transfers within the cell
structure.
There may be different types of
combustion processes like rapid
combustion, complete combustion and
incomplete combustion. We can define
oxidation as a process in which
oxygen reacts with the substances
that come in its contact and form
substances which have different
properties. For example, iron or Fe
gets converted to Fe3O4 when oxygen
reacts with it. This is also termed as
rusting that occurs in our day to day
life. Oxidation can take place in case
of living organisms too.
Combustion takes place in the liquid
fuels that you burn in your vehicles.
This process takes place in an
atmosphere where oxygen is available
and the entire reaction takes place in
a gas phase.
Summary:
1. In combustion process organic
compounds are oxidized in carbon and
H2O molecules. The process requires
oxygen participation. Whereas in
oxidation, an ion is lost by the addition
of oxygen.
2. In combustion, oxidation is the end
process but same is not true for the
oxidation process.
3. In combustion heat and light are
produced but this is not the same with
the oxidation.
Reply
all the above answers are partly correct and partly not correct. In both the cases, heat and light energy are released. In normal combustion, the combustible elements react with atmospheric oxygen present in the atmospheric air, whereas , in oxidation or chemical combustion, it wont use the atmospheric air. Instead, it takes some oxygen from the available chemical compound, like iron oxide etc. and form into co2, h2o etc. Formation these end products also release heat energy which is known as formation enthalpy energy.
Reply