What is Green Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry?
While environmental chemistry is associated with the impact of polluting chemicals on the natural resources, green or sustainable chemistry focuses on the impact of environmental factors or attributes with respect to chemistry, reduction in the consumption of conventional resources and technological solutions for preventing pollution.
Both the concepts are different from each other

What is Green Chemistry?
Green chemistry, also termed as sustainable chemistry is that branch of chemical sciences that emphasizes on design of chemical processes and products that minimize generation of hazardous chemical substances.
The principles of Green Chemistry allow policy people, institutions, scientists and engineers to safeguard and benefit the economy, planet, nature, resources and people by identifying innovative methods to minimize waste, conserve energy, and identify and discover alternatives for hazardous substances.

What is Environmental Chemistry?
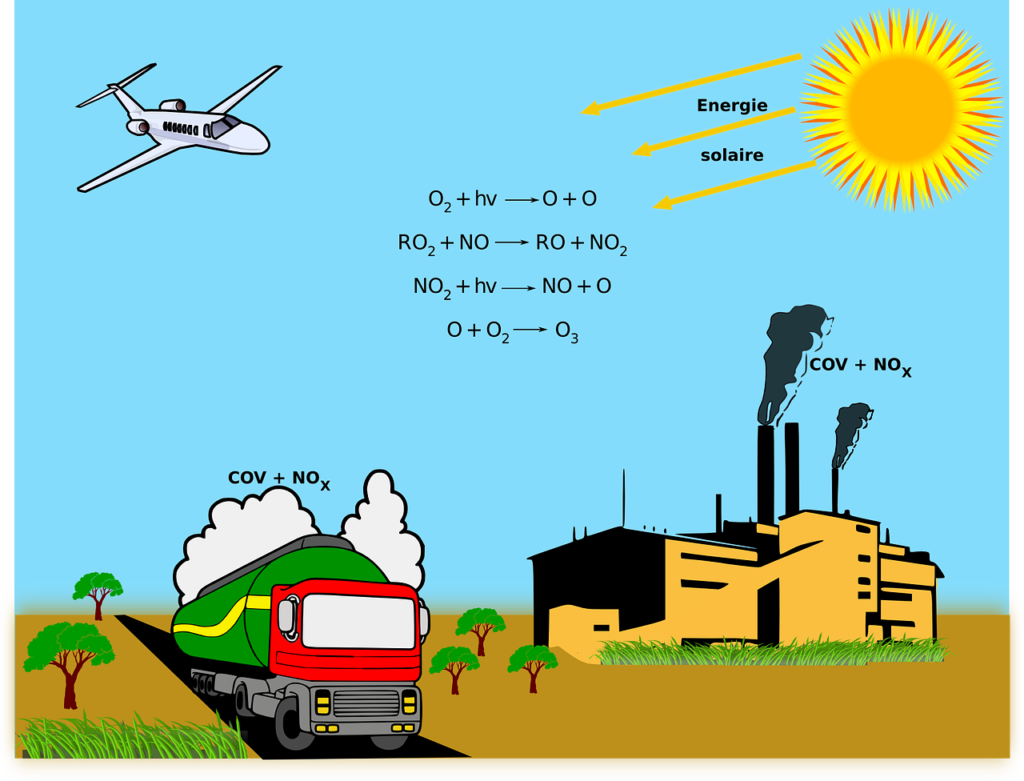
Environmental chemistry is the branch of science that involves the study of biochemical processes that occur in nature. It involves the understanding of how the uncontaminated environment works, and which naturally occurring chemicals are present, in what concentrations and with what effects. In the absence of this branch of science, it would not be possible to accurately evaluate, assess and identify the anthropogenic effects like release of hazardous chemical from industries and pollution on the natural environment. It is a multi-disciplinary science that, in addition to chemistry, involves physics, life science, agriculture, material science, public health, sanitary engineering, and so on. To sum up, it can be said that Environmental chemistry, is the study of the impacts, source points, reactions, destination of chemical species in the air, water, and land, transport, and the impact of human actions on various components of environment, such as hydrosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere.
Difference between Green Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry
Definition
Green Chemistry
It is an area of chemical engineering that has established and created a set of guidelines, principles, products, and processes that alleviate or eliminate the utilization and generation of hazardous substances at the source.
Green Chemistry is a key to sustainable development, as it directs and drives the scientific community to the remedial and innovative solutions for the existing environmental problems.
Environmental Chemistry
Environmental chemistry is the branch of science that focusses on the biochemical process occurring in air, water, aquatic and terrestrial establishments and the impacts of pollution and other anthropogenic activities on them.
This concept should not be confused with sustainable or green chemistry, which emphasizes to minimize pollution at its source.
Environmental chemistry includes topics such as marine chemistry, environmental modelling, biochemistry, geography, astrochemistry, atmospheric chemistry, geochemistry, and pollution remediation.
Principles
Green Chemistry
- Designing Safer Chemicals
- Prevention
- Safer Solvents and Auxiliaries
- The design of energy efficient processes
- Less Hazardous Chemical Syntheses
- The use of Renewable Energy resources and Feedstocks
- Reduce Derivatives
- Catalysis
- Design for Degradation
- Inherently Safer Chemistry for Accident Prevention
- Real-time analysis for Pollution Prevention
- Atom Economy
Environmental Chemistry
Environmental Chemistry does not have any principles but parameters and measurable factors that focus on identification of natural resources, source of pollutants and their impacts. These can include:
- Organometallic compounds, heavy metal contamination of land by industry, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon, Nutrients leaching from agricultural land into water courses (algae), urban runoff of pollutants like include gasoline, motor oil and other hydrocarbon compounds
- Contamination of air, water and soil
- Environmental indicators – pollution parameters
- Method of monitoring / testing
- Mitigation or control
- Elimination, Recycle, Reduction and Efficient Treatment
Benefits of green chemistry
Green Chemistry
The environmental and societal benefits of green chemistry include:
- Minimising negative environmental effects of chemical processing and manufacturing
- Developing and offering technologies that are beneficial and economically competitive for industry
- Using renewable resources and minimizing consumption of non-renewable resources
- Avoiding the use of bio accumulative, persistent, toxic, and otherwise hazardous materials
Environmental Chemistry
Human Health
- Cleaner air
- Cleaner water
- Reduced use of toxic and hazardous materials and maximum safety for workers in the chemical establishment
- Safer consumer products of all types
- Less exposure to such toxic chemicals as endocrine disruptors (chemicals that interfere with hormonal systems at certain doses)
- Safer and healthy food – removal of tenacious toxic chemicals that are prevalent in the food chain
Environment
- Less suffering to the wildlife, forests and plants due to reduction in release of chemicals ending up in the environment
- Less chemical disruption of ecosystems
- Lower potential for ozone depletion, global warming, and smog formation
- Minimization in dumping of hazardous wastes in the landfills
Economy and business:
- Higher yields for chemical reactions
- Minimal synthetic steps and swift manufacturing process
- Saving of energy and water and increased plant capacity
- Waste minimization
- Minimal investment on remedial measures
- Reduction in use of fossil fuels thereby minimizing their depletion
- Minimized size of manufacturing and processing plant or carbon footprint through maximized throughput
- Improved competitiveness of chemical manufacturers and their customers
Summary
The points of difference between Green Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry have been summarized as below:

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024