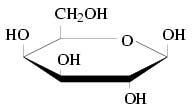
 Although the molecular formula of glucose and galactose are identical, they have distinct structural formulas.
Although the molecular formula of glucose and galactose are identical, they have distinct structural formulas.
Glucose is a simple sugar (monosaccharide) and also termed as blood sugar, grape sugar or corn sugar. It is a vital carbohydrate in biology. It is a premium source of energy for the living cells and also acts as a metabolic intermediate. It is among the chief products extorted from the process of photosynthesis. On the other hand, galactose also comes under the family of monosaccharide and it is a type of sugar that is less sweet in comparison to glucose. It consists of food energy (expressed in calories or joules) and termed as nutritive sweetener.
There are only two stereoisomers actually known as glucose in the category of aldohexose sugars. In these two stereoisomers, only dextrose monohydrate (commonly known as D-glucose) is organically active. In contrast, there is polymer of sugar galactose called galactan. It exists in the body to maintain the supply of galactose. It is stored inside the body in bulk form at a place called hemicellulose. Whenever there will be an additional requirement of galactose than the process of hydrolysis takes place and galactan is eventually converted into galactose.
Coming back to glucose, besides D-glucose there is one more glucose, which is biologically inactive. The inactive form of glucose is termed as L-glucose. It is not possible to metabolize the molecules of L-glucose by the process called glycolysis.
Glucose and galactose are also synthesized by the body. However, the external sources will vary from each other. Glucose can be divided into two types: simple carbohydrate and complex carbohydrate. Simple carbohydrates easily get to digest and their main sources include fruits and their juices, alcoholic beverages, sweets and table sugar. Complex carbohydrates get digested slowly. Their major sources include beans and legumes, whole grains, breads, cereals and nuts.
The major sources of galactose include sugar beets, dairy products and different gums & mucilages. Galactose is also synthesized by the body. It forms a part of glycoproteins and glycolipids in various tissues.
Glucose and galactose can also be differentiated on the basis of their melting point. The standard melting point of galactose is 167°C and the melting point for α-D-glucose is 146 °C and β-D-glucose is 150 °C.
- Difference Between Flammable and Combustible - October 8, 2009
- Difference Between a CEO and a President - October 8, 2009
- Difference Between Ghosts and Spirits - October 8, 2009

i am studenty leaning about biochemistory so that i want or need supportes some chemical
Reply