Difference Between DNA and Genes
In genetics, DNA and genes are often used interchangeably, but they are significantly different. To enhance your knowledge as a genetics expert, it makes sense to learn to distinguish between both terms. We’ve compiled a guide to show you the difference between DNA and genes.

What is DNA?
DNA, also known as deoxyribonucleic acid, is a biomolecule discovered in 1869 by Johannes Freidrich Miescher, a Swiss biologist. Miescher found that this molecule had twisted strands filled with complementary genetic information. These strands form a nucleotide ladder twisted at both ends, with DNA nucleotides comprising phosphate groups, sugar, and nitrogen bases.
Simply put, these nucleotide strands are the genetic material that copies information about replication, hereditary traits, and mutation. It also contains information about the equal distribution of DNA during cell division. DNA is present in every human cell and is the primary transmitter of your genetic code.
What are Genes?
Genes are the unit building blocks of the human body and are made of DNA. They are an exciting subdivision of DNA transmitted from parent to offspring. The body is filled with packets of human genes, also known as chromosomes. However, there are 23 pairs of 46 chromosomes in every human being.
During fertilization, the fetus will receive one pair of chromosomes from the mother and another pair from the father. These chromosomes control the functioning of DNA and RNA. A full-grown adult has over thirty thousand genes in every human cell.
Similarities Between DNA and Genes
We’ve broken down the meaning and significance of DNA and genes. It’s clear that both terms are crucial aspects of human biology, but what are their similarities? They include:
- Both are important in the efficient transmission of different traits from parents to offspring.
- Both are crucial to the organism’s biological characteristics and development.
- Both are crucial in fields such as agriculture, medicine, and forensics.
What is the Difference Between DNA and Genes?
It’s important to avoid using DNA and genes interchangeably. If you study both concepts closely, you’ll notice distinct differences between both in terms of:
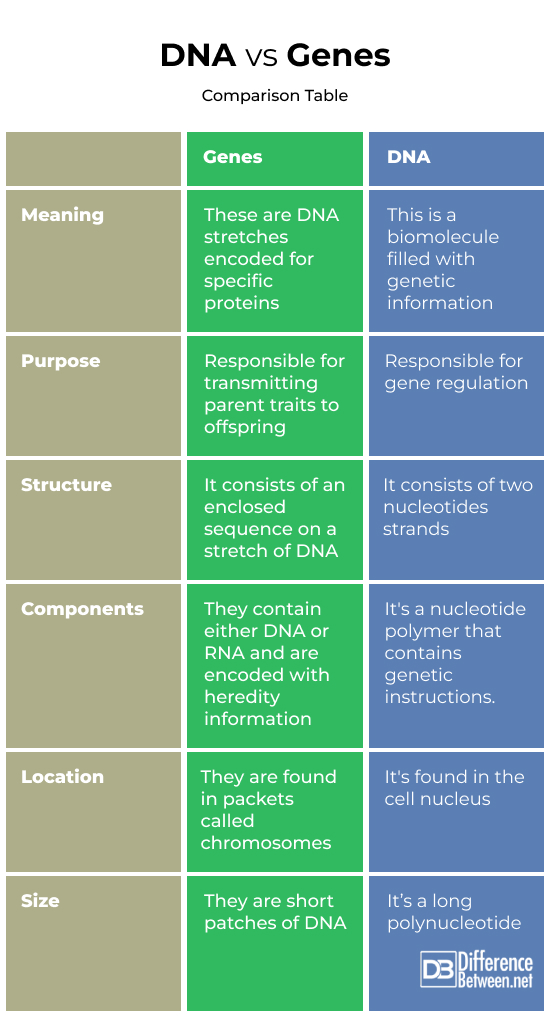
- Purpose: DNA is a chemical that stores the genetic information of organisms and is designed for gene regulation. On the other hand, genes are DNA stretches encoded for specific proteins, copying unique traits, and supporting seamless inheritance.
- Structure: DNA exists as long strands of nucleotides, forming a double-helix structure. Human gene structure comprises regulatory and coding sequences, with the coding sequence consisting of introns, untranslated regions, and exons, and the regulatory sequence including the promoter region.
- Location: Most of human DNA is found in the cell nucleus, with trace amounts in the mitochondria. Genes are found in a part of the cell nucleus called chromosomes, with 23 pairs in the human cell.
- Components: DNA comprises nucleotide sequences combined with sugar-phosphate bonds, while genes are mostly made up of DNA with few RNA.
DNA vs. Genes Comparison Table
Summary
When you review the details about DNA and genes, their differences are apparent. While genes are comprised of DNA and(or) RNA, they serve different functions. Each individual DNA is responsible for gene regulation, while genes transmit traits between generations.
FAQs
Is genes and DNA the same thing?
DNA and genes are use interchangeably but they aren’t the same thing.
Is genes a part of DNA?
Genes are made up of DNA and RNA.
What is the difference between DNA and genes and proteins?
A small portion of a DNA is called a gene. Certain genes are responsible for the production of a particular protein in the body. This protein will serve different traits.
Why is DNA called a gene?
The complete set of human DNA is called a genome.
Which is bigger gene or DNA?
A gene is bigger than DNA. Genes are short DNA stretches while DNA is a polynucleotide.
How much of DNA is genes?
There are 25,000 genres in a complete DNA set.
Do genes make up 100% of DNA?
Genes are only 1-2% of human DNA. The remaining 98-99% is called non-coding DNA.
Is DNA 100% Correct?
DNA replicates itself using masses of bases and are exactly 99% identical in every person.
How much DNA does everyone have?
This human DNA comprises 3.2 billion chemical base pairs equaling a total of 25,000 genes.
What is DNA explained simply?
DNA can simply be defined as a polynucleotide molecule containing genetic data.
Do all humans have the same DNA?
Humans have 99% identical DNA. Our unique features come from a 1% variation.
Does all life have DNA?
There’s DNA in all living things. You’ll find a complete DNA set in every cell of a multicellular organism.
- Difference Between Radiation and Chemo - February 15, 2024
- Difference Between DNA and Genes - February 15, 2024
- Difference Between Aorta and Pulmonary Arteries - December 16, 2009
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
15 Comments
Trackbacks
- Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes | Difference Between
- Difference Between DNA and RNA | Difference Between | DNA vs RNA
- Difference Between Fraternal and Identical Twins | Difference Between | Fraternal vs Identical Twins
- Difference Between Skin And Shell | Difference Between | Skin And Shell
- Different Between UVA and UVB | Difference Between | Different Between UVA vs UVB
- Difference Between Gene and Allele | Difference Between | Gene vs Allele
- Difference Between Gene and Allele | Difference Between | Gene vs Allele
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAFI4BSWWd0-dna-gene-helix-spiral-molecule-structure/
[1]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADCTtRC53o-chromosome-scientific-concept-medical-symbol-for-gene-therapy-with-depth/
[2]Genetic Alliance; The New York-Mid-Atlantic Consortium for Genetic and Newborn Screening Services. Understanding Genetics: A New York, Mid-Atlantic Guide for Patients and Health Professionals. Washington (DC): Genetic Alliance; 2009 Jul 8. CHAPTER 1, GENETICS 101.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK115568/
[3]Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000. Heredity, Genes, and DNA. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9944/
[4]Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2002. From DNA to RNA.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26887/

Make sure that you don’t end up looking out of proportion. In the
right portions the foods you eat can actually stimulate your body to burn fat.
The amount of muscle lost during a vacation from weight training can be significant if the time
away from such workouts is excessive, so my recommended period of time to vacation from weight training workouts is seven days, and preferably, a vacation from weight training should never exceed two weeks, as the body begins to reduce the amount of muscle after a 1-2 week period
(dependent upon genetics). To add calories to
the diet you can replace water in sauces, hot cereals and soups with
full cream milk. We must remember that it
is very important to the correct path, you have to control weight and not sacrifice performance strictly by the fact
lift more weight.
Thanks for your help…….it’s great to get such differences clearly……..
Its very informatory
How come DNA is traceable back to forever, when genes are diluted 50/50 with every generation? You are 50% of your mother and father; but only 25% of your grandfather and 12,5% of your great grandfather
Here,it is said that DNA contains 2 copies of 23 chromosomes each…..but as far as I know chromosomes contain DNA
That Picture explained it all.
Honestly its very informative..we really appreciate this and such hope for the next.
Some people say that DNA and gene r not same
Why plz
One sentence for me