Difference between Creatine and Creatinine
What is Creatine & Creatinine?
Both Creatine and Creatinine are two proteins found in the blood in the body. Both Creatine and creatine are in homeostasis, in human bodies. They are obtained from proteins and that is why the levels of creatinine and creatine are greater in meat. Hence, these levels are higher in people who eat meat as compared to people who are vegetarian.
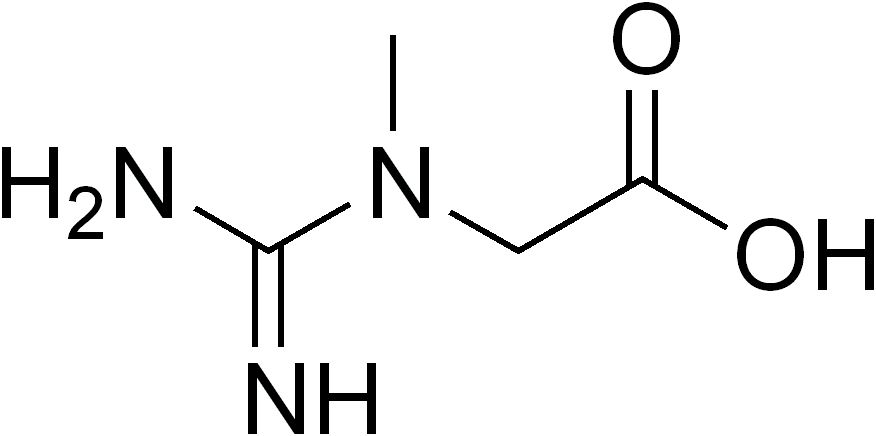
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a substance which is naturally present in vertebrates. Creatine is an amino acid stored mostly in the body’s muscles and the brain. Though creatine can be created synthetically, it is mostly derived from seafood and red meat. It is made in liver, pancreas and kidneys and it is a nitrogenous substance and possesses a carboxylic group to it. Creatine is produced from glycine, L-arginine, and L-methionine amino acids.
People consume creatine orally to treat brain disorders and conditions, heart diseases and other neurological issues. Topical creatine is used to treat ageing skin.
Creatine also treats; depression, fibromyalgia, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, muscle atrophy and cramps, head trauma, diabetes, schizophrenia, muscle breakdown in the spine, Rett syndrome, gyrate atrophy (eye disease), Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, breathing problems in infants during sleeping, and recovery from surgery.
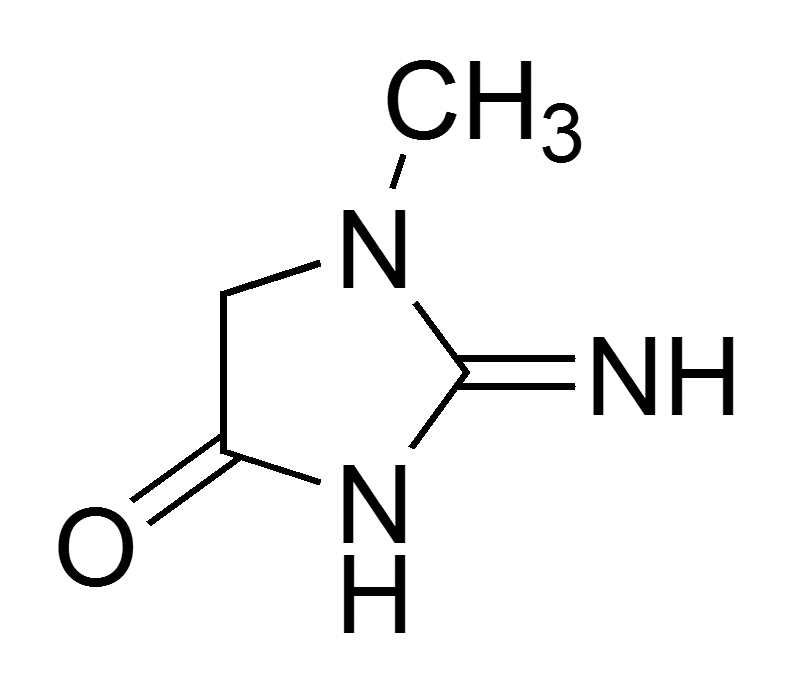
What is Creatinine?
Creatinine is a chemical waste product formed by the breakdown of creatine in muscle cells. The production of creatine phosphate depends on the muscle mass of an individual and is eliminated from the body through kidneys. It is transported into the kidney and through the bloodstream and filtered and excreted from the body in urine. The creatinine levels in men is higher in men as compared to women. This is because men possess more skeletal muscles than women.
Blood and urine creatinine levels are assessed to calculate the creatinine clearance and exhibit the glomerular filtration rate. Malfunctioning and damage of kidneys If the kidneys are severely damaged and malfunctioning, creatinine dispensation rate will indicate that. Low levels of creatinine indicate Muscle atrophy, sedentary lifestyle, malnutrition / debility and multiple sclerosis.
Some benefits of creatinine clearance are;
- It does not require I.V administration
- It can be easily estimated
- It is a normal metabolite of the body
- In early stages, it has got advantage over S. Creatinine.
Difference between Creatine & Creatinine
Definition
Creatine
Creatine is an amino acid produced naturally in the human body by the kidney, liver and pancreas.
Creatinine
It is a biological waste product that is produced by muscles by the breakdown of a compound called creatine.
Molecular formulae and scientific name
Creatine
Molecular formula – The chemical formula for creatine is C4H9N3O2
Scientific name – 2- (carboximidoyl-methyl- amino) acetic acid.
Creatinine
Molecular formulae – The chemical formula for creatinine is C4H7N3O
Scientific name – 2-amino-1-methyl-5h-imidazol-4-one
Significance
Creatine
Creatine is very important for the body. It is an organic acid. It is a natural compound created in the body and is obtained from the diet through meat products. It helps the muscle tissues generate more energy, speeds up growth of muscles, helps combat neurological and Parkinson’s diseases, reduce diabetes and improves high-intensity exercise performance. It is used as a dietary supplement meant for improving athletic performance and muscle strength.
Creatinine
Creatinine does not perform any vital function in the body. It is not an organic acid. However, Creatinine levels in the blood can help your doctor assess how well your kidneys are working. The test helps to diagnose certain diseases and to check for any issues and conditions with your kidney function.
If the kidneys are not performing as they should, however, creatinine levels in blood can elevate. When tests report that amount of this compound is very high, a doctor usually carries out additional testing to ascertain the extent of the issues with a person’s kidneys.
Purpose
Creatine
It is stored in the muscles and increases the muscle mass.
Creatinine
Creatinine production reduces the muscle mass.
Side effects
Creatine
High levels of creatine can cause;
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Muscle cramping
- Stomach pain
- Irregular heartbeat in some people
Creatinine
High levels of creatinine can cause;
- Possible malfunction or failure of the kidneys
- Swelling or oedema
- Confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dehydration
Structure
Creatine
Creatine has a linear molecule.
Creatinine
Creatinine has a heterocyclic structure.
Molar Mass
Creatine
The molar mass of creatine is 131.13 g/mol.
Creatinine
The molar mass of creatinine is 113.12 g/mol.
Summary of Creatine Vs. Creatinine: Tabular Form
The points of difference between Creatine and Creatinine have been summarized below:

- Difference Between Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect - May 18, 2024
- Difference Between Vaccination and Immunization - March 3, 2024
- Difference Between Selective Mutism and Autism - February 25, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Cooper, R., Naclerio, F., Allgrove, J., & Jimenez, A. (2012). Creatine supplementation with specific view to exercise/sports performance: an update. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 9(1), 33.
[1]Kreider, R. B. (2003). Effects of creatine supplementation on performance and training adaptations. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 244(1-2), 89-94.
[2]Lee, I. T., Sheu, W. H., & Lin, S. Y. (2016). The impact of creatinine clearance rate, daily urinary albumin, and their joint effect on predicting death in diabetic inpatients after discharge: an observational study. Medicine, 95(6).
[3]Levey, A. S., Bosch, J. P., Lewis, J. B., Greene, T., Rogers, N., & Roth, D. (1999). A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Annals of internal medicine, 130(6), 461-470.
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Creatine_neutral.png
[5]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Creatinine.png
