Difference Between Allodynia and Dysesthesia
Allodynia and dysesthesia are conditions that involve unusual sensations of pain. They are also associated with several underlying illnesses such as diabetes. Specifically, allodynia is the experience of pain from stimuli that are not normally painful while dysesthesia is defined as any impairment of the senses, particularly the sense of touch, which results from nerve damage. The following discussions further delve into these distinctions.
What is Allodynia?
Allodynia came from the Greek words “allos” which means “other” and “odyni” which means pain. It is defined as the experience of pain from stimuli (i.e., light touch, brushing hair, slight poke, etc.) which are not normally painful. This is a usual side effect of migraine; an affected individual may experience this when he washes his face, lays his head on a pillow, or other simple activities (American Migraine Foundation, 2019). This can also be symptom of a nerve condition or it can occur on its own.
The pain can vary from mild to severe. It can be felt as a burning sensation, an ache, or a squeezing pain. Allodynia’s complications include anxiety, sleep disturbances, depression, and fatigue. Its types include the following (De Pietro, 2017):
Thermal Allodynia
This type causes temperature-related pain; it occurs when there is a slight change of temperature on the skin. For instance, a drop of cold water may be felt as painful.
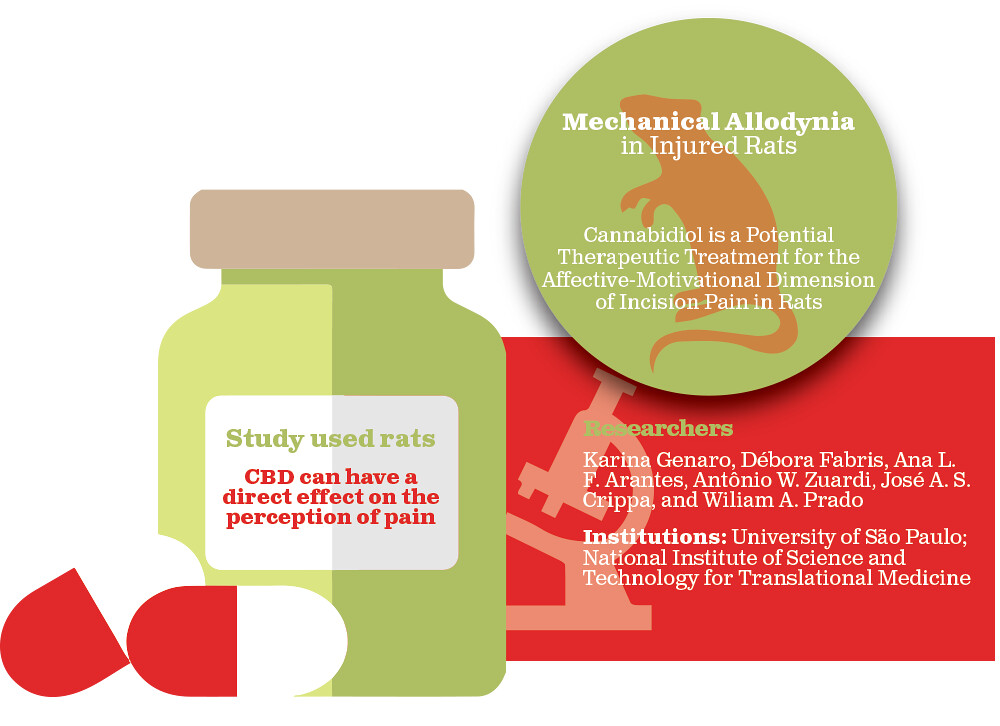
Mechanical Allodynia
This type is caused by movement across the skin. For example, a feather lightly brushing along the person’s arm may be perceived as extremely painful.
Tactile or Static Allodynia
This type occurs due to light pressure or light touch. For example, a mere shoulder tap may make a person with tactile allodynia yelp in pain.
The specific cause of allodynia is not known. Findings suggest that it is due to the malfunction or increased sensitivity of a particular type of nerve called nociceptors or pain receptors. The risk factors include migraines, postherpetic neuralgia (complication of shingles), fibromyalgia, diabetes, and complex regional pain syndrome.
Since there is no cure, the treatment for allodynia is focused on decreasing pain with the use of medications (i.e. Pregabalin, creams containing lidocaine, etc.), treatment of underlying condition (migraines, diabetes, etc.), and lifestyle changes (healthy diet, enough sleep, light exercise, quitting smoking, lessening stressors, etc.).

What is Dysesthesia?
Dysesthesia came from the Greek words “dys” which means “not normal” and “aesthesis” which translates to “sensation”. This condition is defined as any impairment of the senses, particularly the sense of touch (Dictionary.com). The usual symptoms include itching, burning sensation, feels like something is crawling on or under the skin, restrictive feeling (usually on the torso), radiating, sharp, or stabbing pains, aches like to that of sore muscles, tingling sensation, electric shocks sensation, an inexplicable feeling which is similar to that of hitting the “funny bone”, and hair loss.
The sensations may be acute or chronic; the following are the different types of dysesthesia (Huizen, 2019):
Cutaneous dysesthesia
Most individuals with scalp dysesthesia have sensitive skin. They may experience sensations of pain, irritation or burning when triggered by breezes or loose-fitting clothes.
Scalp dysesthesia
This is felt as an intensely painful burning sensation on or under the scalp’s skin. Those with this condition often scratch their scalps in vain and experience hair loss. This may also be caused by a condition that affects the bones in the neck and spine.
Occlusal dysesthesia
Without any apparent reason, those with this condition experience uncomfortable sensations when they bite. It is an uncommon complication of dental procedures.
Oral dysesthesia
This type is also known as “burning mouth syndrome”. It is experienced as unexplained burning or painful sensation in the mouth. Those with this condition may also experience changes in responses to temperature and their sense of taste. Oral dysesthesia has no exact cause and it may sometimes be attributed to a psychological disorder; however, it may also be a symptom of various conditions.
It is caused by nerve damage that leads to the stimulation of abnormal sensations. For instance, incorrect signals from damaged sensory nerves can cause the brain to prompt painful sensations in the leg even if there is nothing wrong (Pietrangelo & Goldman, 2020). Other conditions that this can occur with include multiple sclerosis, diabetes, Lyme disease, Guillain-Barre syndrome, HIV, shingles, stroke, nerve injuries, HIV, and overuse or withdrawal from drugs. Treatment of the underlying condition can usually lessen the symptoms, medications (anti-seizure, antidepressants, pain relievers, etc.) are also prescribed, and natural remedies (warm and cold compresses, hydration, skin-calming lotions, mindfulness, hypnosis, acupuncture, etc.).
Difference between Allodynia and Dysesthesia
Definition
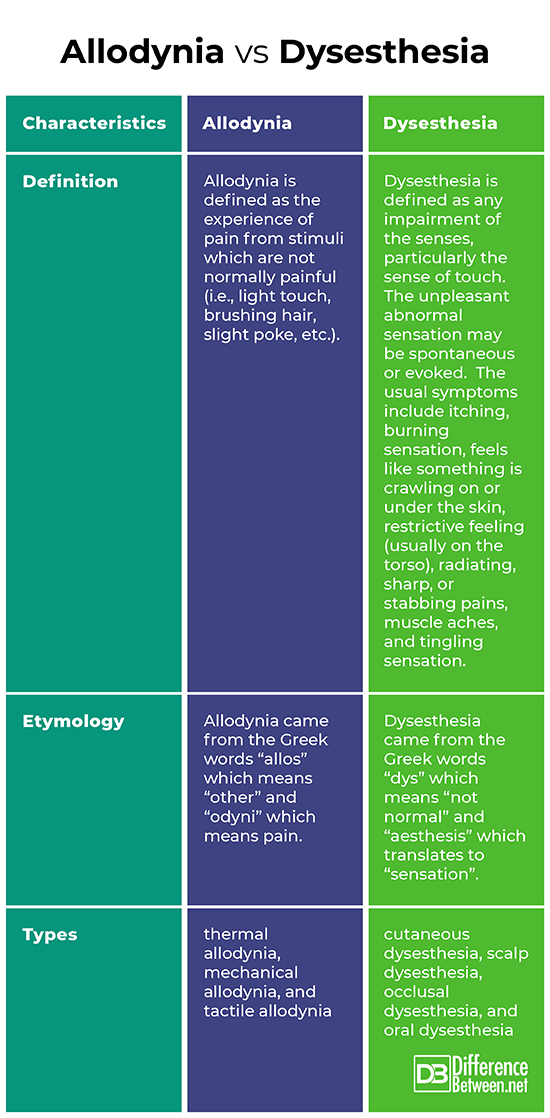
Allodynia is defined as the experience of pain from stimuli (i.e., light touch, brushing hair, slight poke, etc.) which are not normally painful. An affected individual may experience this when he washes his face, lays his head on a pillow, or other simple activities. In comparison, dysesthesia is defined as any impairment of the senses, particularly the sense of touch. The unpleasant abnormal sensation may be spontaneous or evoked. The usual symptoms include itching, burning sensation, feels like something is crawling on or under the skin, restrictive feeling (usually on the torso), radiating, sharp, or stabbing pains, aches like to that of sore muscles, tingling sensation, electric shocks sensation, an inexplicable feeling which is similar to that of hitting the “funny bone”, and hair loss.
Etymology
Allodynia came from the Greek words “allos” which means “other” and “odyni” which means pain. On the other hand, dysesthesia came from the Greek words “dys” which means “not normal” and “aesthesis” which translates to “sensation”.
Types
The types of allodynia include thermal allodynia, mechanical allodynia, and tactile allodynia. As for dysesthesia, the types include cutaneous dysesthesia, scalp dysesthesia, occlusal dysesthesia, and oral dysesthesia.
Allodynia vs Dysesthesia
Summary
- Allodynia is the experience of pain from stimuli that are not normally painful.
- Dysesthesia is defined as any impairment of the senses, particularly the sense of touch. The unpleasant abnormal sensation may be spontaneous or evoked.
- The types of dysesthesia include cutaneous, scalp, occlusal, and oral.
- The types of allodynia include thermal, mechanical, and tactile.
- Difference Between Hematoma and Melanoma - February 9, 2023
- Difference Between Bruising and Necrosis - February 8, 2023
- Difference Between Brain Hematoma and Brain Hemorrhage - February 8, 2023
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]American Migraine Foundation (2019). What to know about allodynia. https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/resource-library/what-to-know-about-allodynia/
[1]De Pietro, M. (2017). What to know about allodynia. Medical News Today. medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318867
[2]Dictionary.com. Dysesthesia. https://www.dictionary.com/browse/dysesthesia?s=t
[3]Huizen, J. (2019). All you need to know about dysesthesia. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319700
[4]Pietrangelo, A. & Goldman, L. (2020). Everything you need to know about dysesthesia. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/dysesthesia
[5]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/4605/28028362689_124c20a884_b.jpg
[6]Image credit: https://post.healthline.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Woman-Lotions-Hands-732x549-thumbnail.jpg
