Difference Between Agglutination and Precipitation
One of the fundamental characteristics of an antibody is its specificity to target antigen, which is basically the ability to bind to epitopes. This forms the basis of numerous serological assays. The interaction between an antibody and its corresponding antigen is used to identify several microorganisms. This interaction results in one of the following reactions: agglutination, precipitation, and complement activation.
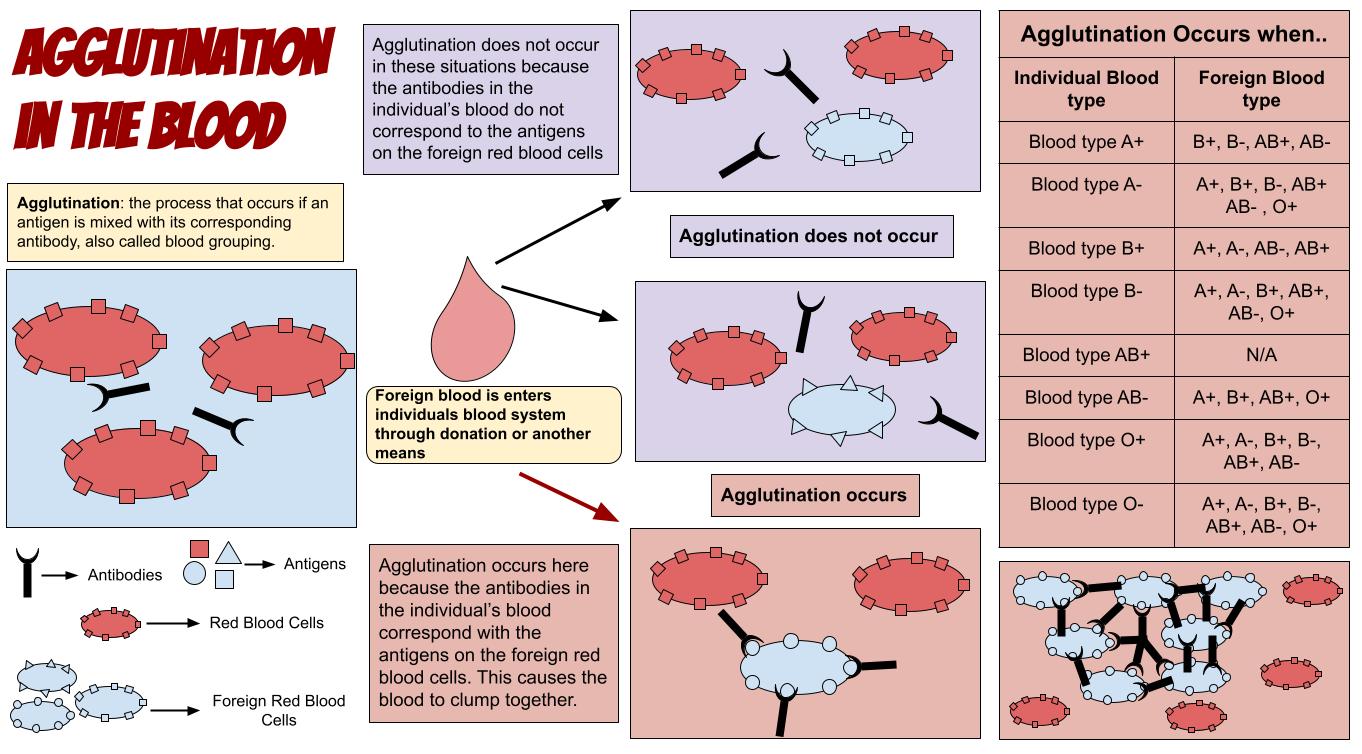
What is Agglutination?
Agglutination is the clumping of cells as the result of aggregation of antigens and antibodies. This visual expression occurs because one antibody simultaneously binds multiple antigens, which creates larger complexes. It is believed to be the oldest antibody-based reaction in medical diagnostics, which involve particulate antigens capable of binding antibody molecules. Particulate antigens include bacteria, or it could be white blood cells (WBCs) and red blood cells (RBCs), or it could be in the form of latex particles. The agglutination reaction is current used in haematology and diagnostic microbiology. This technique is commonly used as a simple and rapid means of determining blood groups. This is used as an indicator to detect the presence of antibodies against bacteria or red blood cells.
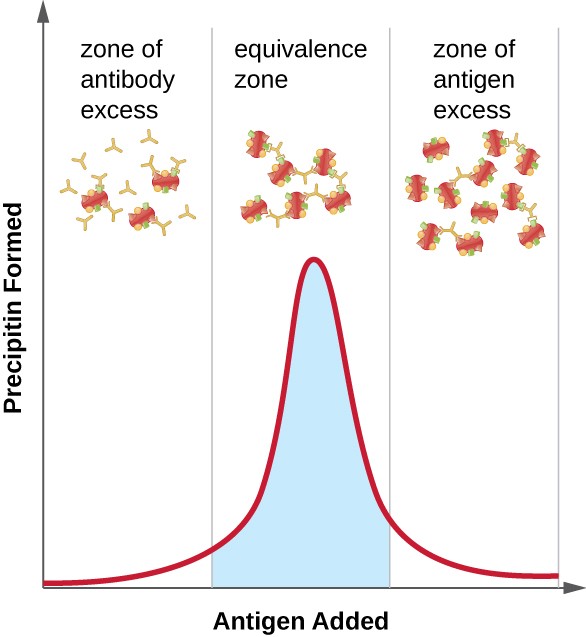
What is Precipitation?
When soluble antigens are aggregated by the corresponding antibody molecules, it forms immune complexes and when they become large enough to precipitate out of the solution, they become visible. This formation of large insoluble complexes is called precipitation reaction. Like the agglutination reaction, it is based on the interaction of antibodies and antigens, but the result is an insoluble product, the precipitate. This is basically a reaction between a soluble antigen and its corresponding antibody molecules in the presence of an electrolyte at an optimum temperature and pH. This underlying principle is based on the diffusion of antibody and antigen through a matrix, and the formation of a visible precipitate upon encounter. An antibody that aggregates soluble antigen is called precipitin. Quantitative analysis in precipitates is generally expressed in terms of nitrogen (N).
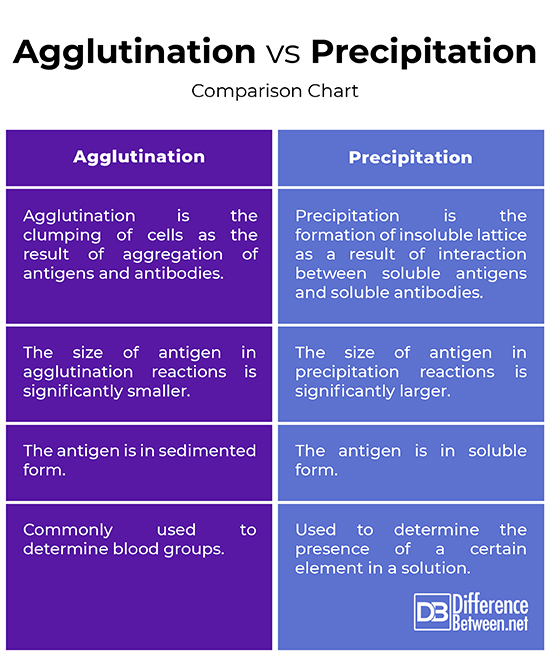
Difference between Agglutination and Precipitation
Process
– Both agglutination and precipitation reactions are the result of interaction between antibody molecules and the corresponding antigen molecules. However, agglutination is when one antibody simultaneously binds multiple antigens resulting in the clumping of cells. Precipitation, on the other hand, is the interaction of soluble antigens with soluble antibodies resulting in a visible insoluble compound called the precipitate.
Working Principle
– Agglutination occurs when an antigen of interest binds with a matching antibody, referred to as isoagglutinin, in the presence of an electrolyte at optimum temperature and pH, resulting in the formation of visible clumps or aggregates. Precipitation occurs when a soluble antigen interacts with the corresponding antigen in the presence of an electrolyte at optimum temperature and pH, resulting in the formation of cross-linkages or precipitates that settle down in the solution.
Antigen Size
– One of the primary differences between the two is the size of the antigen used in the reaction. The antigen-antibody reactions occur in varying proportions, with respect to volumes and strength of reactants used. However, precipitation requires considerable amounts of antigen to detect the presence of antibody in a sample. The size of antigen in agglutination reactions is significantly smaller than the antigens in precipitation reactions.
Agglutination vs. Precipitation: Comparison Chart
Summary
While methods in the precipitation reactions category are less specific than agglutination reactions, some remain the gold standard among serological techniques in the clinical testing. While the underlying principle of both the reactions is based on the binding of an antibody with the corresponding antigens, the end product is very different. Agglutination is the formation of large solid clumps as a result of antibody-antigen interaction, while precipitation is the formation of visible insoluble lattices or cross-linkages.
What is difference between agglutination and precipitation?
For agglutination and precipitation reactions to happen, the antigen must be multivalent and the antibody divalent. Agglutination is the formation of large complexes as a result of an antibody simultaneously binding multiple antigens, finally resulting in the clumping of cells. Precipitation, on the other hand, is the formation of a visible precipitate as a result of the interaction between antigens and their corresponding antibody molecules.
What is precipitation in antibody?
Precipitation is the result of interaction between two soluble reactants that come together to create one final insoluble compound called the precipitate. It is a popular in vitro method for estimating the concentration of antibody in serum or other fluids.
What are the 2 stages of agglutination?
Agglutination is a two-stage process – sensitization and the agglutination reaction. In the first phase, red cell is coated with antibodies. There is no visible clumping yet. The second stage is when a visible red clumping occurs as a result of the binding of the antibodies with the corresponding antigens.
What is an example of agglutination?
One of the best examples of agglutination in immunology is the visible clumping of cells such as bacteria. The first example of serum diagnosis underlying the principle of agglutination was applied in a typhoid fever diagnosis in 1896 by the French physician Fernand Widal, who developed the Widal test.
What is the precipitation test used for?
It remains the gold standard among serological techniques in the clinical laboratory. It works best when antigens and antibodies are at optimal proportions. It is used in the detection of immunoglobulin levels from the serum collected from an infected patient.
What is blood precipitation?
Blood precipitation is the interaction between two soluble reactants that result in the formation of insoluble lattice.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Alhabbab, Rowa Yousef. Basic Serological Testing. Berlin, Germany: Springer, 2018. Print
[1]Williams, Curtis A. and Merrill W. Chase. Agglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4. Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press, 2014. Print
[2]Wanger, Audrey, et al. Microbiology and Molecular Diagnosis in Pathology: A Comprehensive Review for Board Preparation, Certification and Clinical Practice. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2017. Print
[3]Williams, Curtis A. and Merrill W. Chase. Reactions of Antibodies with Soluble Antigens: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 3. Massachusetts, United States: Academic Press, 2014. Print
[4]Pavia, Charles S. Methods in Microbiology. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2020. Print
[5]Image credit: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1094/2016/11/03172856/OSC_Microbio_20_02_Precipform.jpg
[6]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Agglutination_in_the_blood.jpg
