Difference Between Caucus and Primary
You might already know that before a general election, candidates are chosen. It’s the most bewildering process in the American electoral system. When choosing presidential candidates, states have two ways of collecting votes: primaries and caucuses.
Primaries and caucuses are events where political parties choose their candidate for the presidency. Without them, there could be dozens of people on the ballot running for president. It’s necessary to narrow down the candidates. It’s a way to make sure the voices of the people are heard throughout the election process.
So what are primaries and caucuses, and how do they work?

What are Primaries?
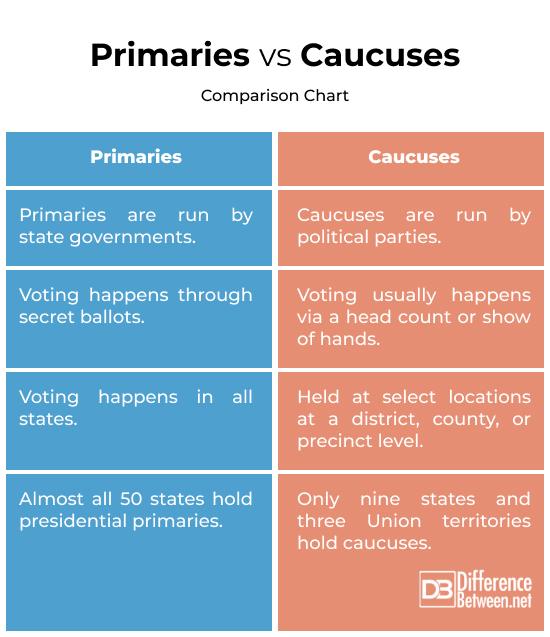
Most states in the U.S. hold primaries before the election to elect the president. It’s a simple process: voters in each state go to the polling booths and cast their votes for their preferred candidate. Primaries are generally held six to nine months before the general election. The state prints the primary ballots and sets the rules for ballot access.
The candidate who receives the most votes in a state gains delegates, and these delegates later attend the national party convention. The primary helps decide which candidate gets the party’s official backing. The chosen candidate then goes face-to-face with the nominee from the opposing party.

What are Caucuses?
Caucuses are a different story altogether. Some states hold caucuses in the months leading up to a presidential election to decide which candidate should represent their political party for president. Caucuses are small party meetings where voting usually happens via a head count or a secret ballot.
Caucuses today represent the first local level of delegate selection. Depending on the state, that level may be the precinct, the county, or the legislative district.
The number of caucus states has been reduced from 1972 to present. Today, only nine states and three Union territories hold caucuses. These are held as the starting point for the selection of delegates to the national convention. Finally, the number of votes each candidate gets determines how many delegates they get.
Difference between Primaries and Caucuses
Voting Process
A primary is a simple, straightforward voting process where voters in each state go to the polling booths to cast their votes for their preferred candidate. Voting happens through a secret ballot.
Caucuses are small party meetings where voting usually happens via a head count or a show of hands. The number of votes each candidate receives determines how many delegates they get. People gather at meetings or get into a debate to express their support for a candidate.
Representation
Primaries are generally held six to nine months before the general election. The primary season usually runs from February to June. Voters can cast their ballots throughout the day at their convenience within specified voting hours.
Caucuses are meetings run by political parties to vote on potential candidates. They are hosted at select locations at a district, county, or precinct level. In some meetings, candidates are chosen through secret ballots. Other meetings will have speeches and debates.
Decision-Making
The candidate who receives the most votes in a state gains delegates, and these delegates later attend the national party convention. The primary helps decide which candidate gets the party’s official backing.
Caucuses are held as the starting point for the selection of delegates to the national convention. Voters arrive at the location at a scheduled time, and party officials verify that they are eligible to vote. The number of votes each candidate gets decides how many delegates they get.
Primaries vs. Caucuses: Comparison Chart
Summary
The number of votes a candidate receives in a primary or caucus decides how many delegates he gets. All presidential candidates hope to win a majority of delegates. Each state holds caucuses and primaries differently. Depending on the state and the rules set by the political party, caucuses and primaries can be open or closed, or a mix of the two.
FAQs
How presidential primaries and caucuses work?
The general election for the presidency starts with primaries and caucuses. These are distinct methods that states use to select presidential nominees for each political party. These are the early stages where political parties choose their candidate for the presidency.
What does caucus mean in Canada?
In Canada, the term ‘caucus’ refers to all members of a particular political party within a legislative body. It’s a closed-door meeting where members discuss party policies, strategies, and internal matters.
What is a caucus in British English?
In British English, “caucus” generally refers to a closed meeting of a political group or party members.
What is the American caucus?
In the American electoral system, caucus refers to the process by which political parties in certain states choose their candidates for the presidency.
What is the synonym for caucus?
Synonyms of caucus are meeting, assembly, gathering, convention, conference, conclave, etc.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Smith, Steven S. and Melanie J. Springer. Reforming the Presidential Nomination Process. Rowman & Littlefield, 2009.
[1]Busch, Andrew E. The Rules and Politics of American Primaries: A State-by-State Guide to Republican and Democratic Primaries and Caucuses. Bloomsbury Publishing USA, 2019.
[2]Parshall, Lisa K. Reforming the Presidential Nominating Process: Front-Loading's Consequences and the National Primary Solution. Routledge, 2018.
[3]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEby3TRWWI-caucus-in-the-dictionary/
[4]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEEloI8kfw-presidential-primaries/
