Difference Between HSA and HRA
Looking for a way to save some dollars on your medical expenses? HRA and HAS are two types of financial accounts that help employed and self-employed individuals manage healthcare costs. Both accounts assist individuals and employees manage their healthcare expenses. HSA provides a personal savings plan, while HRA offers employer-sponsored support.
Here are some important details about HRA and HAS. We also break down some fundamental differences between HRA and HSA.

What is an HRA?
The term “health reimbursement arrangement” (HRA) refers to a benefit plan that is sponsored by a company and provides assistance to employees in covering medical expenses that are eligible. As a form of group health insurance, it is provided by employers to their employees. There is a predetermined amount that employers contribute to the HRA, and the majority of the time, the employer is able to deduct this financing from their taxes.
These health reimbursement accounts (HRAs) pay for your medical bills, including deductibles, co-payments, prescription drugs, and other costs associated with healthcare. Employers have the ability to prescribe the categories of costs that are eligible for reimbursement.
HRAs are frequently connected with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs), and in order for employees to receive the benefits of HRAs, they may be required to enroll in the health insurance plan that is associated with the HRA. Generally speaking, reimbursements from the HRA are exempt from taxation. On the other hand, depending on the plan, any monies that are not utilized at the conclusion of employment may be forfeited.

What is an HSA?
A health savings account, sometimes known as an HSA, is a type of bank account that serves a specific purpose and allows individuals to save money and pay for medical expenses that meet certain criteria. HSAs, in contrast to HRAs, are held by the individual participant rather than the employer. This indicates that the account remains with the individual even if they work at a different place of employment. Contributions to a health savings account (HSA) are eligible for tax deductions, and any interest or investment gains that are accumulated within the HSA are exempt from taxation.
With a health savings account (HSA), the account is portable, which means that money remains with you even if you switch employers or health insurance coverage. An HSA, in contrast to other health-related accounts, allows for the rollover of excess monies from one year to the next. A provision that states “use it or lose it” does not exist.
Individuals have access to a significant tool for managing their healthcare costs through the usage of health savings accounts (HSAs), which offer tax advantages and flexibility in the use of funds.
Difference between HRA and HSA
Ownership
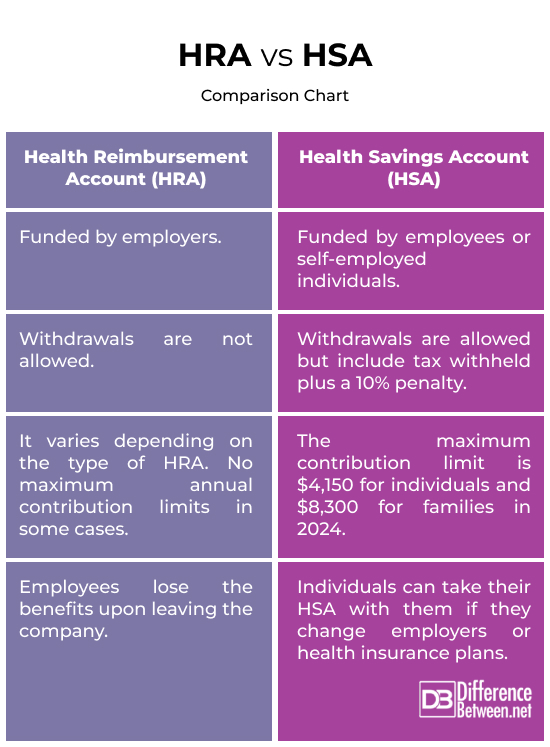
HRAs are entirely employer-funded. The employer contributes a specific amount to the HRA, and this funding is tax-deductible for the employer. HSAs, on the other hand, are owned by the individual. They are funded by the individual, their employer, or both. Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, and individuals have control over the account even if they change jobs.
Portability
HRAs are generally not portable. If an employee leaves the company, they typically lose access to the HRA funds. Some HRAs may allow limited portability, depending on plan rules. HSAs, however, are portable. Individuals can take their HSA with them if they change employers or health insurance plans. The account stays with the individual, providing continuity of savings.
Funds Rollover
The rollover of unused funds in an HRA depends on the employer’s plan rules. Employers may allow some rollover or have a “use it or lose it” provision. HSAs have a rollover feature, allowing individuals to carry over unused funds from year to year. There is no expiration of funds, and individuals can accumulate savings over time.
Tax Benefits
Reimbursements from HRAs are generally tax-free for employees. However, any unused funds at the end of employment may be forfeited. HSAs offer a triple tax advantage. Contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. Additionally, after the age of 65, individuals can withdraw funds for non-medical purposes without penalty, though income tax may apply.
HRA vs. HSA: Comparison Chart
Summary
In simple terms, an HSA is like a savings account where you can put money before taxes to cover medical costs. Usually, it’s linked to a high-deductible health plan. On the flip side, an HRA is funded by your employer and repays you for approved medical expenses. Your employer decides how much and when you can use your HRA.
Knowing these distinctions helps you pick the healthcare benefit that suits your needs and preferences.
FAQs
How does an HSA work?
With an HSA, you can toss in money before taxes, and it’s used for medical expenses. Contributions are tax-deductible, and your funds can grow through investments over time.
What can you use HSA for?
HSA can cover various medical expenses, like deductibles, co-pays, prescriptions, vision and dental care, and some preventive care costs.
Can you use HRA for glasses?
Some HRAs might cover vision costs, including glasses. Check your HRA plan details to be sure.
How much should you contribute to the HSA?
Your HSA contribution depends on factors like expected medical costs, IRS contribution limits, and your financial situation.
Do you get HSA money back?
HSAs work on a reimbursement basis. When you have a medical cost, use your HSA funds to pay for it – no “getting money back” in the usual sense.
What is covered under HSA?
An HSA can cover doctor visits, hospital costs, prescriptions, vision and dental care, and some preventive care costs.
What happens to HSA if you don’t use it?
Unused HSA money stays put. There’s no expiration – the cash stays until you use it for qualified medical expenses.
Can I use HSA for dental?
Absolutely! HSAs cover dental expenses like check-ups, cleanings, fillings, and other dental treatments.
How long does money stay in your HSA?
HSA money sticks around indefinitely. No rush – accumulate savings over time and use them when needed for medical expenses.
- Difference Between Caucus and Primary - June 18, 2024
- Difference Between PPO and POS - May 30, 2024
- Difference Between RFID and NFC - May 28, 2024
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
2 Comments
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MAEHR_DMAmw-health-savings-account-hsa-is-shown-on-the-conceptual-business-photo/
[1]Image credit: https://www.canva.com/photos/MADX_9TAC4s-health-reimbursement-account-hra-with-clipboard-on-desk-/

One of the most important things to note about a HSA is that it is the employees responsibility to manage their healthcare expenses. Since it is a high deductible plan out of pocket costs can be considerable. Our site was developed with the aim of helping people become more educated about their healthcare options and to save on out of pocket expenses. See how it can help you save on out of pocket healthcare costs.
See this easy to understand chart comparing HSA, FSA, & HRA:
http://www.myhealthandmoney.com/health-savings-accounts/hsa-vs-hra-vs-fsa
This chart shows the Key Differences Between the Three Consumer Health Accounts