Difference Between Austerity and Keynesian
Economic stability remains a major concern globally. Economists and policymakers are constantly on the lookout for policies that will lead to increased economic growth or stability. In an economy, key measures of economic growth include government borrowing, income inequality, poverty levels, human development index, labour productivity, investment levels, real disposable incomes and exchange rates. Among policies that may be used to stabilize an economy include austerity and stimulus. The Keynesian theory has also been used to explain ways in which an economy can stabilize.
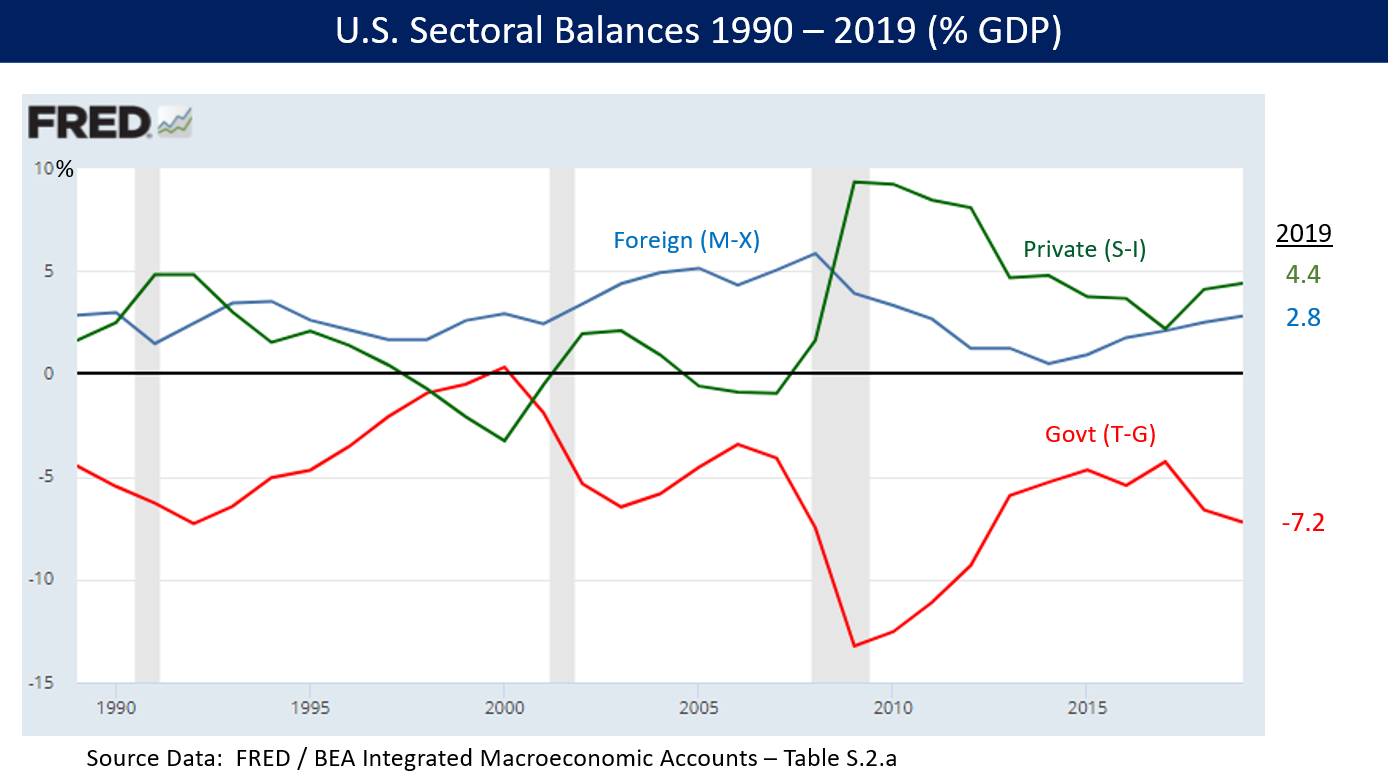
What is Austerity?
This is a set of economic policies implemented by a government to control public sector debt. This only occurs when the gap between government expenditure and government receipt reduces. Economists argue that a reduction in government spending does not equal austerity measures.
Types of austerity include:
- Revenue generation-focused austerity- This supports more government spending to stimulate growth.
- Angela Merkel model- This focuses on the increase of taxes while reducing nonessential government spending.
- Austerity featuring lower government spending and lower taxes.
Economists however disagree on the effect of tax policy on the government budget. Arthur Laffer, former Ronald Reagan advisor argued that cutting taxes would increase economic growth leading to more revenue. However, most policymakers and economists argue that the increase in taxes raises revenues.
Austerity whereby government spending is reduced has been deemed more effective. For instance, the government may stop hiring and instead lay off redundant employees or cut interest on newly issued government securities. The government may also increase income, property, corporate and sales taxes.
Austerity is however controversial as the national outcomes can even be more damaging to the economy as massive deficits can suffocate economic growth.

What is Keynesian ?
Developed by John Maynard Keynes, a British economist, this is a macroeconomic economic theory that focuses on economic changes in the short run. It is based on the theory of spending in an economy and its effects on employment, output and inflation and is classified as a demand-side theory.
It was the first economic theory to advocate for lower taxes and increased government spending to stimulate demand and get the economy out of depression.
According to Keynes, an increase in government spending leads to more business activities hence more spending. Since spending generates more income and boosts aggregate output, the result would be a growth in the GDP. In this theory, every one dollar used in fiscal stimulus creates more than one dollar.
Similarities between Austerity and Keynesian
- Both address economic stability issues
Differences between Austerity and Keynesian
Definition
Austerity refers to a set of economic policies implemented by a government to control public sector debt. On the other hand, Keynesian refers to a macroeconomic economic theory that focuses on economic changes in the short run.
Scope
While austerity advocates for a reduction in government spending to stimulate economic growth, Keynesian theory advocates for lower taxes and increased government spending to stimulate demand and get the economy out of depression.
Austerity vs. Keynesian: Comparison Table

Summary of Austerity vs. Keynesian
Austerity refers to a set of economic policies implemented by a government to control public sector debt. On the other hand, Keynesian refers to a macroeconomic economic theory that focuses on economic changes in the short run.
- Difference Between Profit Center and Investment Center - July 2, 2022
- Difference Between Anti-Trust and Anti-Competition - June 6, 2022
- Difference Between Stocktaking and Stock Control - June 6, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Meeropol M. & Sherman H. Principles of Macroeconomics: Activist vs Austerity Policies. Routledge, 2015.https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=m_8TBwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+austerity+and+keynesian&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj_pb3KpeztAhUE1BoKHSoHA6kQ6AEwA3oECAAQAg#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20austerity%20and%20keynesian&f=false
[1]Kriesler P. & Harcourt G. The Oxford Handbook of Post-Keynesian Economics, Volume 2: Critiques and Methodology. Oxford University Press, 2013. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=xRMoAAAAQBAJ&pg=PT889&dq=Difference+between+austerity+and+keynesian&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj_pb3KpeztAhUE1BoKHSoHA6kQ6AEwBXoECAQQAg#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20austerity%20and%20keynesian&f=false
[2]Canterbery E. The Rise And Fall Of Global Austerity. World Scientific, 2014. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=Sw-3CgAAQBAJ&pg=PA49&dq=Difference+between+austerity+and+keynesian&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj_pb3KpeztAhUE1BoKHSoHA6kQ6AEwAnoECAIQAg#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20austerity%20and%20keynesian&f=false
[3]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sectoral_Financial_Balances_in_U.S._Economy.png
[4]Image credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Keynesian_Economic_Growth_Graph.png
