Bookkeeping is vital for all types of businesses irrespective of the type and kind. Most businesses that have collapsed could have been saved by simple bookkeeping. And it all starts with understanding basic accounting, which may not be too basic for most people. Let’s start with depreciation. This is the loss of the value of an asset with time and is hence used as a method of allocating the cost of vital assets in business. Different concepts of depreciation that are applicable in a business include tax depreciation and book depreciation. It is important to differentiate these terms and how they should be applied in business entities.

What is Tax Depreciation?
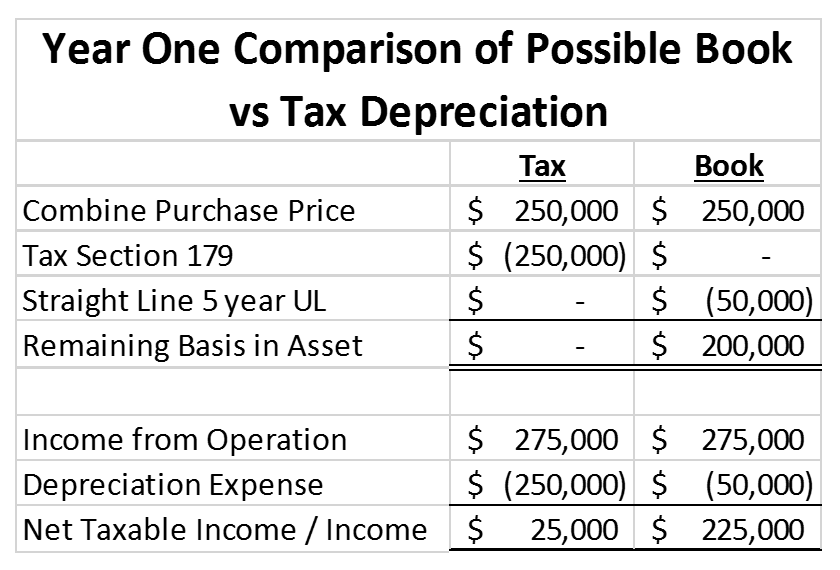
This is the depreciation expense as listed on a tax return by a taxpayer during a specific tax period. Tax rules in certain jurisdictions allow individuals and businesses to claim the loss value of tangible assets during a certain period. Tax depreciation helps businesses reduce the taxable income when deducted. What most business owners ignore is that not all assets warrant tax deductions. The type of assets allowed for tax deductions depends on the location of the business and the laws that govern these principles.
Some principles of tax deductions include:
- The asset must be owned by the tax owner
- The asset is used by the owner for income-generating activities
- The asset has a useful life of over one year
- The asset has a useful life that can be determined
What is Book Depreciation?
Also referred to as accounting depreciation, this is the cost that a company allocates to a tangible asset over its productive years. This, however, does not represent a business’s actual cash flow. It is recorded on the income statement and reduces a company’s net income, hence lowering the tax amounts. Most jurisdictions also require businesses to disclose the amount of accumulated depreciation on the balance sheet.
Book depreciation can be calculated using accelerated and straight-line methods. The straight-line method equally distributes expenses over the period the asset is useful. However, the accelerated method deducts more depreciation expenses during the earlier stages and less in the later stages of an asset’s life.
Similarities between Tax depreciation and Book depreciation
- Both expenses are deducted from a company’s revenue hence lowering the tax obligations
Differences between Tax depreciation and Book depreciation
Definition
Tax depreciation refers to the depreciation expense as listed on a tax return by a taxpayer during a specific tax period. On the other hand, book depreciation refers to the cost that a company allocates to a tangible asset over its productive years.
Use
Tax depreciation should be used by entities for their income tax returns. On the other hand, book depreciation should be used by entities for their financial statements.
Rigidity
The basis of tax depreciation is rigid rules that allow depreciation based on the type of assets regardless of the life or usage of an asset. On the other hand, book depreciation is based on an asset’s actual usage and rates.
Preparation guide
While tax depreciation preparation must comply with tax laws, book depreciation preparation must comply with company laws and accounting purposes.
Tax depreciation vs. Book depreciation: Comparison Table

Summary of Tax depreciation vs. Book depreciation
Tax depreciation should be used by entities for their income tax returns. It follows rigid rules that allow depreciation based on the type of assets regardless of the life or usage of an asset. On the other hand, book depreciation should be used by entities for their financial statements and is based on an asset’s actual usage and rates.
What is the difference between book and tax accounting?
Tax depreciation refers to the depreciation expense as listed on a tax return by a taxpayer during a specific tax period. It should be used by entities for their income tax returns and follows rigid rules that allow depreciation based on the type of assets regardless of the life or usage of an asset. On the other hand, book depreciation refers to the cost that a company allocates to a tangible asset over its productive years. It must comply with company laws and accounting purposes.
What does it mean when tax depreciation exceeds book depreciation?
Sometimes, tax depreciation may exceed book depreciation. This is because tax depreciation makes depreciation expenses more rapid when it comes to depreciation expenses.
What is a book-tax difference?
This is the variance between the adjustable tax basis and the carrying value of an asset.
What is a book to tax reconciliation?
This is the reconciliation of the net income based on the books reported through the addition and subtraction of the non-tax items.
Are any meals 100% deductible?
The new 2021 and 2022 mandate all business meals that are issued by restaurants to be 100% deductible.
- Difference Between Profit Center and Investment Center - July 2, 2022
- Difference Between Anti-Trust and Anti-Competition - June 6, 2022
- Difference Between Stocktaking and Stock Control - June 6, 2022

