Difference Between Tax and Tariff
Most people have remitted tax in one way or the other, be it income or taxes on purchases. However, not many people have directly paid tariff taxes. The terms tax and tariffs are often interchanged. However, the two have differences. The main difference between taxes and tariffs is that taxes are levied to governments by individuals as well as corporations based on their incomes while tariffs are taxes levied on the import of goods.

What is Tax?
These are mandatory contributions paid by corporations and individuals to a government. This can be national, regional and even local. While there are different types of taxes, their main role is to finance government activities such as building schools, roads, Medicare and other public infrastructure.
Among the types of taxes include:
- Income tax- This is a tax that is paid on income to the federal governments. Most countries have a progressive tax system where high-income individuals remit higher taxes while low-income individuals remit lower taxes.
- Payroll tax- This is a tax paid by an employee to fund social security systems and Medicare. These taxes are withheld by an employer whereby both employees and employers have their portion. Self-employed persons must also pay an equivalent of the employee and employer portion.
- Sales taxes- These are taxes charged at the point of sale when a customer is executing the payment of services and goods. These funds are then remitted to the government by the business entity. Different jurisdictions have varying sales taxes.
- Corporate taxes- These are taxes paid by a company based on their taxable income. The rates differ in different countries and states.
- Property taxes- These are taxes charged on properties. The amount of tax to be remitted is based on the property’s assessed value.
- Tariffs- This is a tax that is imposed by a country on services and goods imported from a different country. The importance of tariffs is to encourage domestic consumption.
- Estate taxes- These are taxes levied on estates as per the set state exclusions.
Different tax laws differ with states and countries. Understanding your tax situation and obligations can help taxpayers effectively manage their tax obligations.

What is Tariff?
This is a type of tax that is paid on services and goods imported from other nations. The governments impose these taxes to raise revenue, have political leverage on other countries and protect the domestic sectors in the country. Often, tariffs cause higher prices in the imported products and services. This forces consumers to purchase goods and services produced in the country as opposed to imported ones. This has led to a debate on whether tariffs are bad or good policies.
There are two types of tariffs namely:
A specific tariff- This is a tariff levied on a fixed fee that is based on the type of a good. For instance, a country could set a $1,000 tariff on certain machinery.
Ad-valorem tariff- This is a tariff that is based on the value of an item. For instance, you could pay 10% of the value of the machinery.
While tariffs help countries raise revenue, they have various disadvantages. Among these include:
- They can make domestic industries less innovative and less efficient since they hinder competition
- Prices of goods produced locally can increase
- They can create tensions between different regions
- They can result to trade wars
Similarities between Tax and Tariff
- Both are remitted to the authorities
Differences between Tax and Tariff
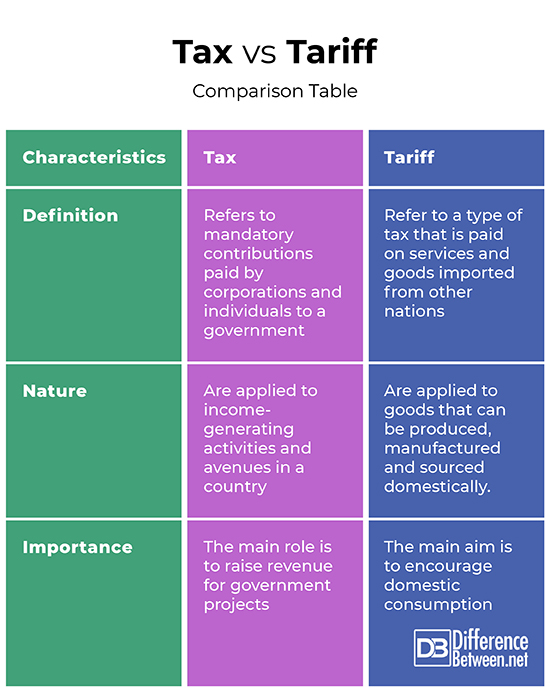
Definition
Tax refers to mandatory contributions paid by corporations and individuals to a government. On the other hand, tariffs refer to a type of tax that is paid on services and goods imported from other nations.
Nature
While taxes are applied to income-generating activities and avenues in a country, tariffs are applied to goods that can be produced, manufactured and sourced domestically.
Importance
The importance of taxes is to raise revenue for government projects. On the other hand, the importance of tariffs is to encourage domestic consumption.
Tax vs. Tariff: Comparison Table
Summary of Tax vs. Tariff
Tax refers to mandatory contributions paid by corporations and individuals to a government. On the other hand, tariffs refer to a type of tax that is paid on services and goods imported from other nations. The main difference between these two is the aim. The role of taxes is to raise money for government projects. On the other hand, the role of tariffs is to encourage domestic consumption while still adding to government funds. Tariffs, however, are a form of tax.
Are tariffs a form of tax?
Yes. Tariffs are a form of tax.
What type of tax is a tariff?
A tariff is a tax that is applied on goods imported from other countries. While government tariff tax laws and regulations differ, most authorities have higher tariffs on goods that are also available locally. This encourages domestic production.
What is the difference between tariff and custom duty?
Tariffs refer to taxes levied on goods mainly to protect the local markets. On the other hand, custom duties are the funds collected from tariff taxes.
Is tariff a direct tax?
Yes, a tariff is a direct tax. This is because it is levied on the purchaser of the as opposed to the goods or services.
- Difference Between Profit Center and Investment Center - July 2, 2022
- Difference Between Anti-Trust and Anti-Competition - June 6, 2022
- Difference Between Stocktaking and Stock Control - June 6, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
1 Comment
Leave a Response
References :
[0]United Nations. International Classification of Non-Tariff Measures 2019. United Nations, 2019. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=yFzBDwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Tax+and+Tariff&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiHneaLn7DxAhXoz4UKHUHPDL84ChDoATAFegQIChAC#v=onepage&q&f=false
[1]Thuronyi V & Daniel P. International Taxation and the Extractive Industries. Taylor & Francis, 2016. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=GjolDwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Tax+and+Tariff&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwid4MmAn7DxAhXW3oUKHXd2Ad4Q6AEwA3oECAgQAg#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Tax%20and%20Tariff&f=false
[2]Perry V & Keen M. The Modern VAT. International Monetary Fund, 2001. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=qnI5E3m09d0C&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Tax+and+Tariff&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiHneaLn7DxAhXoz4UKHUHPDL84ChDoATACegQIBxAC#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Tax%20and%20Tariff&f=false
[3]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/65535/48138015422_1670bc88c1_b.jpg
[4]Image credit: https://live.staticflickr.com/6056/6355404323_cf97f9c58e_b.jpg

What could be the penalty if tax and tariff isn’t paid on imported goods’ and what’s the different between taxs and vat? Do responds via sms to +2349079763043 Because i have no access to my e-mail recently.