Difference Between Growth and Dividend
Growth and dividends are terms used in companies relating to an increase in wealth and its distribution to the organizational shareholders.

What is Dividend?
Dividend refers to the amount of money that is distributed to the owners of the organization after recording growth regarding profits earned in a specific period.
The amount to be a dividend to the owners of the organization is determined by the board of directors managing the operations of the company.
The portion to be divided to the shareholders of the company is the net profit of the enterprise. Dividends can also be issued regarding shares of stock or other properties.
What is Growth?
Growth refers to the expansion of organizational activities and operations, which is realized after a continued period of hard work and strategy implementations.
The growth of any enterprise may be recorded regarding the profits earned by the organization, increased number of employees, and the opening of new organization branches in other parts of the industry.

Difference Between Growth and Dividend
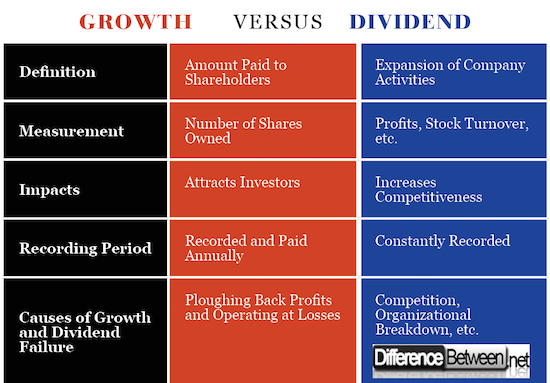
Meaning Growth and Dividend
One of the main difference between growth and dividend is depicted from the meaning of the two terms, which are used continuously in a business environment. Growth is defined as the expansion of the organization, which is recorded after a specific period.
On the other hand, dividend refers to the proportion of income or profits that are shared with the shareholders of the organization that is decided by the board of directors. Dividends are divided to all the shareholders concerning the proportion of their investment in the company.
Measurement of Growth and Dividend
The method of analysis between dividends and growth of the organization uses different techniques of measurements or parameters. The growth of the enterprise uses several metrics to measure growth in a specific period.
The expansion of the organization can be measured using parameters like the profits earned in a defined financial period, the opening of new branches in other parts of the industry, increase in the number of workers, an increase in the number of goods and services offered to the customers.
The amounts shared to the shareholders of the company uses a specific parameter in determining the proportion allocated to each shareholder. It is the number of shares that determine the number of dividends that an individual can get.
The more the number of shares, the higher the dividends one will get and the lower the number of units of ownership the lower the bonuses allocated.
Impacts of Growth and Dividend Payment
Both growths of the entity and dividend payment to the company owners have significant impacts on the operations of the company.
Growth highlights that the organization has been operating efficiently and has a high potential for growth. This attracts a large number of investors who bring resources to the organization hence making it buy new equipment and increase its efficiency.
Corporations, which pay dividends to their shareholders, increase their reputations to the members of the community while also attracting potential investors who may wish to buy stocks in the company because they are guaranteed of payment.
Recording of Growth and Payment of Dividends
The other significant difference to note between growth and dividends is the period at which increase is recorded and the period at which bonuses are allocated to the shareholders of the company.
Some parameters that are used to measure the growth of the organization are affected on a daily basis as the company undergoes its day-to-day operations, which means that growth of the company can be recorded on a continuing basis.
Nevertheless, some of the parameters used to measure growth can only be determined after a precisely defined period. For example, profits of the organization are identified after one year after deducting all expenses used in the production process.
On the other hand, dividends are only paid on a yearly basis. Unlike growth, which can be recorded in weekly terms depending on stock turnover, organizational shareholders, are only entitled to dividends after the fiscal year of the organization.
Growth and Dividend Failure
Growth failure is recorded when the organization fails to record growth in any of the parameters of the organization. This means that the company was operating poorly such that neither profits were recorded.
Some of the factors that may lead to growth failure of a company include increasing competition in the industry, low stock turnover, poor management strategies, and breakdown in production activities.
On the other hand, dividend failure is recorded in situations where the company fails to pay dividends to the shareholders of the organization.
Some factors influence dividend failure in the organization, which includes plowing back profits to increase organizational growth, increasing cash reserves by reducing dividends payment and lack of benefits in the organization.
Difference Between Growth and Dividend
Summary of Growth vs. Dividend
- Growth records the expansion of the organization, which is measured in several parameters, which include some customers, stock turnover, opening up of new branches, and increased company profits.
- Dividends are the amount that is allocated to the shareholders of the organization. The board of the company determines the amount of the enterprise records profits in a specific financial period.
- A company that records growth has the capability of attracting investors who are guaranteed profits while an organization that pays dividends to the shareholders attracts capital to the company leading to increasing.
- Difference Between Gross NPA and Net NPA - April 20, 2018
- Difference Between Job Description and Job Specification - April 13, 2018
- Difference Between Yoga and Power Yoga - April 10, 2018
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://pixabay.com/en/growth-chart-map-graph-arrow-1140534/
[1]Image credit: http://www.creative-commons-images.com/finance/images/stock-dividend.jpg
[2]Campbell, John Y., and Robert J. Shiller. "The dividend-price ratio and expectations of future dividends and discount factors." The Review of Financial Studies 1.3 (1988): 195-228.
[3]Evans, David S. "The relationship between firm growth, size, and age: Estimates for 100 manufacturing industries." The journal of industrial economics (1987): 567-581.
[4]Lintner, John. "Distribution of incomes of corporations among dividends retained earnings and taxes." The American Economic Review 46.2 (1956): 97-113.
