Difference Between Disposable and Discretionary Income
Finances form a major part of not only the economy but also personal finance. Despite the importance of personal financial control, the majority of people do not have full control of their finances, in terms of expenses as well as savings. To measure the economic performance of an economic resources, two major indicators are used, namely, discretionary and disposable income. Although used interchangeably, they have differences.

What is Disposable Income?
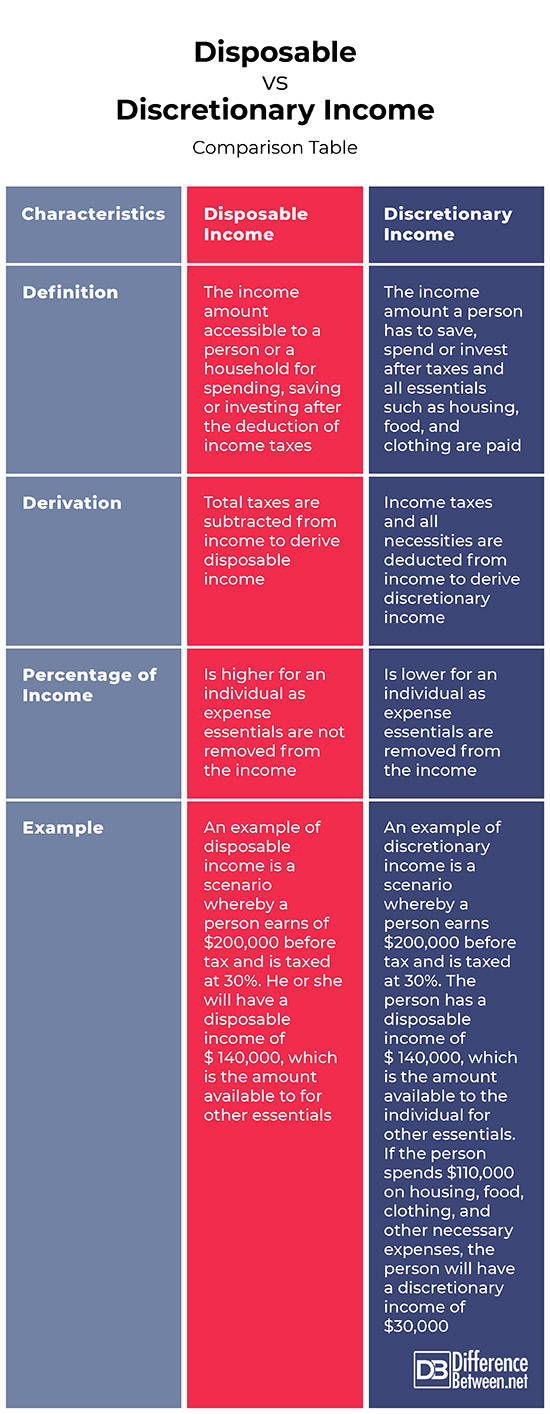
Also referred to as take-home-pay, this is the income amount accessible to a person for spending, saving or investing after the deduction of income taxes. Disposable income is higher in comparison to discretionary income for an individual as essentials expenses are not removed from the disposable income. To derive disposable income, total taxes are subtracted from income.
An example of disposable income is a scenario whereby a person earns of $200,000 before tax and is taxed at 30%. He or she will have a disposable income of $ 140,000, which is the amount available to for other essentials.

What is Discretionary Income?
This is the income amount a person has to save, spend or invest after taxes and all essentials such as housing, food, and clothing is paid. To derive discretionary income, income taxes and all necessities are deducted from income.
An example of discretionary income is a scenario whereby a person earns $200,000 before tax and is taxed at 30%. The person has a disposable income of $ 140,000, which is the amount available to the individual for other essentials. If the person spends $110,000 on housing, food, clothing, and other necessary expenses, the person will have a discretionary income of $30,000.
Similarities between Disposable and Discretionary Income
- Both are used as a measure of consumer spending habits
- Both are affected by the people’s willingness to spend
Differences between Disposable and Discretionary Income
Definition
Disposable income refers to the income amount accessible to a person or a household for spending, saving or investing after the deduction of income taxes while discretionary income refers to the income amount a person has to save, spend or invest after taxes and all essentials such as housing, food, and clothing are paid.
Derivation
While total taxes are subtracted from income to derive disposable income, income taxes and all necessities are deducted from income to derive discretionary income.
Percentage of Income
Disposable income is higher for an individual as expense necessities are not removed from the income while discretionary income is lower for an individual as essentials expenses are removed from the income.
Example
An example of disposable income is a scenario whereby a person earns of $200,000 before tax and is taxed at 30%. He or she will have a disposable income of $ 140,000, which is the amount available to for other essentials. In contrast, an example of discretionary income is a scenario whereby a person earns $200,000 before tax and is taxed at 30%. The person has a disposable income of $ 140,000, which is the amount available to the individual for other essentials. If the person spends $110,000 on housing, food, clothing, and other necessary expenses, the person will have a discretionary income of $30,000.
Disposable vs. Discretionary Income: Comparison Table
Summary of Disposable vs. Discretionary Income
Disposable income refers to the income amount accessible to a person or a household for spending, saving or investing after the deduction of income taxes. On the contrary, discretionary income refers to the income amount a person has to save, spend or invest after taxes and all necessities such as housing, food, and clothing are paid. The knowledge of disposable and discretionary income is important for better personal finance planning.
- Difference Between Profit Center and Investment Center - July 2, 2022
- Difference Between Anti-Trust and Anti-Competition - June 6, 2022
- Difference Between Stocktaking and Stock Control - June 6, 2022
Search DifferenceBetween.net :
Leave a Response
References :
[0]Image credit: https://media.defense.gov/2017/Aug/16/2001793523/780/780/0/170809-F-CQ002-1005.JPG
[1]Image credit: http://www.thebluediamondgallery.com/typewriter/images/disposable-income.jpg
[2]United States. Bureau of the Census, United States & Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce. Survey of Current Business, Volume 90, Issues 1-4. U.S. Department of Commerce, 2010. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=zkRNAQAAMAAJ&pg=RA3-PA16&dq=Difference+between+Disposable+and+Discretionary+Income&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiU7J6Zs8TkAhXFnVwKHU2rAUwQ6AEIMTAB#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Disposable%20and%20Discretionary%20Income&f=false
[3]Kapoor J & Pride W. Foundations of Business. Cengage Learning, 2014. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=tTAaCgAAQBAJ&pg=PT334&dq=Difference+between+Disposable+and+Discretionary+Income&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiU7J6Zs8TkAhXFnVwKHU2rAUwQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Disposable%20and%20Discretionary%20Income&f=false
[4]Supan A. Life-Cycle Savings and Public Policy: A Cross-National Study of Six Countries. Elsevier Publisher, 2003. https://books.google.co.ke/books?id=1uh4Dob7uNoC&printsec=frontcover&dq=Difference+between+Disposable+and+Discretionary+Income&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiU7J6Zs8TkAhXFnVwKHU2rAUwQ6AEIPjAD#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Disposable%20and%20Discretionary%20Income&f=false
